Maximum satisfiability problem
In computational complexity theory, the Maximum Satisfiability problem (MAX-SAT) is the problem of determining the maximum number of clauses, of a given Boolean formula, that can be satisfied by some assignment. It is an FNP generalization of SAT.
The MAX-SAT problem is NP-hard, since its solution easily leads to the solution of the boolean satisfiability problem, which is NP-complete. In particular 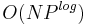 for unweighted, and
for unweighted, and 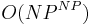 for weighted.
for weighted.
From another point of view, it is also APX-complete, and thus does not admit a PTAS unless P = NP.[1][2][3] MAX-SAT is one of the optimization extensions of the boolean satisfiability problem, which is the problem of determining if the variables of a given Boolean formula can be assigned in such a way as to make the formula evaluate to TRUE. If the clauses are restricted to have at most 2 literals, as in 2-satisfiability, we get the MAX-2SAT problem. If they are restricted to at most 3 literals per clause, as in 3-satisfiability, we get the MAX-3SAT problem.
Contents |
Related problems
There are several extensions to MAX-SAT:
- The weighted maximum satisfiability problem (Weighted MAX-SAT) asks for the maximum weight which can be satisfied by any assignment, given a set of weighted clauses.
- The partial maximum satisfiability problem (PMAX-SAT) asks for the maximum number of clauses which can be satisfied by any assignment of a given subset of clauses. The rest of the clauses must be satisfied.
- The soft satisfiability problem (soft-SAT), given a set of SAT problems, asks for the maximum number of sets which can be satisfied by any assignment[4].
- The minimum satisfiability problem.
Many exact solvers for MAX-SAT have been developed during recent years, and many of them were presented in the well-known conference on the boolean satisfiability problem and related problems, the SAT Conference. In 2006 the SAT Conference hosted the first MAX-SAT evaluation comparing performance of practical solvers for MAX-SAT, as it has done in the past for the pseudo-boolean satisfiability problem and the quantified boolean formula problem. Because of its NP-hardness, large-size MAX-SAT instances cannot be solved exactly, and one must resort to approximation algorithms and heuristics [5]
Solvers
There are several solvers submitted to the last Max-SAT Evaluations:
- Branch and Bound based: Clone, MaxSatz (based on Satz), IncMaxSatz, IUT_MaxSatz, WBO.
- Satisfiability based: SAT4J, QMaxSat.
- Unsatisfiability based: msuncore, WPM1, PM2.
See also
External links
- SAT and MAX-SAT for the lay-researcher
- http://www.satisfiability.org/
- http://www.iiia.csic.es/~maxsat06
- http://www.maxsat.udl.cat
- Weighted Max-2-SAT Benchmarks with Hidden Optimum Solutions
- Lecture Notes on MAX-SAT Approximation
References
- ^ Mark Krentel. The Complexity of Optimization Problems. Proc. of STOC '86. 1986.
- ^ Christos Papadimitriou. Computational Complexity. Addison-Wesley, 1994.
- ^ Cohen, Cooper, Jeavons. A complete characterization of complexity for boolean constraint optimization problems. CP 2004.
- ^ Josep Argelich and Felip Manyà. Exact Max-SAT solvers for over-constrained problems. In Journal of Heuristics 12(4) pp. 375-392. Springer, 2006.
- ^ R. Battiti and M. Protasi. Approximate Algorithms and Heuristics for MAX-SAT Handbook of Combinatorial Optimization, Vol 1, 1998, 77-148, Kluwer Academic Publishers.