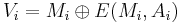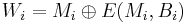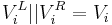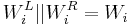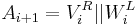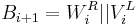MDC-2
In cryptography, MDC-2 (Modification Detection Code 2, sometimes called Meyer-Schilling) is a cryptographic hash function. MDC-2 is a hash function based on a block cipher with a proof of security in the ideal-cipher model[1]. The length of the output hash depends on the underlying block cipher used.
Contents |
Algorithm
For a given message  to hash and a given block cipher encryption function
to hash and a given block cipher encryption function 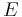 , the MDC-2 algorithm proceed as followed. Let
, the MDC-2 algorithm proceed as followed. Let  be the block length,
be the block length, 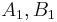 two different constants of size
two different constants of size  . If
. If 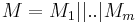 where each
where each 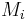 has size
has size  , then the hash
, then the hash 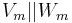 of the message is given by:
of the message is given by:
- for
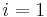 to
to 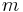 :
:
- return
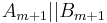
MDC-2DES hashes
When MDC-2 uses the DES block cipher, the 128-bit (16-byte) MDC-2 hashes are typically represented as 32-digit hexadecimal numbers. The following demonstrates a 43-byte ASCII input and the corresponding MDC-2 hash:
MDC2("The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog")
= 000ed54e093d61679aefbeae05bfe33a
Even a small change in the message will (with probability) result in a completely different hash, e.g. changing d to c:
MDC2("The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy cog")
= 775f59f8e51aec29c57ac6ab850d58e8
The hash of the zero-length string is:
MDC2("")
= 52525252525252522525252525252525
Patent issues
MDC-2 was covered by U.S. Patent 4,908,861, issued on March 13, 1990 but filed by IBM on August 28, 1987.
For this reason, support for MDC-2 has been disabled in OpenSSL on most Linux distributions and is not implemented by many other cryptographic libraries.
But the maximum lifespan of 20 years from filing date means that the U.S. Patent 4,908,861 could not have lasted beyond August 28, 2007 ; in fact it has expired in 2002[2], because IBM has not paid the renewal fee. The same goes for the Canadian patent. There is no patent for Europe.
This means that MDC2 can be freely used.
See also
Notes
- ^ Steinberger, John (June 23, 2007). "The Collision Intractability of MDC-2 in the Ideal-Cipher Model". Advances in Cryptology - EUROCRYPT 2007. Springer-Verlag. pp. 34–51. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-72540-4_3. http://eprint.iacr.org/2006/294. Retrieved January 31, 2008.
- ^ USPTO - Patent Maintenance Fees. United States Patent Office. March 13, 2002. https://ramps.uspto.gov/eram/getMaintFeesInfo.do?patentNum=4908861&applicationNum=07090633. Retrieved 2008-01-31 (Click on "Bibliographic data".)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||