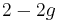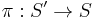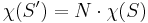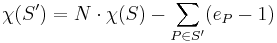Riemann–Hurwitz formula
In mathematics, the Riemann–Hurwitz formula, named after Bernhard Riemann and Adolf Hurwitz, describes the relationship of the Euler characteristics of two surfaces when one is a ramified covering of the other. It therefore connects ramification with algebraic topology, in this case. It is a prototype result for many others, and is often applied in the theory of Riemann surfaces (which is its origin) and algebraic curves.
Contents |
Statement
For an orientable surface S the Euler characteristic χ(S) is
where g is the genus (the number of handles), since the Betti numbers are 1, 2g, 1, 0, 0, ... . In the case of an (unramified) covering map of surfaces
that is surjective and of degree N, we should have the formula
That is because each simplex of S should be covered by exactly N in S′ — at least if we use a fine enough triangulation of S, as we are entitled to do since the Euler characteristic is a topological invariant. What the Riemann–Hurwitz formula does is to add in a correction to allow for ramification (sheets coming together).
Now assume that S and S′ are Riemann surfaces, and that the map π is complex analytic. The map π is said to be ramified at a point P in S′ if there exist analytic coordinates near P and π(P) such that π takes the form π(z) = zn, and n > 1. An equivalent way of thinking about this is that there exists a small neighborhood U of P such that π(P) has exactly one preimage in U, but the image of any other point in U has exactly n preimages in U. The number n is called the ramification index at P and also denoted by eP. In calculating the Euler characteristic of S′ we notice the loss of eP − 1 copies of P above π(P) (that is, in the inverse image of π(P)). Now let us choose triangulations of S and S′ with vertices at the branch and ramification points, respectively, and use these to compute the Euler characteristics. Then S′ will have the same number of d-dimensional faces for d different from zero, but fewer than expected vertices. Therefore we find a "corrected" formula
(almost all P have eP = 1, so this is quite safe). This formula is known as the Riemann–Hurwitz formula and also as Hurwitz's theorem.
Examples
The Weierstrass 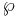 -function, considered as a meromorphic function with values in the Riemann sphere, yields a map from an elliptic curve (genus 1) to the projective line (genus 0). It is a double cover (N = 2), with ramification at four points only, at which e = 2. The Riemann–Hurwitz formula then reads
-function, considered as a meromorphic function with values in the Riemann sphere, yields a map from an elliptic curve (genus 1) to the projective line (genus 0). It is a double cover (N = 2), with ramification at four points only, at which e = 2. The Riemann–Hurwitz formula then reads
- 0 = 2·2 − Σ 1
with the summation taken over four values of P.
The formula may also be used to calculate the genus of hyperelliptic curves.
As another example, the Riemann sphere maps to itself by the function zn, which has ramification index n at 0, for any integer n > 1. There can only be other ramification at the point at infinity. In order to balance the equation
- 2 = n·2 − (n − 1) − (e∞ − 1)
we must have ramification index n at infinity, also.
Consequences
Several results in algebraic topology and complex analysis follow.
Firstly, there are no ramified covering maps from a curve of lower genus to a curve of higher genus – and thus, since non-constant meromorphic maps of curves are ramified covering spaces, there are no non-constant meromorphic maps from a curve of lower genus to a curve of higher genus.
As another example, it shows immediately that a curve of genus 0 has no cover with N > 1 that is unramified everywhere: because that would give rise to an Euler characteristic > 2.
Generalizations
For a correspondence of curves, there is a more general formula, Zeuthen's theorem, which gives the ramification correction to the first approximation that the Euler characteristics are in the inverse ratio to the degrees of the correspondence.
References
- Hartshorne, Robin (1977), Algebraic Geometry, Berlin, New York: Springer-Verlag, ISBN 978-0-387-90244-9, MR0463157, OCLC 13348052, section IV.2.