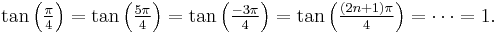Multivalued function
In mathematics, a multivalued function (shortly: multifunction, other names: many-valued function, set-valued function, set-valued map, multi-valued map, multimap, correspondence, carrier) is a left-total relation; i.e. every input is associated with one or more outputs. Strictly speaking, a "well-defined" function associates one, and only one, output to any particular input. The term "multivalued function" is, therefore, a misnomer since functions are single-valued. Multivalued functions often arise from functions which are not injective. Such functions do not have an inverse function, but they do have an inverse relation. The multivalued function corresponds to this inverse relation.
Contents |
Examples
- Every real number greater than zero or every complex number except 0 has two square roots. The square roots of 4 are in the set {+2,−2}. The square roots of 0 are described by the multiset {0,0}, because 0 is a root of multiplicity 2 of the polynomial x².
- Each complex number has three cube roots.
- The complex logarithm function is multiple-valued. The values assumed by log(1) are
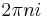 for all integers
for all integers  .
.
- Inverse trigonometric functions are multiple-valued because trigonometric functions are periodic. We have
- Consequently arctan(1) is intuitively related to several values: π/4, 5π/4, −3π/4, and so on. We can treat arctan as a single-valued function by restricting the domain of tan x to -π/2 < x < π/2 – a domain over which tan x is monotonically increasing. Thus, the range of arctan(x) becomes -π/2 < y < π/2. These values from a restricted domain are called principal values.
- The indefinite integral is a multivalued function of real-valued functions. The indefinite integral of a function is the set of functions whose derivative is that function. The constant of integration comes follows from the fact that the difference between any two indefinite integrals is a constant,
These are all examples of multivalued functions which come about from non-injective functions. Since the original functions do not preserve all the information of their inputs, they are not reversible. Often, the restriction of a multivalued function is a partial inverse of the original function.
Multivalued functions of a complex variable have branch points. For example the nth root and logarithm functions, 0 is a branch point; for the arctangent function, the imaginary units i and −i are branch points. Using the branch points these functions may be redefined to be single valued functions, by restricting the range. A suitable interval may be found through use of a branch cut, a kind of curve which connects pairs of branch points, thus reducing the multilayered Riemann surface of the function to a single layer. As in the case with real functions the restricted range may be called principal branch of the function.
Riemann surfaces
A more sophisticated viewpoint replaces "multivalued functions" with functions whose domain is a Riemann surface (so named in honor of Bernhard Riemann).
Set-valued analysis
Set-valued analysis is the generalization, to set-valued functions, of ideas from mathematical analysis and topology such as continuity, differentiation, integration, implicit function theorem, contraction mappings, measure theory, fixed-point theorems, optimization, topological degree theory. Equations and inequalities can be generalized to intervals and then to inclusions.
Types of multivalued functions
One can differentiate many continuity concepts, primarily closed graph property and upper and lower hemicontinuity. (One should be warned that often the terms upper and lower semicontinuous are used instead of upper and lower hemicontinuous reserved for the case of weak topology in domain; yet we arrive at the collision with the reserved names for upper and lower semicontinuous real-valued function). There exist also various definitions for measurability of multifunction.
History
The practice of allowing function in mathematics to mean also multivalued function dropped out of usage at some point in the first half of the twentieth century. Some evolution can be seen in different editions of A Course of Pure Mathematics by G. H. Hardy, for example. It probably persisted longest in the theory of special functions, for its occasional convenience.
The theory of multivalued functions was fairly systematically developed for the first time in C. Berge "Topological spaces" 1963.
Applications
Multifunctions arise in optimal control theory, especially differential inclusions and related subjects as game theory, where the Kakutani fixed point theorem for multifunctions has been applied to prove existence of Nash equilibria. This amongst many other properties loosely associated with approximability of upper hemicontinuous multifunctions via continuous functions explains why upper hemicontinuity is more preferred than lower hemicontinuity.
Nevertheless, lower hemicontinuous multifunctions usually possess continuous selections as stated in the Michael selection theorem which provides another characterisation of paracompact spaces (see: E. Michael, Continuous selections I" Ann. of Math. (2) 63 (1956), and D. Repovs, P.V. Semenov, Ernest Michael and theory of continuous selections" arXiv:0803.4473v1). Other selection theorems, like Bressan-Colombo directional continuous selection, Kuratowski—Ryll-Nardzewski measurable selection, Aumann measurable selection, Fryszkowski selection for decomposable maps are important in optimal control and the theory of differential inclusions.
In physics, multivalued functions play an increasingly important role. They form the mathematical basis for Dirac's magnetic monopoles, for the theory of defects in crystal and the resulting plasticity of materials, for vortices in superfluids and superconductors, and for phase transitions in these systems, for instance melting and quark confinement. They are the origin of gauge field structures in many branches of physics.
References
- Jean-Pierre Aubin, Arrigo Cellina Differential Inclusions, Set-Valued Maps And Viability Theory, Grundl. der Math. Wiss., vol. 264, Springer - Verlag, Berlin, 1984
- J.-P. Aubin and H. Frankowska Set-Valued Analysis, Birkhäuser, Basel, 1990
- Klaus Deimling Multivalued Differential Equations, Walter de Gruyter, 1992
- Kleinert, Hagen, Multivalued Fields in in Condensed Matter, Electrodynamics, and Gravitation, World Scientific (Singapore, 2008) (also available online)
- Kleinert, Hagen, Gauge Fields in Condensed Matter, Vol. I, "SUPERFLOW AND VORTEX LINES", pp. 1—742, Vol. II, "STRESSES AND DEFECTS", pp. 743-1456, World Scientific (Singapore, 1989); Paperback ISBN 9971-5-0210-0 (also available online: Vol. I and Vol. II)
- Aliprantis, Kim C. Border Infinite dimensional analysis. Hitchhiker's guide Springer
- J. Andres, L. Górniewicz Topological Fixed Point Principles for Boundary Value Problems, Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2003
- Topological methods for set-valued nonlinear analysis, Enayet U. Tarafdar, Mohammad Showkat Rahim Chowdhury, World Scientific, 2008, ISBN 9789812704672