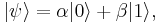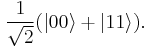Qubit
| Fundamental units of information |
|---|
In quantum computing, a qubit ( /ˈkjuːbɪt/) or quantum bit is a unit of quantum information—the quantum analogue of the classical bit—with additional dimensions associated to the quantum properties of a physical atom. The physical construction of a quantum computer is itself an arrangement of entangled atoms, and the qubit represents both the state memory and the state of entanglement in a system. A quantum computation is performed by initializing a system of qubits with a quantum algorithm —"initialization" here referring to some advanced physical process that puts the system into an entangled state.
The qubit is described by a quantum state in a two-state quantum-mechanical system, which is formally equivalent to a two-dimensional vector space over the complex numbers. One example of a two-state quantum system is the polarization of a single photon: here the two states are vertical polarization and horizontal polarization. In a classical system, a bit would have to be in one state or the other, but quantum mechanics allows the qubit to be in a superposition of both states at the same time, a property which is fundamental to quantum computing.
Contents |
Bit versus qubit
A bit is the basic unit of computer information. Regardless of its physical realization, a bit is always understood to be either a 0 or a 1. An analogy to this is a light switch— with the off position representing 0 and the on position representing 1.
A qubit has some similarities to a classical bit, but is overall very different. Like a bit, a qubit can have two possible values—normally a 0 or a 1. The difference is that whereas a bit must be either 0 or 1, a qubit can be 0, 1, or a superposition of both.
Representation
The two states in which a qubit may be measured are known as basis states (or basis vectors). As is the tradition with any sort of quantum states, Dirac, or bra-ket notation, is used to represent them. This means that the two computational basis states are conventionally written as 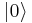 and
and 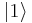 (pronounced "ket 0" and "ket 1").
(pronounced "ket 0" and "ket 1").
Qubit states
A pure qubit state is a linear superposition of the basis states. This means that the qubit can be represented as a linear combination of 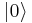 and
and 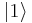 :
:
where α and β are probability amplitudes and can in general both be complex numbers.
When we measure this qubit in the standard basis, the probability of outcome 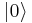 is
is 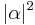 and the probability of outcome
and the probability of outcome 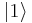 is
is 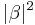 . Because the absolute squares of the amplitudes equate to probabilities, it follows that α and β must be constrained by the equation
. Because the absolute squares of the amplitudes equate to probabilities, it follows that α and β must be constrained by the equation
simply because this ensures you must measure either one state or the other.
Bloch Sphere
The possible states for a single qubit can be visualised using a Bloch sphere (see diagram). Represented on such a sphere, a classical bit could only be at the "North Pole" or the "South Pole", in the locations where 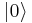 and
and 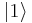 are respectively. The rest of the surface of the sphere is inaccessible to a classical bit, but a pure qubit state can be represented by any point on the surface. For example the pure qubit state
are respectively. The rest of the surface of the sphere is inaccessible to a classical bit, but a pure qubit state can be represented by any point on the surface. For example the pure qubit state 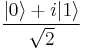 would lie on the equator of the sphere, on the positive y axis.
would lie on the equator of the sphere, on the positive y axis.
The surface of the sphere is two-dimensional space, which represents the state space of the pure qubit states. This state space has two local degrees of freedom. It might at first sight seem that there should be four degrees of freedom, as α and β are complex numbers with two degrees of freedom each. However, one degree of freedom is removed by the constraint 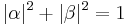 . Another, the overall phase of the state, has no physically observable consequences, so we can arbitrarily choose α to be real, leaving just two degrees of freedom.
. Another, the overall phase of the state, has no physically observable consequences, so we can arbitrarily choose α to be real, leaving just two degrees of freedom.
It is possible to put the qubit in a mixed state, a statistical combination of different pure states. Mixed states can be represented by points inside the Bloch sphere.
Operations on pure qubit states
There are various kinds of physical operations that can be performed on pure qubit states.
- A quantum logic gate can operate on a qubit: mathematically speaking, the qubit undergoes a unitary transformation. Unitary transformations correspond to rotations of the Bloch sphere.
- Standard basis measurement is an operation in which information is gained about the state of the qubit. The result of the measurement will be either
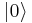 , with probability
, with probability 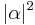 , or
, or 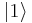 , with probability
, with probability 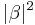 . Measurement of the state of the qubit alters the values of α and β. For instance, if the result of the measurement is
. Measurement of the state of the qubit alters the values of α and β. For instance, if the result of the measurement is 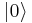 , α is changed to 1 (up to phase) and β is changed to 0. Note that a measurement of a qubit state entangled with another quantum system transforms a pure state into a mixed state.
, α is changed to 1 (up to phase) and β is changed to 0. Note that a measurement of a qubit state entangled with another quantum system transforms a pure state into a mixed state.
Entanglement
An important distinguishing feature between a qubit and a classical bit is that multiple qubits can exhibit quantum entanglement. Entanglement is a nonlocal property that allows a set of qubits to express higher correlation than is possible in classical systems. Take, for example, two entangled qubits in the Bell state
In this state, called an equal superposition, there are equal probabilities of measuring either 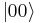 or
or 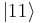 , as
, as 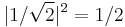 .
.
Imagine that these two entangled qubits are separated, with one each given to Alice and Bob. Alice makes a measurement of her qubit, obtaining—with equal probabilities—either 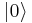 or
or 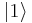 . Because of the qubits' entanglement, Bob must now get exactly the same measurement as Alice; i.e., if she measures a
. Because of the qubits' entanglement, Bob must now get exactly the same measurement as Alice; i.e., if she measures a 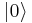 , Bob must measure the same, as
, Bob must measure the same, as 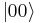 is the only state where Alice's qubit is a
is the only state where Alice's qubit is a 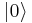 .
.
Entanglement also allows multiple states (such as the Bell state mentioned above) to be acted on simultaneously, unlike classical bits that can only have one value at a time. Entanglement is a necessary ingredient of any quantum computation that cannot be done efficiently on a classical computer.
Many of the successes of quantum computation and communication, such as quantum teleportation and superdense coding, make use of entanglement, suggesting that entanglement is a resource that is unique to quantum computation.
Quantum register
A number of entangled qubits taken together is a qubit register. Quantum computers perform calculations by manipulating qubits within a register. A qubyte is a collection of eight entangled qubits. It was first demonstrated by a team at the Institute of Quantum Optics and Quantum Information at the University of Innsbruck in Austria in December 2005.[1]
Variations of the qubit
Similar to the qubit, a qutrit is a unit of quantum information in a 3-level quantum system. This is analogous to the unit of classical information trit. The term "qudit" is used to denote a unit of quantum information in a d-level quantum system. A quiet qubit refers to a qubit that can be efficiently decoupled from the environment.[2]
Physical representation
Any two-level system can be used as a qubit. Multilevel systems can be used as well, if they possess two states that can be effectively decoupled from the rest (e.g., ground state and first excited state of a nonlinear oscillator). There are various proposals. Several physical implementations which approximate two-level systems to various degrees were successfully realized. Similarly to a classical bit where the state of a transistor in a processor, the magnetization of a surface in a hard disk and the presence of current in a cable can all be used to represent bits in the same computer, an eventual quantum computer is likely to use various combinations of qubits in its design.
The following is an incomplete list of physical implementations of qubits, and the choices of basis are by convention only.
| Physical support | Name | Information support |  |
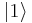 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Photon | Polarization encoding | Polarization of light | Horizontal | Vertical |
| Number of photons | Fock state | Vacuum | Single photon state | |
| Time-bin encoding | Time of arrival | Early | Late | |
| Coherent state of light | Squeezed light | Quadrature | Amplitude-squeezed state | Phase-squeezed state |
| Electrons | Electronic spin | Spin | Up | Down |
| Electron number | Charge | No electron | One electron | |
| Nucleus | Nuclear spin addressed through NMR | Spin | Up | Down |
| Optical lattices | Atomic spin | Spin | Up | Down |
| Josephson junction | Superconducting charge qubit | Charge | Uncharged superconducting island (Q=0) | Charged superconducting island (Q=2e, one extra Cooper pair) |
| Superconducting flux qubit | Current | Clockwise current | Counterclockwise current | |
| Superconducting phase qubit | Energy | Ground state | First excited state | |
| Singly charged quantum dot pair | Electron localization | Charge | Electron on left dot | Electron on right dot |
| Quantum dot | Dot spin | Spin | Down | Up |
Qubit storage
In a paper entitled: "Solid-state quantum memory using the 31P nuclear spin," published in the October 23, 2008 issue of the journal Nature,[3] an international team of scientists that included researchers with the U.S. Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) reported the first relatively long (1.75 seconds) and coherent transfer of a superposition state in an electron spin 'processing' qubit to a nuclear spin 'memory' qubit. This event can be considered the first relatively consistent quantum Data storage, a vital step towards the development of quantum computing.
Origin of the concept and term
The concept of the qubit was unknowingly introduced by Stephen Wiesner in 1983, in his proposal for unforgeable quantum money, which he had tried to publish for over a decade. [4] [5]
The coining of the term "qubit" is attributed to Benjamin Schumacher.[6] In the acknowledgments of his paper, Schumacher states that the term qubit was invented in jest (due to its phonological resemblance with an ancient unit of length called cubit), during a conversation with William Wootters. The paper describes a way of compressing states emitted by a quantum source of information so that they require fewer physical resources to store. This procedure is now known as Schumacher compression.
See also
References
- ^ UIBK.ac.at
- ^ L. B. Ioffe, V. B. Geshkenbein, M. V. Feigel'man, A. L. Fauchère and G. Blatter (1999). "Environmentally decoupled sds-wave Josephson junctions for quantum computing". Nature 398 (6729): 679. arXiv:cond-mat/9809116. Bibcode 1999Natur.398..679I. doi:10.1038/19464.
- ^ J. J. L. Morton; et al. (2008). "Solid-state quantum memory using the 31P nuclear spin". Nature 455 (7216): 1085–1088. Bibcode 2008Natur.455.1085M. doi:10.1038/nature07295.
- ^ S. Weisner (1983). "Conjugate coding". Association of Computing Machinery, Special Inter- est Group in Algorithms and Computation Theory 15: 78–88.
- ^ A. Zelinger, Dance of the Photons, Farrar, Straus, Giroux, New York, 2010, pp. 189, 192.
- ^ B. Schumacher (1995). "Quantum coding". Physical Review A 51 (4): 2738–2747. Bibcode 1995PhRvA..51.2738S. doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.51.2738.
External links
- An update on qubits in the Oct 2005 issue of Scientific American
- Qubit.org cofounded by one of the pioneers in quantum computation, David Deutsch
- Quantum Computing Reading on Quantum Computing
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||