Newton metre
A newton metre is a unit of torque (also called "moment") in the SI system. The symbolic form is N m or N·m,[1] and sometimes hyphenated newton-metre. One newton metre is equal to the torque resulting from a force of one newton applied perpendicularly to a moment arm which is one metre long.
It is also used less commonly as a unit of energy, in which case it is equivalent to the more common and standard SI unit of energy, the joule.[2] In this very different usage the metre term represents the distance traveled or displacement in the direction of the force, and not the perpendicular distance from a fulcrum as it does when used to express torque. This usage is discouraged by the SI authority, since it can lead to confusion as to whether a given quantity expressed in newton metres is a torque or a quantity of energy.[3]
N·m in terms of torque can be used in to calculate joules consumed by multiplying it by the angle (in radians) through which a body rotates in the direction of the torque. Or it can be used to calculate power output in watts by multiplying it by the speed of rotation (in radians per second). [4]
Conversion factors
- 1 newton meter = 0.7375621 foot-pound force (often "foot-pound")
- 1 kilogram-force meter = 9.80665 N·m[5][6]
- 1 foot-pound force (often "foot-pounds") = 1k pound-force foot (often "pound-foot") ≈ 1.3558 N·m
- 1 inch ounce-force = 7.0615518 mN·m
- 1 dyne centimetre = 10−7 N·m
See also
References
- ^ BIPM - unit symbols
- ^ For example: Eshbach's handbook of engineering fundamentals - 10.4 Engineering Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer "In SI units the basic unit of energy is Newton-Meter".
- ^ BIPM - special names
- ^
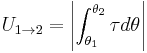
Ferdinand Beer et al., Vector Mechanics for Engineers page 1084. - ^ Mechanical Engineering Formulas Pocket Guide, p6
- ^ Concise encyclopedia of plastics, by Donald V. Rosato, Marlene G. Rosato, Dominick V. Rosato, p621