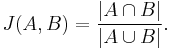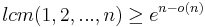MinHash
In computer science, MinHash (or the min-wise independent permutations locality sensitive hashing scheme) is a technique for quickly estimating how similar two sets are. The scheme was invented by Andrei Broder (1997),[1] and initially used in the AltaVista search engine to detect duplicate web pages and eliminate them from search results.[2] It has also been applied in large-scale clustering problems, such as clustering documents by the similarity of their sets of words.[1]
Contents |
Jaccard similarity and minimum hash values
The Jaccard similarity coefficient of two sets A and B is defined to be[3]
It is a number between 0 and 1; it is 0 when the two sets are disjoint, 1 when they are equal, and strictly between 0 and 1 otherwise. It is a commonly used indicator of the similarity between two sets: two sets are more similar when their Jaccard index is closer to 1, and more dissimilar when their Jaccard index is closer to 0.
Let h be a hash function that maps the members of A and B to distinct integers, and for any set S define hmin(S) to be the member x of S with the minimum value of h(x). Then hmin(A) = hmin(B) exactly when the minimum hash value of the union A ∪ B lies in the intersection A ∩ B. Therefore,
- Pr[hmin(A) = hmin(B)] = J(A,B).
In other words, if r is a random variable that is one when hmin(A) = hmin(B) and zero otherwise, then r is an unbiased estimator of J(A,B), although it has too high a variance to be useful on its own. The idea of the MinHash scheme is to reduce the variance by averaging together several variables constructed in the same way.
Algorithm
Variant with many hash functions
The simplest version of the minhash scheme uses k different hash functions, where k is a fixed integer parameter, and represents each set S by the k values of hmin(S) for these k functions.
To estimate J(A,B) using this version of the scheme, let y be the number of hash functions for which hmin(A) = hmin(B), and use y/k as the estimate. This estimate is the average of k different 0-1 random variables, each of which is one when hmin(A) = hmin(B) and zero otherwise, and each of which is an unbiased estimator of J(A,B). Therefore, their average is also an unbiased estimator, and by standard Chernoff bounds for sums of 0-1 random variables, its expected error is O(1/√k). Therefore, for any constant ε > 0 there is a constant k = O(1/ε2) such that the expected error of the estimate is at most ε. For example, 400 hashes would be required to estimate J(A,B) with an expected error less than or equal to .05.
Variant with a single hash function
It may be computationally expensive to compute multiple hash functions, but a related version of MinHash scheme avoids this penalty by using only a single hash function and uses it to select multiple values from each set rather than selecting only a single minimum value per hash function. Let h be a hash function, and let k be a fixed integer. If S is any set of k or more values in the domain of h, define h(k)(S) to be the subset of the k members of S that have the smallest values of h. This subset h(k)(S) is used as a signature for the set S, and the similarity of any two sets is estimated by comparing their signatures.
Specifically, let A and B be any two sets. Then X = h(k)(h(k)(A) ∪ h(k)(B)) = h(k)(A ∪ B) is a set of k elements of A ∪ B, and if h is a random function then any subset of k elements is equally likely to be chosen; that is, X is a simple random sample of A ∪ B. The subset Y = X ∩ h(k)(A) ∩ h(k)(B) is the set of members of X that belong to the intersection A ∩ B. Therefore, |Y|/k is an unbiased estimator of J(A,B). The difference between this estimator and the estimator produced by multiple hash functions is that Y always has exactly k members, whereas the multiple hash functions may lead to a smaller number of sampled elements due to the possibility that two different hash functions may have the same minima. However, when k is small relative to the sizes of the sets, this difference is negligible.
By standard Chernoff bounds for sampling without replacement, this estimator has expected error O(1/√k), matching the performance of the multiple-hash-function scheme.
Time analysis
The estimator |Y|/k can be computed in time O(k) from the two signatures of the given sets, in either variant of the scheme. Therefore, when ε and k are constants, the time to compute the estimated similarity from the signatures is also constant. The signature of each set can be computed in linear time, so when many pairwise similarities need to be estimated this method can lead to a substantial savings in running time compared to doing a full comparison of the members of each set.
Min-wise independent permutations
In order to implement the MinHash scheme as described above, one needs the hash function h to define a random permutation on n elements, where n is the total number of distinct elements in the union of all of the sets to be compared. But because there are n! different permutations, it would require Ω(n log n) bits just to specify a truly random permutation, an infeasibly large number for even moderate values of n. Because of this fact, by analogy to the theory of universal hashing, there has been significant work on finding a family of permutations that is "min-wise independent", meaning that for any subset of the domain, any element is equally likely to be the minimum. It has been established that a min-wise independent family of permutations must include at least
different permutations, and therefore that it needs Ω(n) bits to specify a single permutation, still infeasibly large.[2]
Because of this impracticality, two variant notions of min-wise independence have been introduced: restricted min-wise independent permutations families, and approximate min-wise independent families. Restricted min-wise independence is the min-wise independence property restricted to certain sets of cardinality at most k.[4] Approximate min-wise independence has at most a fixed probability ε of varying from full independence.[5]
Applications
The original applications for MinHash involved clustering and eliminating near-duplicates among web documents, represented as sets of the words occurring in those documents.[1][2] Similar techniques have also been used for clustering and near-duplicate elimination for other types of data, such as images: in the case of image data, an image can be represented as a set of smaller subimages cropped from it, or as sets of more complex image feature descriptions.[6]
Schleimer, Wilkerson & Aiken (2003) used MinHash as part of a scheme for the detection of plagiarism in digital documents, by finding pieces of text that were copied from some large database of documents. Their scheme involves representing a document as the set of its substrings of a given length, partitioning the document into larger fixed-length windows, and using the substring with the minimum hash value as a representative value for each window. If a copied portion of text is longer than twice the window length, then its representative value will be sure to match one of the representatives stored in the database, and that window can be examined to determine how much of it was copied.[7]
In data mining, Cohen et al. (2001) use MinHash as a tool for association rule learning. Given a database in which each entry has multiple attributes (viewed as a 0-1 matrix with a row per database entry and a column per attribute) they use MinHash-based approximations to the Jaccard index to identify candidate pairs of attributes that frequently co-occur, and then compute the exact value of the index for only those pairs to determine the ones whose frequencies of co-occurrence are below a given strict threshold.[8]
Related topics
The MinHash scheme may be seen as an instance of locality sensitive hashing, a collection of techniques for using hash functions to map large sets of objects down to smaller hash values in such a way that, when two objects have a small distance to each other, their hash values are likely to be the same. In this instance, the signature of a set may be seen as its hash value. Other locality sensitive hashing techniques exist for Hamming distance between sets and cosine distance between vectors; locality sensitive hashing has important applications in nearest neighbor search algorithms.[9]
References
- ^ a b c Broder, Andrei Z. (1997), "On the resemblance and containment of documents", Compression and Complexity of Sequences: Proceedings, Positano, Amalfitan Coast, Salerno, Italy, June 11-13, 1997, IEEE, pp. 21–29, doi:10.1109/SEQUEN.1997.666900.
- ^ a b c Broder, Andrei Z.; Charikar, Moses; Frieze, Alan M.; Mitzenmacher, Michael (1998), "Min-wise independent permutations", Proc. 30th ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing (STOC '98), New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, pp. 327–336, doi:10.1145/276698.276781.
- ^ Jaccard, Paul (1901), "Étude comparative de la distribution florale dans une portion des Alpes et des Jura", Bulletin de la Société Vaudoise des Sciences Naturelles 37: 547–579.
- ^ Matoušek, Jiří; Stojaković, Miloš (2003), "On restricted min-wise independence of permutations", Random Structures and Algorithms 23 (4): 397–408, doi:10.1002/rsa.10101.
- ^ Saks, M.; Srinivasan, A.; Zhou, S.; Zuckerman, D. (2000), "Low discrepancy sets yield approximate min-wise independent permutation families", Information Processing Letters 73 (1–2): 29–32, doi:10.1016/S0020-0190(99)00163-5.
- ^ Chum, Ondřej; Philbin, James; Isard, Michael; Zisserman, Andrew (2007), "Scalable near identical image and shot detection", Proceedings of the 6th ACM International Conference on Image and Cideo Retrieval (CIVR'07), doi:10.1145/1282280.1282359; Chum, Ondřej; Philbin, James; Zisserman, Andrew (2008), "Near duplicate image detection: min-hash and tf-idf weighting", Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference, 3, p. 4, http://www.bmva.org/bmvc/2008/papers/119.pdf.
- ^ Schleimer, Saul; Wilkerson, Daniel S.; Aiken, Alex (2003), "Winnowing: local algorithms for document fingerprinting", Proceedings of the 2003 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data (SIGMOD '03), pp. 76–85, doi:10.1145/872757.872770.
- ^ Cohen, E.; Datar, M.; Fujiwara, S.; Gionis, A.; Indyk, P.; Motwani, R.; Ullman, J. D.; Yang, C. (2001), "Finding interesting associations without support pruning", IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering 13 (1): 64–78, doi:10.1109/69.908981.
- ^ Andoni, Alexandr; Indyk, Piotr (2008), "Near-optimal hashing algorithms for approximate nearest neighbor in high dimensions", Communications of the ACM 51 (1): 117–122, doi:10.1145/1327452.1327494.