Neher–McGrath
The Neher–McGrath calculations calculate underground cable temperatures or maximum current ratings. From the basic principles that electric current leads to thermal heating and thermal power transfer to the ambient environment requires some temperature difference, it follows that the current leads to a temperature rise in the conductors. The ampacity, or maximum allowable current, of an electric power cable depends on the allowable temperatures of the cable and any adjacent materials such as insulation or termination equipment. For insulated cables, the insulation maximum temperature is normally the limiting material property that constrains ampacity. For uninsulated cables (typically used in overhead installation), the tensile strength of the cable (as affected by temperature) is normally the limiting material property. The Neher–McGrath method is the electrical industry standard for calculating cable ampacity, most often employed via lookup in tables of precomputed results for common configurations.
Neher and McGrath are the surnames of two electricians who wrote a famous article about how to calculate the capacity of current (ampacity) of cables. Their article is so useful that it is used as reference for the ampacity in most of the standard tables.
The equation in section 310-15(C) of the National Electrical Code, called the Neher–McGrath equation (given below), may be used to estimate the effective ampacity I of a cable. In the Neher–McGrath (NM) equation, TC is normally the limiting conductor temperature derived from the insulation or tensile strength limitations. 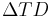 is a term added to the ambient temperature, TA, to compensate for heat generated in the jacket and insulation for higher voltages.
is a term added to the ambient temperature, TA, to compensate for heat generated in the jacket and insulation for higher voltages. 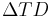 is called the dielectric loss temperature rise and is generally regarded as insignificant for voltages below 2000 V. Another term in the Neher–McGrath equation, (1+YC), is a multiplier used to convert direct current resistance (RDC) to the effective alternating current resistance (which typically includes conductor skin effects and eddy current losses). For wire sizes smaller than AWG No. 2, this term is generally regarded as insignificant. RCA is the effective thermal resistance between the conductor and the ambient conditions, which can require significant empirical and/or theoretical effort to estimate. With respect to the AC-sensitive terms, tabular presentation of the NM equation results in the National Electrical Code was developed assuming the standard North American power frequency of 60 hertz and sinusoidal wave forms for current and voltage.
is called the dielectric loss temperature rise and is generally regarded as insignificant for voltages below 2000 V. Another term in the Neher–McGrath equation, (1+YC), is a multiplier used to convert direct current resistance (RDC) to the effective alternating current resistance (which typically includes conductor skin effects and eddy current losses). For wire sizes smaller than AWG No. 2, this term is generally regarded as insignificant. RCA is the effective thermal resistance between the conductor and the ambient conditions, which can require significant empirical and/or theoretical effort to estimate. With respect to the AC-sensitive terms, tabular presentation of the NM equation results in the National Electrical Code was developed assuming the standard North American power frequency of 60 hertz and sinusoidal wave forms for current and voltage.
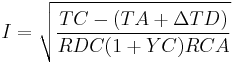
The challenges posed by the complexity of estimating RCA and of estimating the local increase in ambient temperature obtained by co-locating many cables (in a duct bank) create a market niche in the electric power industry for software dedicated to ampacity estimation.
References
- J. H. Neher and M. H. McGrath, The Calculation of the Temperature Rise and Load Capability of Cable Systems, AIEE Transactions, Part III, Volume 76, pp 752–772, October, 1957.
- neher-mcgrath.com