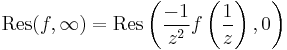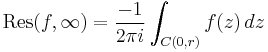Residue at infinity
In complex analysis a branch of mathematics, the residue at infinity is a residue of a holomorphic function on an annulus having an infinite external radius. The infinity  is a point added to the local space
is a point added to the local space  in order to render it compact (in this case it is a one-point compactification). This space noted
in order to render it compact (in this case it is a one-point compactification). This space noted 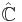 is isomorphic to the Riemann sphere.[1] One can use the residue at infinity to calculate some integrals.
is isomorphic to the Riemann sphere.[1] One can use the residue at infinity to calculate some integrals.
Definition
Given a holomorphic function f on an annulus 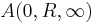 (centered at 0, with inner radius
(centered at 0, with inner radius 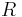 and infinite outer radius), the residue at infinity of the function f can be defined in terms of the usual residue as follows:
and infinite outer radius), the residue at infinity of the function f can be defined in terms of the usual residue as follows:
Thus, one can transfer the study of 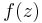 at infinity to the study of
at infinity to the study of 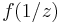 at the origin.
at the origin.
Note that 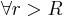 , we have
, we have
See also
References
- This article incorporates information from this version of the equivalent article on the French Wikipedia.
- ^ Michèle AUDIN, Analyse Complexe, cursus notes of the university of Strasbourg available on the web, pp. 70–72
- Murray R. Spiegel, Variables complexes, Schaum, ISBN 2-7042-0020-3
- Henri Cartan, Théorie analytique des fonctions d'une ou plusieurs varaiables complexes, Hermann, 1961