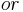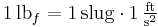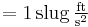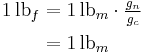Pound (force)
The pound force (symbol: lb, lbf, lbf) is a unit of force in some systems of measurement including English engineering units and British gravitational units.[1]
Contents |
Definitions
The pound-force is equal to the gravitational force exerted on a mass of one avoirdupois pound on the surface of Earth. Since the 18th century, the unit has been used in low-precision measurements, for which small changes in Earth's gravity (which varies from place to place by up to half a percent) can safely be neglected.[2]
The 20th century, however, brought the need for a more precise definition. A standardized value for acceleration due to gravity was therefore needed. Today, in accordance with the General Conference on Weights and Measures, standard gravity is usually taken to be 9.80665 m/s2 (32.174 049 ft/s2).[3][4]
The acceleration of the standard gravitational field (gn) and the international avoirdupois pound (lbm) define the pound-force as:[5]
Note that this is not to say that the pound-force of an object of weight n pounds is equal to n•lbm. In fact, on or near the surface of the earth, 1 lbf = 1 lbm. By Newton's Second Law of Motion, the force that acts on an object is defined by F=m•a. In applying this to the concept of the pound force it is important to realize that the relevant unit is not the pound-mass lbm but rather the slug.
Thus, the definition of pound-force can be rephrased in the appropriate terms. A slug has a mass unit equivalent of 32.174049 lbm. A pound-force is the amount of force required to accelerate a slug at a rate of 1 ft/s2, so:
Alternatively, to solve for lbf = F = m•a, convert lbm to slugs by dividing by 32.174049 to yield lbf = F = lbm•a. Near the surface of the earth, gn = 32.174049ft/s2, and this value can be used for a. Converting slugs back into lbm reveals lbf = lbm. This holds true while near the earth's surface where gravitational difference are relatively minor.
This results in the following (again, near the earth's surface):
Conversion to other units
| newton (SI unit) |
dyne | kilogram-force, kilopond |
pound-force | poundal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 N | ≡ 1 kg·m/s² | = 105 dyn | ≈ 0.10197 kp | ≈ 0.22481 lbF | ≈ 7.2330 pdl |
| 1 dyn | = 10−5 N | ≡ 1 g·cm/s² | ≈ 1.0197×10−6 kp | ≈ 2.2481×10−6 lbF | ≈ 7.2330×10−5 pdl |
| 1 kp | = 9.80665 N | = 980665 dyn | ≡ gn·(1 kg) | ≈ 2.2046 lbF | ≈ 70.932 pdl |
| 1 lbF | ≈ 4.448222 N | ≈ 444822 dyn | ≈ 0.45359 kp | ≡ gn·(1 lb) | ≈ 32.174 pdl |
| 1 pdl | ≈ 0.138255 N | ≈ 13825 dyn | ≈ 0.014098 kp | ≈ 0.031081 lbF | ≡ 1 lb·ft/s² |
| The value of gn as used in the official definition of the kilogram-force is used here for all gravitational units. | |||||
Foot-pound-second systems of units
In some contexts, the term "pound" is used almost exclusively to refer to the unit of force and not the unit of mass. In those applications, the preferred unit of mass is the slug, i.e. lbf·s2/ft. In other contexts, the unit "pound" refers to a unit of mass. In circumstances where there may otherwise be ambiguity, the symbols "lbf" and "lbm" and the terms "pounds-force" and "pounds-mass" can be used to distinguish.
| Base | force, length, time | weight, length, time | mass, length, time | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Force (F) | 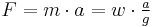 |
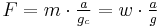 |
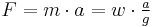 |
|||||
| Weight (w) | 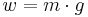 |
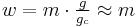 |
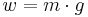 |
|||||
| System | BG | GM | EE | M | AE | CGS | MTS | SI |
| Acceleration (a) | ft/s2 | m/s2 | ft/s2 | m/s2 | ft/s2 | Gal | m/s2 | m/s2 |
| Mass (m) | slug | hyl | lbm | kg | lb | g | t | kg |
| Force (F) | lb | kp | lbF | kp | pdl | dyn | sn | N |
| Pressure (p) | lb/in2 | at | PSI | atm | pdl/ft2 | Ba | pz | Pa |
In the gravitational systems, the weight of the mass unit (pound-mass) on Earth's surface is approximately equal to the force unit (pound-force). This is convenient because one pound mass exerts one pound force due to gravity. Note, however, unlike the other systems the force unit is not equal to the mass unit multiplied by the acceleration unit[8]—the use of Newton's Second Law, F = m·a, requires another factor, gc, usually taken to be 32.174049 lbm·ft/lbf·s2 = 32.174049 lbm/slug. "Absolute" systems are coherent systems of units: by using the slug as the unit of mass, the "engineering" FPS system avoids the need for such a constant. The SI is an "absolute" metric system with kilogram and meter as base units.
See also
- Poundal
- Foot-pound (energy)
- Pound-mass
- Force
- mass
- Mass versus weight for the difference between the two physical properties
- Weight for a more complete discussion of customary units of force and mass
- Pounds per square inch, a unit of pressure
- Mass in general relativity
- Mass in special relativity
Notes and references
- Obert, Edward F., “THERMODYNAMICS”, D.J. Leggett Book Company Inc., New York 1948; Chapter I, Survey of Dimensions and Units, pages 1-24.
- ^ The Engineering ToolBox
- ^ Acceleration due to gravity varies over the surface of the Earth, generally increasing from about 9.78 m/s2 (32.1 ft/s2) at the equator to about 9.83 m/s2 (32.3 ft/s2) at the poles.
- ^ In 1901 the third CGPM declared (second resolution) that:
The value adopted in the International Service of Weights and Measures for the standard acceleration due to Earth's gravity is 980.665 cm/s2, value already stated in the laws of some countries.
This value was the conventional reference for calculating the kilogram-force, a unit of force whose use has been deprecated since the introduction of SI.
- ^ Barry N. Taylor, Guide for the Use of the International System of Units (SI), 1995, NIST Special Publication 811, Appendix B note 24
- ^ The international avoirdupois pound is defined to be exactly 0.45359237 kg.
- ^ Lindeburg, Michael, Civil Engineering Reference Manual for the PE Exam
- ^ Wurbs, Ralph A, Fort Hood Review Sessions for Professional Engineering Exam, http://engineeringregistration.tamu.edu/tapedreviews/Fluids-PE/PDF/Fluids-PE.pdf, retrieved October 26, 2011
- ^ The acceleration unit is the distance unit divided by the time unit squared.