SIMP
In astrophysics SIMP is an abbreviation of Strongly Interacting Massive Particle. SIMPs could form the inferred dark matter despite their strong interactions with ordinary matter.[1]
SIMPs have been proposed as a solution for the ultra high energy cosmic ray problem[2][3] and for the absence of cooling flows.[4][5] Various experiments and observations have set constraints on SIMP dark matter.[1][6][7][8][9][10][11][12]
See also
References
- ^ a b B. D. Wandelt, R. Dave, G. R. Farrar, P. C. McGuire, D. N. Spergel and P. J. Steinhardt, Self-Interacting Dark Matter, Marina del Rey 2000, Sources and detection of dark matter and dark energy in the universe, 263 (2000), preprint.
- ^ D. Chung, G. R. Farrar and E. W. Kolb, Are ultrahigh energy cosmic rays signals of supersymmetry?, Phys. Rev. D 57, 4606 (1998) preprint.
- ^ I. F. M. Albuquerque, G. R. Farrar and E. W. Kolb, Exotic massive hadrons and ultra-high energy cosmic rays, Phys. Rev. D 59, 015021 (1999) preprint.
- ^ B. Qin and X. P. Wu, Constraints on the Interaction between Dark Matter and Baryons from Cooling Flow Clusters, Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 061301 (2001) preprint.
- ^ L. Chuzhoy and A. Nusser, A limit on the dark matter and baryons interaction cross-section in galaxy clusters, preprint.
- ^ G. D. Starkman, A. Gould, R. Esmailzadeh, and S. Dimopoulos, Opening the window on strongly interacting dark matter, Phys. Rev. D 41, 3594 (1990).
- ^ P. C. McGuire and P. J. Steinhardt, Cracking Open the Window for Strongly Interacting Massive Particles as the Halo Dark Matter, Proceedings of the International Cosmic Ray Conference, Hamburg, Germany, 1566 (2001), preprint.
- ^ R. H. Cyburt, B. D. Fields, V. Pavlidou and B. D. Wandelt, Constraining Strong Baryon-Dark Matter Interactions with Primordial Nucleosynthesis and Cosmic Rays, Phys. Rev. D 65, 123503 (2002) preprint.
- ^ S. Mitra, Uranus's anomalously low excess heat constrains strongly interacting dark matter, Phys. Rev. D 70, 103517 (2004) preprint.
- ^ G. D. Mack, J. F. Beacom and G. Bertone, Towards Closing the Window on Strongly Interacting Dark Matter: Far-Reaching Constraints from Earth's Heat Flow, Phys. Rev. D 76, 043523 (2007) preprint.
- ^ G. Zaharijas and G. R. Farrar, Window in the dark matter exclusion limits, Phys. Rev. D 72, 083502 (2005) preprint.
- ^ D. Javorsek II, E. Fischbach and V. Teplitz, New experimental bounds on the contributions to the cosmological density parameter
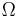 from strongly interacting massive particles, ApJ 568, 1 (2002).
from strongly interacting massive particles, ApJ 568, 1 (2002).
Further reading
- Bertone, Gianfranco (2010). Particle Dark Matter: Observations, Models and Searches. Cambridge University Press. pp. 762. ISBN 9780521763684.