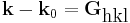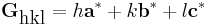Low-energy electron microscopy
Low-energy electron microscopy, or LEEM, is an analytical surface science technique invented by Ernst Bauer in 1962, however, not fully developed (by Ernst Bauer and Wolfgang Telieps) until 1985. LEEM is a technique used by surface scientists to image atomically clean surfaces, atom-surface interactions, and thin (crystalline) films. In LEEM, high-energy electrons (15-20 keV) are emitted from an electron gun, focused using a set of condenser optics, and sent through a magnetic beam deflector (usually 60˚ or 90˚). The “fast” electrons travel through an objective lens and begin decelerating to low energies (1-100 eV) near the sample surface because the sample is held at a potential near that of the gun. The low-energy electrons are now termed “surface-sensitive” and the near-surface sampling depth can be varied by tuning the energy of the incident electrons (difference between the sample and gun potentials minus the work functions of the sample and system). The low-energy elastically backscattered electrons travel back through the condenser lens, reaccelerate to the gun voltage (because the condenser lens is grounded), and pass through the beam separator again. However, now the electrons travel away from the condenser optics and into the projector lenses. Imaging of the back focal plane of the objective lens into the object plane of the projector lens (using an intermediate lens) produces a diffraction pattern (low-energy electron diffraction, LEED) at the imaging plane and recorded in a number of different ways. The intensity distribution of the diffraction pattern will depend on the periodicity at the sample surface and is a direct result of the wave nature of the electrons. One can produce individual images of the diffraction pattern spot intensities by turning off the intermediate lens and inserting a contrast aperture in the back focal plane of the objective lens (or, in state-of-the-art instruments, in the center of the separator, as chosen by the excitation of the objective lens), thus allowing for real-time observations of dynamic processes at surfaces. Such phenomena include (but are not limited to): tomography, phase transitions, adsorption, reaction, segregation, thin film growth, etching, strain relief, sublimation, and magnetic microstructure. These investigations are only possible because of the accessibility of the sample; allowing for a wide variety of in situ studies over a wide temperature range.
Contents |
Introduction
LEEM differs from conventional electron microscopies in four main ways:
- The sample must be illuminated on the same side of the imaging optics, i.e. through the objective lens, because samples are not transparent to low-energy electrons.
- In order to separate the incident and elastically scattered low energy electrons, scientists use magnetic “electron prism” beam separators which focus electrons both in and out of the plane of the beampath (to avoid distortions in the image and diffraction patterns).
- Rather than have the electron gun at a high potential and the rest of the instrument (including electron lenses and specimen) at ground, an electrostatic immersion objective lens brings the sample close to that of the gun, slowing down the high energy electrons to a desired energy only just before interacting with the sample surface.
- The instrument must be able to work under ultra-high vacuum (UHV), or 10−10 torr (760 torr = 1 atm, atmospheric pressure).
Surface Diffraction
Kinematic or elastic backscattering occurs when low energy (1-100 eV) electrons impinge on a clean, well-ordered crystalline specimen. It is assumed that each electron undergoes only one scattering event, and incident electron beam is described as a plane wave with the wavelength:
Scientists use inverse space to describe the periodicity of the lattice and the interaction of the plane wave with the sample surface. In inverse (or "k-space") space, the wave vector of the incident and scattered waves are 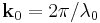 and
and 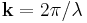 , respectively,
, respectively,
and constructive interference occurs at the Laue condition:
where (h,k,l) is a set of integers and
is a vector of the reciprocal lattice.
Experimental Setup
A typical LEEM setup consists of (see figure):
1. Electron gun, used to generate electrons by way of thermionic or field emission from a source tip. In thermionic emission, electrons escape a source tip (usually made of LaB6) by resistive heating and application of an electric field to effectively lower the energy needed for electrons to escape the surface. Once sufficient thermal vibrational energy is attained electrons may overcome this electrostatic energy barrier, allowing them to travel into vacuum and accelerate down the lens column to the gun potential (because the lenses are at ground). In field emission, rather than heating the tip to vibrationally excite electrons from the surface, the source tip (usually tungsten) is sharpened to a small point such that when large electric fields are applied, they concentrate at the tip, lowering the barrier to escape the surface as well as making tunneling of electrons from the tip to vacuum level more feasible.
2. Condenser/illumination optics, used to focus electrons leaving the electron gun and manipulate and/or translate the illumination electron beam. Electromagnetic quadrupole electron lenses are used, the number of which depends on how much resolution and focusing flexibility the designer wishes. However, the ultimate resolution of LEEM is usually determined by that of the objective lens.
3. Illumination beam aperture allows researchers to control the area of the specimen which is illuminated (LEEM’s version of electron microscopy’s “selected area diffraction”, termed microdiffraction) and is located in the beam separator on the illumination side.
4. Magnetic beam separator, needed to resolve the illuminating and imaging beam (while in turn spatially separating the optics for each). There has been much development on the technology of electron beam separators; the early separators introduced distortion in either the image or diffraction plane. However, IBM recently developed a hybrid prism array/nested quadratic field design, focusing the electron beams both in and out of the plane of the beampath, allowing for deflection and transfer of the image and diffraction planes without distortion or energy dispersion.[1]
5. Electrostatic immersion objective lens, used to form a real image of the sample by way of a 2/3-magnification virtual image behind the sample. The uniformity of the electrostatic field between the objective lens and specimen, limited by spherical and chromatic aberrations larger than those of any other lenses, ultimately determines the overall performance of the instrument.
6. Contrast aperture, located in the center on the projector lens side of the beam separator. In most electron microscopies, the contrast aperture is introduced into the back focal plan of the objective lens (where the actual diffraction plane lies). However, this is not true in the LEEM, because dark-field imaging (imaging of nonspecular beams) would not be possible because the aperture has to move laterally and would intercept the incident beam for large shifts. Therefore, researchers adjust the excitation of the objective lens so as to produce an image of the diffraction pattern in the middle of the beam separator and choose the desired spot intensity to image using a contrast aperture inserted there. This aperture allows scientists to image diffraction intensities that may be of particular interest (dark field).
7. Illumination optics are employed to magnify the image or diffraction pattern and project it onto the imaging plate or screen.
8. Imaging plate or screen, used to image the electron intensity so that we can see it. This can be done many different ways including, phosphorescent screens, imaging plates, CCDs, among others.
Specialized imaging techniques
Low energy electron diffraction (LEED)
After a parallel beam of low-energy electrons interacts with a specimen, the electrons form a diffraction or LEED pattern which depends on periodicity present at the surface and is a direct result of the wave nature of an electron. It is important to point out in LEED is that the entire sample surface is being illuminated by a parallel beams of electrons, and thus the diffraction pattern will contain information about the entire surface. The diffraction pattern is formed in the back focal plane of the objective lens, imaged into the object plane of the projective lens (using an intermediate lens), and the final pattern appears on the phosphorescent screen, photographic plate or CCD.
Microdiffraction
Microdiffraction is exactly like LEED but rather than flood the entire sample with a beam of low-energy electrons, one inserts the illumination/beam aperture into the beampath while imaging a surface and chooses the spot on the surface he/she wants to retrieve a diffraction pattern from. The area chosen is usually micrometers (1/1000000 meter) or fractions of a micrometer. This is a very useful technique for researchers to be able to de-convolute a complicated LEED pattern containing information from the entire specimen surface by simply choosing a particular island, terrace, domain, etc., and retrieve a diffraction pattern composed solely of that particular surface feature.
Bright field imaging
Also known as phase or interference contrast imaging, bright field imaging makes particular use of the wave nature of the electron to generate vertical diffraction contrast, making steps on the surface visible.
Dark field imaging
In dark field imaging (also termed diffraction contrast imaging) researchers adjust the excitation of the objective lens so as to produce an image of the diffraction pattern in the middle of the beam separator and choose a desired spot intensity to image using a contrast aperture inserted there. This aperture allows scientists to image diffraction intensities that may be of particular interest (dark field). For instance, if a researcher wants to map out the origin of some particular diffraction intenisty, dark field analysis allows one to image (in real-space) where the particular intensity originates from.
Photoexcitation electron spectroscopy (PEEM)
In PEEM, upon exposure to electromagnetic radiation (photons), secondary electrons are excited from the surface and imaged. PEEM was first developed in the early 1930s, using ultraviolet (UV) light to induce photoemission of (secondary) electrons. However, since then, this technique has made many advances, the most important of which was the pairing of PEEM with synchrotron radiation, providing tunable, linear polarized, left and right circularized radiation in the soft x-ray range. Such application allows scientist to retrieve topographical, elemental, chemical, and magnetic contrast of surfaces.
Mirror electron microscopy (MEM)
In mirror electron microscopy, electrons are slowed in the retarding field of the condenser lens to the limit of the instrument and thus, only allowed to interact with the “near-surface” region of the sample. It is very complicated to understand the exact contrast variations come from, but the important things to point out here are that height variations at the surface of the region change the properties of the retarding field, therefore influencing the reflected (specular) beam. No LEED pattern is formed, because no scattering events have take place, and therefore, reflected intensity is high.
Reflectivity contrast imaging
The elastic backscattering of low energy electrons from surfaces is strong the reflectivity coefficients of surfaces depend strongly on the energy of incident electrons and the nuclear charge, in a non-monotonic fashion. Therefore, contrast can be maximized by varying the energy of the electrons incident at the surface.
Spin-polarized LEEM (SPLEEM)
SPLEEM uses spin-polarized illumination electrons to image the magnetic structure of a surface by way of spin-spin coupling of the incident electrons with that of the surface.
References
-
- Bauer, Ernst (1998). "LEEM basics". Surface Review and Letters 5 (6): 1275–1286. Bibcode 1998SRL.....5.1275B. doi:10.1142/S0218625X98001614.
- Bauer, Ernst (1994). "Low energy electron microscopy". Rep. Prog. Phys. 57 (9): 895–938. Bibcode 1994RPPh...57..895B. doi:10.1088/0034-4885/57/9/002. http://www.iop.org/EJ/abstract/0034-4885/57/9/002.
- Tromp, R. M. (2000). "Low-energy electron microscopy". IBM J. Res. Develop. 44 (4): 503–516. doi:10.1147/rd.444.0503. http://www.research.ibm.com/journal/rd/444/tromp.pdf.
- Anders, S., et al.; Padmore, Howard A.; Duarte, Robert M.; Renner, Timothy; Stammler, Thomas; Scholl, Andreas; Scheinfein, Michael R.; Stöhr, Joachim et al. (1999). "Photoemission electron microscope for the study of magnetic materials". Review of Scientific Instruments 70 (10): 3973–3981. Bibcode 1999RScI...70.3973A. doi:10.1063/1.1150023. http://link.aip.org/link/?RSINAK/70/3973/1.
![\begin{align}
\lambda = \frac{h}{\sqrt{2mE}}, \qquad \lambda[\textrm{A}]=\sqrt{\frac{150}{E[\textrm{eV}]}}
\end{align}](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/3d8fc93ed4f0b8660a727a36f54b61fb.png)