Protein structure prediction
Protein structure prediction is the prediction of the three-dimensional structure of a protein from its amino acid sequence — that is, the prediction of its secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure from its primary structure. Structure prediction is fundamentally different from the inverse problem of protein design. Protein structure prediction is one of the most important goals pursued by bioinformatics and theoretical chemistry; it is highly important in medicine (for example, in drug design) and biotechnology (for example, in the design of novel enzymes). Every two years, the performance of current methods is assessed in the CASP experiment (Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction).
Protein structure and terminology
Proteins are chain of amino acids joined to gather by peptide bond. Many conformation of chain is possible due to the rotation of the chain about each Cα atom. It is these informational changes that are responsible for differences in the three dimensional structure of proteins. Each amino acid in the chain is polar i.e. it has separated positive and negative charged region with a free C=O group, which can act as hydrogen bond acceptor and an NH group, which can act as hydrogen bond donor. These groups interact in protein structure. The 20 amino acids can be classified according to the chemistry of R group. The R side chain also play an important structural role. Special role are played by glycine, which does not have a R chain and therefore can increase local flexibility in structure and cysteine, which can react with another cysteine and can form cross link and stabilize the structure.
Much of the protein core comprises regular secondary structures, α helices and β sheets, folded into a three-dimensional configuration. In these secondary structures, regular patterns of H bonds are formed between neighboring amino acids, and the amino acids have similar Φ and Ψ angles.
The formation of these structures neutralizes the polar groups on each amino acid. The secondary structures are tightly packed in the protein core in a hydrophobic environment. Each amino acid side group has a limited volume to occupy and a limited number of possible interactions with other near- by side chains, a situation that must be taken into account in molecular modeling and alignments. [1]
α Helix
The α helix is the most abundant type of secondary structure in proteins. The α helix has 3.6 amino acids per turn with an H bond formed between every fourth residue; the average length is 10 amino acids (3 turns) or 10 Å but varies from 5 to 40 (1.5 to 11 turns). The alignment of the H bonds creates a dipole moment for the helix with a resulting partial positive charge at the amino end of the helix. Because this region has free NH2 groups, it will interact with negatively charged groups such as phosphates. The commonest location of α helices is at the surface of protein cores, where they provide an interface with the aqueous environment. The inner-facing side of the helix tends to have hydrophobic amino acids and the outer-facing side hydrophilic amino acids. Thus, every third of four amino acids along the chain will tend to be hydrophobic, a pattern that can be quite readily detected. In the leucine zipper motif, a repeating pattern of leucines on the facing sides of two adjacent helices is highly predictive of the motif. A helical-wheel plot can be used to show this repeated pattern. Other α helices buried in the protein core or in cellular membranes have a higher and more regular distribution of hydrophobic amino acids, and are highly predictive of such structures. Helices exposed on the surface have a lower proportion of hydrophobic amino acids. Amino acid content can be predictive of an α -helical region. Regions richer in alanine (A), glutamic acid (E), leucine (L), and methionine (M) and poorer in proline (P), glycine (G), tyrosine (Y), and serine (S) tend to form an α helix. Proline destabilizes or breaks an α helix but can be present in longer helices, forming a bend. There are computer programs for predicting quite reliably the general location of α helices in a new protein sequence.
β Sheet
β Sheets are formed by H bonds between an average of 5–10 consecutive amino acids in one portion of the chain with another 5–10 farther down the chain. The interacting regions may be adjacent, with a short loop in between, or far apart, with other structures in between. Every chain may run in the same direction to form a parallel sheet, every other chain may run in the reverse chemical direction to form an anti parallel sheet, or the chains may be parallel and anti parallel to form a mixed sheet.The pattern of H bonding is different in the parallel and anti parallel configurations. Each amino acid in the interior strands of the sheet forms two H bonds with neighboring amino acids, whereas each amino acid on the outside strands forms only one bond with an interior strand. Looking across the sheet at right angles to the strands, more distant strands are rotated slightly counterclockwise to form a left-handed twist. The Cα atoms alternate above and below the sheet in a pleated structure, and the R side groups of the amino acids alternate above and below the pleats. The Φ and Ψ angles of the amino acids in sheets vary considerably in one region of the Ramachandran plot. It is more difficult to predict the location of β sheets than of α helices. The situation improves some what when the amino acid variation in multiple sequence alignments is taken into account.
Loop
Loops are regions of a protein chain that are (1) between α helices and β sheets, (2) of various lengths and three-dimensional configurations, and (3) on the surface of the structure. Hairpin loops that represent a complete turn in the polypeptide chain joining two antiparallel β strands may be as short as two amino acids in length. Loops interact with the surrounding aqueous environment and other proteins. Because amino acids in loops are not constrained by space and environment as are amino acids in the core region, and do not have an effect on the arrangement of secondary structures in the core, more substitutions, insertions, and deletions may occur. Thus, in a sequence alignment, the presence of these features may be an indication of a loop. The positions of introns in genomic DNA sometimes correspond to the locations of loops in the encoded protein. Loops also tend to have charged and polar amino acids and are frequently a component of active sites. A detailed examination of loop structures has shown that they fall into distinct families.
Coils
A region of secondary structure that is not a α helix, a β sheet, or a recognizable turn is commonly referred to as a coil. [1]
Protein classification
Proteins may be classified according to both structural and sequence similarity. For structural classification, the sizes and spatial arrangements of secondary structures described in the above paragraph are compared in known three-dimensional structures.Classification based on sequence similarity was historically the first to be used. Initially, similarity based on alignments of whole sequences was per- formed. Later, proteins were classified on the basis of the occurrence of conserved amino acid patterns. Databases that classify proteins by one or more of these schemes are available. In considering protein classification schemes, it is important to keep several observations in mind. First, two entirely different protein sequences from different evolutionary origins may fold into a similar structure. Conversely, the sequence of an ancient gene for a given structure may have diverged considerably in different species while at the same time maintaining the same basic structural features. Recognizing any remaining sequence similarity in such cases may be a very difficult task. Second, two proteins that share a significant degree of sequence similarity either with each other or with a third sequence also share an evolutionary origin and should share some structural features also. However, gene duplication and genetic rearrangements during evolution may give rise to new gene copies, which can then evolve into proteins with new function and structure.[1]
Terms Used for Classifying Protein Structures and Sequences
The more commonly used terms for describing evolutionary and structural relationships among proteins are listed below. Many additional terms are used to describe various kinds of structural features found in proteins. Descriptions of such terms may be found at the CATH Web site the Structural Classification of Proteins (SCOP) Web site and a Glaxo-Wellcome tutorial on the Swiss bioinformatics Expasy Web site.
1.Active site is a localized combination of amino acid side groups within the tertiary (three-dimensional) or quaternary (protein subunit) structure that can interact with a chemically specific substrate and that provides the protein with biological activity. Proteins of very different amino acid sequences may fold into a structure that produces the same active site.
2.Architecture describes the relative orientations of secondary structures in a three- dimensional structure without regard to whether or not they share a similar loop structure.
3.fold is a type of architecture that also has a conserved loop structure.
4.Blocks is a term used to describe a conserved amino acid sequence pattern in a family of proteins. The pattern includes a series of possible matches at each position in the rep- resented sequences, but there are not any inserted or deleted positions in the pattern or in the sequences. By way of contrast, sequence profiles are a type of scoring matrix that represents a similar set of patterns that includes insertions and deletions.
5.Class is a term used to classify protein domains according to their secondary structural content and organization. Four classes were originally recognized by Levitt and Chothia (1976), and several others have been added in the SCOP database . Three classes are given in the CATH database: mainly- α, mainly-β, and α –β, with the α– β class including both alternating α /Β and α+β structures.
6.Core is the portion of a folded protein molecule that comprises the hydrophobic interior of α helices and β sheets. The compact structure brings together side groups of amino acids into close enough proximity so that they can interact. When comparing protein structures, as in the SCOP database, core refers to the region common to most of the structures that share a common fold or that are in the same superfamily. In structure prediction, core is sometimes defined as the arrangement of secondary structures that is likely to be conserved during evolutionary change. 7.Domain (sequence context) Domain refers to a segment of a polypeptide chain that can fold into a three-dimensional structure irrespective of the presence of other segments of the chain. The separate domains of a given protein may interact extensively or may be joined only by a length of polypeptide chain. A protein with several domains may use these domains for functional interactions with different molecules.
8.Family (sequence context) is a group of proteins of similar biochemical function that are more than 50% identical when aligned. This same cutoff is still used by the Protein Information Resource (PIR). A protein family comprises proteins with the same function in different organisms (orthologous sequences) but may also include proteins in the same organism (paralogous sequences) derived from gene duplication and rearrangements. If a multiple sequence alignment of a protein family reveals a common level of similarity throughout the lengths of the proteins, PIR refers to the family as a homeomorphic family. The aligned region is referred to as a homeomorphic domain, and this region may comprise several smaller homology domains that are shared with other families. Families may be further subdivided into subfamilies or grouped into superfamilies based on respective higher or lower levels of sequence similarity . The SCOP database reports 1296 families and the CATH database (version 1.7 beta), reports 1846 families. When the sequences of proteins with the same function are examined in greater detail, some are found to share high sequence similarity. They are obviously members of the same family by the above criteria. However, others are found that have very little, or even insignificant, sequence similarity with other family members. In such cases, the family relationship between two distant family members A and C can often be demonstrated by finding an additional family member B that shares significant similarity with both A and C . Thus, B provides a connecting link between A and C. Another approach is to examine distant alignments for highly conserved matches. At a level of identity of 50%, proteins are likely to have the same three-dimension- al structure, and the identical atoms in the sequence alignment will also superimpose within approximately 1 Å in the structural model. Thus, if the structure of one member of a family is known, a reliable prediction may be made for a second member of the family, and the higher the identity level, the more reliable the prediction. Protein structural modeling can be performed by examining how well the amino acid substitutions fit into the core of the three-dimensional structure.
9.Family (structural context) as used in the FSSP database(Families of structurally similar proteins) and the DALI/FSSP Web site, refers to two structures that have a significant level of structural similarity but not necessarily significant sequence similarity.
10.Fold is a term with similar meaning to structural motif, but in general refers to a somewhat larger combination of secondary structural units in the same configuration. Thus, proteins sharing the same fold have the same combination of secondary structures that are connected by similar loops. An example is the Rossman fold comprising several alternating α helices and parallel β strands. In the SCOP, CATH, and FSSP databases, the known protein structures have been classified into hierarchical levels of structural complexity with the fold as a basic level of classification.
11.Homologous domain (sequence context) refers to an extended sequence pattern, generally found by sequence alignment methods, that indicates a common evolutionary origin among the aligned sequences. A homology domain is generally longer than motifs. The domain may include all of a given protein sequence or only a portion of the sequence. Some domains are complex and made up of several smaller homology domains that became joined to form a larger one during evolution. A domain that covers an entire sequence is called the homeomorphic domain by PIR(Protein Information Resource).
12.Module is a region of conserved amino acid patterns comprising one or more motifs and considered to be a fundamental unit of structure or function. The presence of a module has also been used to classify proteins into families.
13.Motif (sequence context) refers to a conserved pattern of amino acids that is found in two or more proteins. In the Prosite catalog, a motif is an amino acid pattern that is found in a group of proteins that have a similar biochemical activity, and that often is near the active site of the protein. Examples of sequence motif databases are the Prosite catalog (http://www.expasy.ch/prosite) and the Stanford Motifs Database (http://dna.stanford.edu/emotif/).
14.Motif (structural context) refers to a combination of several secondary structural ele- ments produced by the folding of adjacent sections of the polypeptide chain into a specific three-dimensional configuration. An example is the helix-loop-helix motif. Structural motifs are also referred to as supersecondary structures and folds. 15.Position-specific scoring matrix (sequence context, also known as weight or scoring matrix) represents a conserved region in a multiple sequence alignment with no gaps. Each matrix column represents the variation found in one column of the multiple sequence alignment. Position-specific scoring matrix—3D (structural context) represents the amino acid variation found in an alignment of proteins that fall into the same structural class. Matrix columns represent the amino acid variation found at one amino acid position in the aligned structures.
16.Primary structure refers to the linear amino acid sequence of a protein, which chemi- cally is a polypeptide chain composed of amino acids joined by peptide bonds.
17.Profile (sequence context) is a scoring matrix that represents a multiple sequence align- ment of a protein family. The profile is usually obtained from a well-conserved region in a multiple sequence alignment. The profile is in the form of a matrix with each column representing a position in the alignment and each row one of the amino acids. Matrix val- ues give the likelihood of each amino acid at the corresponding position in the alignment. The profile is moved along the target sequence to locate the best scoring regions by a dynamic programming algorithm. Gaps are allowed during matching and a gap penalty is included in this case as a negative score when no amino acid is matched. A sequence profile may also be represented by a hidden Markov model, referred to as a profile HMM(hidden markov model).
18.Profile (structural context) is a scoring matrix that represents which amino acids should fit well and which should fit poorly at sequential positions in a known protein structure. Profile columns represent sequential positions in the structure, and profile rows repre- sent the 20 amino acids. As with a sequence profile, the structural profile is moved along a target sequence to find the highest possible alignment score by a dynamic program- ming algorithm. Gaps may be included and receive a penalty. The resulting score pro- vides an indication as to whether or not the target protein might adopt such a structure.
19.Quaternary structure is the three-dimensional configuration of a protein molecule com- prising several independent polypeptide chains.
20.Secondary structure refers to the interactions that occur between the C O and NH groups on amino acids in a polypeptide chain to form α helices, β sheets, turns, loops, and other forms, and that facilitate the folding into a three-dimensional structure. 21.Superfamily is a group of protein families of the same or different lengths that are related by distant yet detectable sequence similarity. Members of a given superfamily thus have a common evolutionary origin. Originally, Dayhoff defined the cutoff for superfamily status as being the chance that the sequences are not related of 10 6, on the basis of an alignment score (Dayhoff et al. 1978). Proteins with few identities in an alignment of the sequences but with a convincingly common number of structural and functional features are placed in the same superfamily. At the level of three-dimensional structure, superfamily proteins will share common structural features such as a common fold, but there may also be differences in the number and arrangement of secondary structures. The PIR resource uses the term homeomorphic superfamilies to refer to superfamilies that are composed of sequences that can be aligned from end to end, representing a sharing of single sequence homology domain, a region of similarity that extends throughout the alignment. This domain may also comprise smaller homology domains that are shared with other protein families and superfamilies. Although a given protein sequence may contain domains found in several superfamilies, thus indicating a complex evolutionary history, sequences will be assigned to only one homeomorphic superfamily based on the presence of similarity throughout a multiple sequence alignment. The superfamily alignment may also include regions that do not align either within or at the ends of the alignment. In contrast, sequences in the same family align well throughout the alignment.
22.Supersecondary structure is a term with similar meaning to a structural motif. Tertiary structure is the three-dimensional or globular structure formed by the pack- ing together or folding of secondary structures of a polypeptide chain. [1]
Secondary structure
Secondary structure prediction is a set of techniques in bioinformatics that aim to predict the local secondary structures of proteins and RNA sequences based only on knowledge of their primary structure — amino acid or nucleotide sequence, respectively. For proteins, a prediction consists of assigning regions of the amino acid sequence as likely alpha helices, beta strands (often noted as "extended" conformations), or turns. The success of a prediction is determined by comparing it to the results of the DSSP algorithm applied to the crystal structure of the protein; for nucleic acids, it may be determined from the hydrogen bonding pattern. Specialized algorithms have been developed for the detection of specific well-defined patterns such as transmembrane helices and coiled coils in proteins, or canonical microRNA structures in RNA.[1]
The best modern methods of secondary structure prediction in proteins reach about 80% accuracy; this high accuracy allows the use of the predictions in fold recognition and ab initio protein structure prediction, classification of structural motifs, and refinement of sequence alignments. The accuracy of current protein secondary structure prediction methods is assessed in weekly benchmarks such as LiveBench and EVA.
Background
Early methods of secondary structure prediction, introduced in the 1960s and early 1970s,[2] focused on identifying likely alpha helices and were based mainly on helix-coil transition models.[3] Significantly more accurate predictions that included beta sheets were introduced in the 1970s and relied on statistical assessments based on probability parameters derived from known solved structures. These methods, applied to a single sequence, are typically at most about 60-65% accurate, and often underpredict beta sheets.[1] The evolutionary conservation of secondary structures can be exploited by simultaneously assessing many homologous sequences in a multiple sequence alignment, by calculating the net secondary structure propensity of an aligned column of amino acids. In concert with larger databases of known protein structures and modern machine learning methods such as neural nets and support vector machines, these methods can achieve up 80% overall accuracy in globular proteins.[4] The theoretical upper limit of accuracy is around 90%,[4] partly due to idiosyncrasies in DSSP assignment near the ends of secondary structures, where local conformations vary under native conditions but may be forced to assume a single conformation in crystals due to packing constraints. Limitations are also imposed by secondary structure prediction's inability to account for tertiary structure; for example, a sequence predicted as a likely helix may still be able to adopt a beta-strand conformation if it is located within a beta-sheet region of the protein and its side chains pack well with their neighbors. Dramatic conformational changes related to the protein's function or environment can also alter local secondary structure.
Chou-Fasman method
The Chou-Fasman method was among the first secondary structure prediction algorithms developed and relies predominantly on probability parameters determined from relative frequencies of each amino acid's appearance in each type of secondary structure.[5] The original Chou-Fasman parameters, determined from the small sample of structures solved in the mid-1970s, produce poor results compared to modern methods, though the parameterization has been updated since it was first published. The Chou-Fasman method is roughly 50-60% accurate in predicting secondary structures.[1]
GOR method
The GOR method, named for the three scientists who developed it — Garnier, Osguthorpe, and Robson — is an information theory-based method developed not long after Chou-Fasman. It uses a more powerful probabilistic techniques of Bayesian inference.[6] The method is a specific optimized application of mathematics and algorithms developed in a series of papers by Robson and colleagues, eg.[7] and [8]). The GOR method is capable of continued extension by such principles, and has gone through several versions. The GOR method takes into account not only the probability of each amino acid having a particular secondary structure, but also the conditional probability of the amino acid assuming each structure given the contributions of its neighbors (it does not assume that the neighbors have that same structure). The approach is both more sensitive and more accurate than that of Chou and Fasman because amino acid structural propensities are only strong for a small number of amino acids such as proline and glycine. Weak contributions from each of many neighbors can add up to strong effect overall. The original GOR method was roughly 65% accurate and is dramatically more successful in predicting alpha helices than beta sheets, which it frequently mispredicted as loops or disorganized regions.[1] Later GOR methods considered also pairs of amino acids, significantly improving performance. The major difference from the following technique is perhaps that the weights in an implied network of contributing terms are assigned a priori, from statistical analysis of proteins of known structure, not by feedback to optimize agreement with a training set of such.
Machine learning
Neural network methods use training sets of solved structures to identify common sequence motifs associated with particular arrangements of secondary structures. These methods are over 70% accurate in their predictions, although beta strands are still often underpredicted due to the lack of three-dimensional structural information that would allow assessment of hydrogen bonding patterns that can promote formation of the extended conformation required for the presence of a complete beta sheet.[1]
Support vector machines have proven particularly useful for predicting the locations of turns, which are difficult to identify with statistical methods.[9] The requirement of relatively small training sets has also been cited as an advantage to avoid overfitting to existing structural data.[10]
Extensions of machine learning techniques attempt to predict more fine-grained local properties of proteins, such as backbone dihedral angles in unassigned regions. Both SVMs[11] and neural networks[12] have been applied to this problem.[9]
Other improvements
It is reported that in addition to the protein sequence, secondary structure formation depends on other factors. For example, it is reported that secondary structure tendencies depend also on local environment,[13] solvent accessibility of residues,[14] protein structural class,[15] and even the organism from which the proteins are obtained.[16] Based on such observations, some studies have shown that secondary structure prediction can be improved by addition of information about protein structural class,[17] residue accessible surface area[18][19] and also contact number information.[20]
Sequence covariation methods rely on the existence of a data set composed of multiple homologous RNA sequences with related but dissimilar sequences. These methods analyze the covariation of individual base sites in evolution; maintenance at two widely separated sites of a pair of base-pairing nucleotides indicates the presence of a structurally required hydrogen bond between those positions. The general problem of pseudoknot prediction has been shown to be NP-complete.[21]
Tertiary structure
The practical role of protein structure prediction is now more important than ever. Massive amounts of protein sequence data are produced by modern large-scale DNA sequencing efforts such as the Human Genome Project. Despite community-wide efforts in structural genomics, the output of experimentally determined protein structures—typically by time-consuming and relatively expensive X-ray crystallography or NMR spectroscopy—is lagging far behind the output of protein sequences.
The protein structure prediction remains an extremely difficult and unresolved undertaking. The two main problems are calculation of protein free energy and finding the global minimum of this energy. A protein structure prediction method must explore the space of possible protein structures which is astronomically large. These problems can be partially bypassed in "comparative" or homology modeling and fold recognition methods, in which the search space is pruned by the assumption that the protein in question adopts a structure that is close to the experimentally determined structure of another homologous protein. On the other hand, the de novo or ab initio protein structure prediction methods must explicitly resolve these problems. The progress and challenges in protein structure prediction has been reviewed in Zhang 2008.[22]
Ab initio protein modelling
Ab initio- or de novo- protein modelling methods seek to build three-dimensional protein models "from scratch", i.e., based on physical principles rather than (directly) on previously solved structures. There are many possible procedures that either attempt to mimic protein folding or apply some stochastic method to search possible solutions (i.e., global optimization of a suitable energy function). These procedures tend to require vast computational resources, and have thus only been carried out for tiny proteins. To predict protein structure de novo for larger proteins will require better algorithms and larger computational resources like those afforded by either powerful supercomputers (such as Blue Gene or MDGRAPE-3) or distributed computing (such as Folding@home, the Human Proteome Folding Project and Rosetta@Home). Although these computational barriers are vast, the potential benefits of structural genomics (by predicted or experimental methods) make ab initio structure prediction an active research field.[22]
As an intermediate step towards predicted protein structures, contact map predictions have been proposed.
Comparative protein modeling
Comparative protein modelling uses previously solved structures as starting points, or templates. This is effective because it appears that although the number of actual proteins is vast, there is a limited set of tertiary structural motifs to which most proteins belong. It has been suggested that there are only around 2,000 distinct protein folds in nature, though there are many millions of different proteins.
These methods may also be split into two groups [22]:
- Homology modeling
- is based on the reasonable assumption that two homologous proteins will share very similar structures. Because a protein's fold is more evolutionarily conserved than its amino acid sequence, a target sequence can be modeled with reasonable accuracy on a very distantly related template, provided that the relationship between target and template can be discerned through sequence alignment. It has been suggested that the primary bottleneck in comparative modelling arises from difficulties in alignment rather than from errors in structure prediction given a known-good alignment.[23] Unsurprisingly, homology modelling is most accurate when the target and template have similar sequences.
- Protein threading[24]
- scans the amino acid sequence of an unknown structure against a database of solved structures. In each case, a scoring function is used to assess the compatibility of the sequence to the structure, thus yielding possible three-dimensional models. This type of method is also known as 3D-1D fold recognition due to its compatibility analysis between three-dimensional structures and linear protein sequences. This method has also given rise to methods performing an inverse folding search by evaluating the compatibility of a given structure with a large database of sequences, thus predicting which sequences have the potential to produce a given fold.
Side-chain geometry prediction
Accurate packing of the amino acid side chains represents a separate problem in protein structure prediction. Methods that specifically address the problem of predicting side-chain geometry include dead-end elimination and the self-consistent mean field methods. The side chain conformations with low energy are usually determined on the rigid polypeptide backbone and using a set of discrete side chain conformations known as "rotamers." The methods attempt to identify the set of rotamers that minimize the model's overall energy.
These methods use rotamer libraries, which are collections of favorable conformations for each residue type in proteins. Rotamer libraries may contain information about the conformation, its frequency, and the standard deviations about mean dihedral angles, which can be used in sampling.[25] Rotamer libraries are derived from structural bioinformatics or other statistical analysis of side-chain conformations in known experimental structures of proteins, such as by clustering the observed conformations for tetrahedral carbons near the staggered (60°, 180°, -60°) values.
Rotamer libraries can be backbone-independent, secondary-structure-dependent, or backbone-dependent. Backbone-independent rotamer libraries make no reference to backbone conformation, and are calculated from all available side chains of a certain type (for instance, the first example of a rotamer library, done by Ponder and Richards at Yale in 1987).[26] Secondary-structure-dependent libraries present different dihedral angles and/or rotamer frequencies for 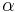 -helix,
-helix, 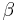 -sheet, or coil secondary structures.[27][28] Backbone-dependent rotamer libraries present conformations and/or frequencies dependent on the local backbone conformation as defined by the backbone dihedral angles
-sheet, or coil secondary structures.[27][28] Backbone-dependent rotamer libraries present conformations and/or frequencies dependent on the local backbone conformation as defined by the backbone dihedral angles  and
and 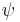 , regardless of secondary structure.[29]
, regardless of secondary structure.[29]
The modern versions of these libraries as used in most software are presented as multidimensional distributions of probability or frequency, where the peaks correspond to the dihedral-angle conformations considered as individual rotamers in the lists. Some versions are based on very carefully curated data and are used primarily for structure validation,[30] while others emphasize relative frequencies in much larger data sets and are the form used primarily for structure prediction, such as the Dunbrack rotamer libraries.[31]
Side-chain packing methods are most useful for analyzing the protein's hydrophobic core, where side chains are more closely packed; they have more difficulty addressing the looser constraints and higher flexibility of surface residues, which often occupy multiple rotamer conformations rather than just one.[32][33]
Prediction of structural classes
Statistical methods have been developed for predicting structural classes of proteins based on their amino acid composition,[34] pseudo amino acid composition[35][36][37][38] and functional domain composition.[39]
Quaternary structure
In the case of complexes of two or more proteins, where the structures of the proteins are known or can be predicted with high accuracy, protein–protein docking methods can be used to predict the structure of the complex. Information of the effect of mutations at specific sites on the affinity of the complex helps to understand the complex structure and to guide docking methods.
Modeling and Simulation as a tool for protein structure prediction
Experimental molecular biology research is often a painstakingly slow process that typically involves a long sequence of carefully performed experiments, using a variety of equipment and laboratory specialists. For example, positively identifying a protein by structure may take years of work. The protein must be isolated, purified, crystallized, and then imaged. Because each step may involve dozens of failed attempts, many scientists not primarily interested in the experimental methods, but simply needing the structure data, look to other non-experimental methods. In determining protein structure, the primary alternative to experimental or wet-lab(wet laboratory) techniques is bioinformatics. Although computational methods may be able to deliver a solution to a molecular biology problem such as structure determination in days or weeks instead of months or years, the solution is only as good as the formulation of the problem. In the case of protein structure determination or prediction, formulating the problem entails creating a model of the molecule and the major environmental factors that may influence its structure. With a valid model definition, arriving at a solution—that is, using the model to drive a simulation of the molecule's behavior and structure is simply a matter of executing a program and then evaluating the results. A valid model that is, one that adequately describes relationships in the real world the spreadsheet provides an environment in which the model can be brought to life, simulating the activity of the real-world system over time or in response to specific events. For example, an accountant might look at the expected profits from a business, given a spreadsheet model that describes sales and business expenses over the course of a year. An engineer might use a model of a steel beam to explore its dynamic stability when used as a supporting structure in a bridge. Similarly, a biologist might examine the population dynamics in a closed ecosystem of various strains of bacteria, based on a model that describes the relationships between population, food supply, and the environment. A spreadsheet model is a set of linear equations relating the values of several variables (cells). Equipped with a spreadsheet and a few equations, a molecular biologist might define a model of a neural network that can learn to recognize amino acid sequences and assign protein structures to certain sequences. The model of a single neuron in the artificial neural network(see figure "Simplified view of a feedforward artificial neural network") defines the output of the neuron as the weighted sum of inputs to the neuron, including feedback from the output: The model of the entire neural network additionally specifies the interconnection of the individual neuron models. Mathematically, the model of an individual neuron that can accept four outputs (W) with their associated fixed weights (W) can be expressed as:
output=∑4OiWi where i=0,
Note that this model for an individual neuron is a greatly simplified representation of the function of an actual neuron in the human nervous system. For example, neurons in the brain are regularly bathed in substances from naturally produced endorphins to drugs such as seratonin release inhibitors that dynamically alter the strength of connections, represented by the fixed weights (w) in the neuron model. The advantage of ignoring the intricacies of the actual nervous system is computational efficiency and lower overhead associated with developing a model. A simpler model is also easier to develop and maintain compared to developing and maintaining a more complex model. The challenge is defining a model that is simple enough computationally and yet is rich enough to accurately define the behavior of the system.
Although spreadsheets are still used for modeling and simulation applications in business, science, and engineering, all but the simplest modeling is performed with software optimized for particular domains. For example, nuclear physicists use custom modeling and simulation programs running on supercomputers to simulate the power of nuclear explosions. Similarly, life scientists use a variety of microcomputer-based simulations to explore everything from population dynamics to the docking of proteins.
The downside of using a general-purpose spreadsheet as a platform for modeling and simulation is related to performance, flexibility, visualization capabilities, standards, and startup time. A general- purpose spreadsheet, like a general-purpose language such as extensible Markup Language (XML) or C++, is designed to solve a variety of problems. As such, it represents a compromise between flexibility and performance. Although a spreadsheet can be used to prototype virtually any type of simulation, the simulation will likely run several orders of magnitudes slower than a simulation developed in an environment designed for modeling and simulation.
Similarly, coding a simulation in C++ may result in a system with a higher performance than can be obtained with a dedicated simulation system. However, the startup time associated with a domain- specific simulation will likely be several orders of magnitude lower that that associated with the general-purpose language. For example, classification systems based on a neural network simulation are typically outperformed by classification systems developed in C++ or some other compiled language. However, creating a classification system with a neural network system may take only minutes. Neural network systems typically provide a library of predefined models that the user can incorporate in a neural network by connecting icons graphically instead of making extensive use of mathematical equations. Like using a high-level programming language, there is no need to develop or even fully understand low-level neuron model operation in these systems to create functional classifiers.
Even if a general-purpose language is used to develop a simulation, there are numerous reasons for going through the time and hassle of developing a model of a real-world system. Simulations allow conditions in the real world to be evaluated in compressed or expanded time and under a variety of conditions that would be too dangerous, too time-consuming, occur too infrequently, or that would otherwise be impractical in the real world. Instead of taking days or weeks to set up and run a series of biological experiments on the population dynamics of yeast under a variety of environmental conditions, the effect of, for example, an increase in temperature, can be explored in a few minutes through a simulation. Common uses of modeling and simulation include predicting the course and results of certain actions, and exploring the changes in outcome that result when actions are modified. Several bioinformatics R&D groups are focused on developing simulation-based systems to determine, for example, if a candidate molecule for a new drug will exhibit toxicity in patients before money is invested in actually synthesizing the drug. In this regard, simulation is a means of identifying problem areas and verifying that all variables are known before construction of the drug development facility is begun. As an analysis tool, simulations help explain why certain events occur, where there are inefficiencies, and whether specific modifications in the system will compensate for or remove these inefficiencies. The range of possible applications of modeling and simulation in bioinformatics is extensive. These applications range from understanding basic metabolic pathways to exploring genetic drift. One of the most promising application areas of modeling and simulation in bioinformatics and the most heavily funded is as a facilitator of drug discovery, which in turn depends on modeling and simulating protein structure and function. Given the exponentially increasing rate at which models of proteins are being added to the Protein Data Bank (PDB), modeling and simulation of proteins and their interaction with other molecules are the most promising means in our lifetimes of linking protein sequence, structure, function, and expression, with the clinical relevance of the proteome.
Applications of Modeling and Simulation in Bioinformatics.
- 1.Clinical What-If Analysis
- 2.Drug Discovery and Development
- 5.Exploring Molecular Mechanisms of Action
- 6.Personal Health Prediction
- 7.Drug Efficacy Prediction
- 12.Protein structure prediction
Software
I-TASSER is the best server for protein structure prediction according to the 2006-2010 CASP experiments (CASP7, CASP8 and CASP9). The standalone I-TASSER package is freely available for download.
RaptorX excels at aligning hard targets according to the 2010 CASP9 experiments. RaptorX generates the significantly better alignments for the hardest 50 CASP9 template-based modeling targets than other servers including those using consensus and refinement methods. The RaptorX server is available at server
MODELLER is a popular software tool for producing homology models using methodology derived from NMR spectroscopy data processing. SwissModel provides an automated web server for basic homology modeling.
HHpred, bioinfo.pl and Robetta widely used servers for protein structure prediction. HHsearch is a free software package for protein threading and remote homology detection.
SPARKSx is one of the top performing servers in the CASP focused on the remote fold recognition.[41]
PEP-FOLD is a de novo approach aimed at predicting peptide structures from amino acid sequences, based on a HMM structural alphabet.[42][43]
Phyre and Phyre2 are amongst the top performing servers in the CASP international blind trials of structure prediction in homology modelling and remote fold recognition, and are designed with an emphasis on ease of use for non-experts.
RAPTOR (software) is a protein threading software that is based on integer programming. The basic algorithm for threading is described in[24] and is fairly straightforward to implement.
QUARK is an on-line server suitable for ab initio protein structure modeling.
Abalone is a Molecular Dynamics program for folding simulations with explicit or implicit water models.
TIP is a knowledgebase of STRUCTFAST[44] models and precomputed similarity relationships between sequences, structures, and binding sites. Several distributed computing projects concerning protein structure prediction have also been implemented, such as the Folding@home, Rosetta@home, Human Proteome Folding Project, Predictor@home, and TANPAKU.
The Foldit program seeks to investigate the pattern-recognition and puzzle-solving abilities inherent to the human mind in order to create more successful computer protein structure prediction software.
Computational approaches provide a fast alternative route to antibody structure prediction. Recently developed antibody FV region high resolution structure prediction algorithms, like RosettaAntibody, have been shown to generate high resolution homology models which have been used for successful docking.[45]
Reviews of software for structure prediction can be found at.[46]
Automatic structure prediction servers
CASP, which stands for Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction, is a community-wide experiment for protein structure prediction taking place every two years since 1994. CASP provides users and research groups with an opportunity to assess the quality of available methods and automatic servers for protein structure prediction. Official results for automatic structure prediction servers in the CASP7 benchmark (2006) are discussed by Battey et al..[47] Official CASP8 results are available for automatic servers and for human and server predictors. Unofficial results for automatic servers of the 2008 CASP8 benchmark are summarized on several lab websites and ranked according to slightly varying criteria: Zhang lab, Grishin lab, McGuffin lab, Baker lab, and Cheng lab.
See also
- Protein design
- Protein structure prediction software
- De novo protein structure prediction
- Molecular design software
- Molecular modeling software
- Modelling biological systems
- Fragment libraries
- Lattice proteins
- Statistical potential
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Mount DM (2004). Bioinformatics: Sequence and Genome Analysis. 2. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. ISBN 0879697121.
- ^ Guzzo, AV (1965). "Influence of Amino-Acid Sequence on Protein Structure". Biophys. J. 5 (6): 809–822. Bibcode 1965BpJ.....5..809G. doi:10.1016/S0006-3495(65)86753-4. PMC 1367904. PMID 5884309. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1367904.
Prothero, JW (1966). "Correlation between Distribution of Amino Acids and Alpha Helices". Biophys. J. 6 (3): 367–370. Bibcode 1966BpJ.....6..367P. doi:10.1016/S0006-3495(66)86662-6. PMC 1367951. PMID 5962284. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1367951.
Schiffer, M; Edmundson AB (1967). "Use of Helical Wheels to Represent Structures of Proteins and to Identify Segments with Helical Potential". Biophys. J. 7 (2): 121–35. Bibcode 1967BpJ.....7..121S. doi:10.1016/S0006-3495(67)86579-2. PMC 1368002. PMID 6048867. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1368002.
Kotelchuck, D; Scheraga HA (1969). "The Influence of Short-Range Interactions on Protein Conformation, II. A Model for Predicting the α-Helical Regions of Proteins". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 62 (1): 14–21. doi:10.1073/pnas.62.1.14. PMC 285948. PMID 5253650. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=285948.
Lewis, PN; Gō N, Gō M, Kotelchuck D, Scheraga HA (1970). "Helix Probability Profiles of Denatured Proteins and Their Correlation with Native Structures". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 65 (4): 810–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.65.4.810. PMC 282987. PMID 5266152. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=282987. - ^ Froimowitz M, Fasman GD (1974). "Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins using the helix-coil transition theory". Macromolecules 7 (5): 583–9. doi:10.1021/ma60041a009. PMID 4371089.
- ^ a b Dor O, Zhou Y (2006). "Achieving 80% tenfold cross-validated accuracy for secondary structure prediction by large-scale training". Proteins 66 (4): 838–45. doi:10.1002/prot.21298. PMID 17177203.
- ^ Chou PY, Fasman GD (1974). "Prediction of protein conformation". Biochemistry 13 (2): 222–245. doi:10.1021/bi00699a002. PMID 4358940.
- ^ Garnier J, Osguthorpe DJ, Robson B (1978). "Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins". J Mol Biol 120 (1): 97–120. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. PMID 642007.
- ^ Robson B, Pain RH (May 1971). "Analysis of the code relating sequence to conformation in proteins: possible implications for the mechanism of formation of helical regions". J. Mol. Biol. 58 (1): 237–59. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(71)90243-9. PMID 5088928. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/0022-2836(71)90243-9.
- ^ Robson B (September 1974). "Analysis of code relating sequences to conformation in globular proteins. Theory and application of expected information". Biochem. J. 141 (3): 853–67. PMC 1168191. PMID 4463965. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1168191.
- ^ a b Pham TH, Satou K, Ho TB (2005). "Support vector machines for prediction and analysis of beta and gamma-turns in proteins". J Bioinform Comput Biol 3 (2): 343–358. doi:10.1142/S0219720005001089. PMID 15852509.
- ^ Zhang Q, Yoon S, Welsh WJ (2005). "Improved method for predicting beta-turn using support vector machine". Bioinformatics 21 (10): 2370–4. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bti358. PMID 15797917.
- ^ Zimmermann O, Hansmann UH (2006). "Support vector machines for prediction of dihedral angle regions". Bioinformatics 22 (24): 3009–15. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btl489. PMID 17005536.
- ^ Kuang R, Leslie CS, Yang AS (2004). "Protein backbone angle prediction with machine learning approaches". Bioinformatics 20 (10): 1612–21. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bth136. PMID 14988121.
- ^ Zhong L, Johnson WC Jr (1992). "Environment affects amino acid preference for secondary structure". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89 (10): 4462–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.10.4462. PMC 49102. PMID 1584778. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=49102.
- ^ Macdonald JR, Johnson WC Jr (2001). "Environmental features are important in determining protein secondary structure". Protein Sci. 10 (6): 1172–7. doi:10.1110/ps.420101. PMC 2374018. PMID 11369855. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2374018.
- ^ Costantini S, Colonna G, Facchiano AM (2006). "Amino acid propensities for secondary structures are influenced by the protein structural class". Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 342 (2): 441–451. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.01.159. PMID 16487481.
- ^ Marashi SA, et al. (2007). "Adaptation of proteins to different environments: a comparison of proteome structural properties in Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli". J Theor Biol 244 (1): 127–132. doi:10.1016/j.jtbi.2006.07.021. PMID 16945389.
- ^ Costantini S, Colonna G, Facchiano AM (2007). "PreSSAPro: a software for the prediction of secondary structure by amino acid properties". Comput Biol Chem 31 (5-6): 389–392. doi:10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2007.08.010. PMID 17888742.
- ^ Momen-Roknabadi A, et al. (2008). "Impact of residue accessible surface area on the prediction of protein secondary structures". BMC Bioinformatics 9: 357. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-9-357. PMC 2553345. PMID 18759992. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2553345.
- ^ Adamczak R, Porollo A, Meller J (2005). "Combining prediction of secondary structure and solvent accessibility in proteins". Proteins 59 (3): 467–475. doi:10.1002/prot.20441. PMID 15768403.
- ^ Lakizadeh A, Marashi SA (2009). "Addition of contact number information can improve protein secondary structure prediction by neural networks". Excli J. 8: 66–73. http://www.excli.de/vol8/lakizadeh_03_2009/lakizadeh_250309a_proof.pdf.
- ^ Lyngsø RB, Pedersen CN (2000). "RNA pseudoknot prediction in energy-based models". J Comput Biol 7 (3-4): 409–427. doi:10.1089/106652700750050862. PMID 11108471.
- ^ a b c Zhang Y (2008). "Progress and challenges in protein structure prediction". Curr Opin Struct Biol 18 (3): 342–8. doi:10.1016/j.sbi.2008.02.004. PMC 2680823. PMID 18436442. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2680823.
- ^ Zhang Y and Skolnick J (2005). "The protein structure prediction problem could be solved using the current PDB library". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102 (4): 1029–34. doi:10.1073/pnas.0407152101. PMC 545829. PMID 15653774. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=545829.
- ^ a b Bowie JU, Luthy R, Eisenberg D (1991). "A method to identify protein sequences that fold into a known three-dimensional structure". Science 253 (5016): 164–170. doi:10.1126/science.1853201. PMID 1853201.
- ^ Dunbrack, RL (2002). "Rotamer Libraries in the 21st Century". Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 12 (4): 431–440. doi:10.1016/S0959-440X(02)00344-5. PMID 12163064.
- ^ Ponder JW, Richards FM (1987). "Tertiary templates for proteins: use of packing criteria in the enumeration of allowed sequences for different structural classes". J. Mol. Biol. 193 (4): 775–791. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(87)90358-5. PMID 2441069.
- ^ Lovell SC, Word JM, Richardson JS, Richardson DC (2000). "The penultimate rotamer library". Proteins: Struc. Func. Genet. 40: 389–408. doi:10.1002/1097-0134(20000815)40:3<389::AID-PROT50>3.0.CO;2-2.
- ^ Richardson Rotamer Libraries
- ^ Shapovalov MV, Dunbrack, RL (2011). "A smoothed backbone-dependent rotamer library for proteins derived from adaptive kernel density estimates and regressions". Structure (Cell Press) 19 (6): 844–858. doi:10.1016/j.str.2011.03.019. PMC 3118414. PMID 21645855. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=3118414.
- ^ MolProbity
- ^ Dunbrack Rotamer Libraries
- ^ Voigt CA, Gordon DB, Mayo SL (2000). "Trading accuracy for speed: A quantitative comparison of search algorithms in protein sequence design". J Mol Biol 299 (3): 789–803. doi:10.1006/jmbi.2000.3758. PMID 10835284.
- ^ Krivov GG, Shapovalov MV, Dunbrack, RL (2009). "Improved prediction of protein side-chain conformations with SCWRL4". Proteins 77 (3): 778–795. doi:10.1002/prot.22488. PMC 2885146. PMID 19603484. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2885146.
- ^ Chou KC, Zhang CT (1995). "Prediction of protein structural classes". Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 30 (4): 275–349. doi:10.3109/10409239509083488. PMID 7587280.
- ^ Chen C, Zhou X, Tian Y, Zou X, Cai P (October 2006). "Predicting protein structural class with pseudo-amino acid composition and support vector machine fusion network". Anal. Biochem. 357 (1): 116–21. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2006.07.022. PMID 16920060.
- ^ Chen C, Tian YX, Zou XY, Cai PX, Mo JY (December 2006). "Using pseudo-amino acid composition and support vector machine to predict protein structural class". J. Theor. Biol. 243 (3): 444–8. doi:10.1016/j.jtbi.2006.06.025. PMID 16908032.
- ^ Lin H, Li QZ (July 2007). "Using pseudo amino acid composition to predict protein structural class: approached by incorporating 400 dipeptide components". J Comput Chem 28 (9): 1463–6. doi:10.1002/jcc.20554. PMID 17330882.
- ^ Xiao X, Wang P, Chou KC (October 2008). "Predicting protein structural classes with pseudo amino acid composition: an approach using geometric moments of cellular automaton image". J. Theor. Biol. 254 (3): 691–6. doi:10.1016/j.jtbi.2008.06.016. PMID 18634802.
- ^ Chou KC, Cai YD (September 2004). "Predicting protein structural class by functional domain composition". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 321 (4): 1007–9. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.07.059. PMID 15358128.
- ^ a b Bryan Bergeron. Bioinformatics computing. Prentice Hall PTR. ISBN 0-13-100825-0.
- ^ Yang, Yuedong; Eshel Faraggi, Huiying Zhao, Yaoqi Zhou (2011). "Improving protein fold recognition and template-based modeling by employing probabilistic-based matching between predicted one-dimensional structural properties of the query and corresponding native properties of templates". Bioinformatics 27 (15): 2076–82. http://bioinformatics.oxfordjournals.org/content/27/15/2076.long.
- ^ Maupetit J, Derreumaux P, Tuffery P (2009). "A fast and accurate method for large-scale de novo peptide structure prediction.". J Comput Chem.: In press..
- ^ Maupetit J, Derreumaux P, Tuffery P (2009). "PEP-FOLD: an online resource for de novo peptide structure prediction.". Nucleic Acids Res. 37 (Web Server issue): W498–503. doi:10.1093/nar/gkp323. PMC 2703897. PMID 19433514. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2703897.
- ^ Debe DA, Danzer JF, Goddard WA, Poleksic A (2006). "STRUCTFAST: Protein sequence remote homology detection and alignment using novel dynamic programming and profile-profile scoring". Proteins 64 (4): 960–7. doi:10.1002/prot.21049. PMID 16786595.
- ^ Sivasubramanian A, Sircar A, Chaudhury S, Gray J J (2009). "Toward high-resolution homology modeling of antibody Fv regions and application to antibody–antigen docking". Proteins 74 (2): 497–514. doi:10.1002/prot.22309. PMC 2909601. PMID 19062174. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2909601.
- ^ Nayeem A, Sitkoff D, Krystek S Jr (2006). "A comparative study of available software for high-accuracy homology modeling: From sequence alignments to structural models". Protein Sci 15 (4): 808–824. doi:10.1110/ps.051892906. PMC 2242473. PMID 16600967. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2242473.
- ^ Battey JN, Kopp J, Bordoli L, Read RJ, Clarke ND, Schwede T (2007). "Automated server predictions in CASP7". Proteins 69 (Suppl 8): 68–82. doi:10.1002/prot.21761. PMID 17894354.
Samudrala R, Moult J (February 1998). "An all-atom distance-dependent conditional probability discriminatory function for protein structure prediction". J. Mol. Biol. 275 (5): 895–916. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1997.1479. PMID 9480776. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0022-2836(97)91479-0.
External links
- NetSurfP — Secondary Structure and Surface Accessibility predictor
- CASP experiments home page
- Structure Prediction Flowchart (a clickable map)
- ExPASy Proteomics tools — list of prediction tools and servers
- DomPred — London's Global University
- DOMpro — University of California Irvine
- DomainSplit — University of Pittsburgh
- Meta-DP — University at Buffalo
- DOMAC — University of Missouri Columbia
- PredictProtein
- Protinfo — comparative and de novo protein structure and complex modelling server
- SCRATCH Protein structure prediction suite that includes SSpro
- PSIPRED The PSIPRED protein structure prediction server
- PSSpred A multiple neural network training program for protein secondary strucure prediction
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||