Katapayadi system
Ka-ṭa-pa-yā-di (Devanagari: कटपयादि) system (also known as Paralppēru, Malayalam: പരല്പ്പേര്) of numerical notation is an ancient Indian system to depict letters to numerals for easy remembrance of numbers as words or verses. Assigning more than one letter to one numeral and nullifying certain other letters as valueless, this system provides the flexibility in forming meaningful words out of numbers which can be easily remembered.
Contents |
History
The oldest available evidence of the use of Kaṭapayādi System is from Grahacāraṇibandhana by Haridatta in 683 CE.[1] It has also been used in Laghubhāskariyavivarana written by Sankaranārāyana in 869 CE.[2]
Some argue that the system originated from Vararuci. [3] In some astronomical texts popular in Kerala planetary positions were encoded in Kaṭapayādi system. The first such work is considered to be the Chandra-vakyani of Vararuci, who is traditionally assigned to the fourth century CE. Therefore, sometime in the early first millennium is a reasonable estimate for the origin of the Kaṭapayādi System.[4]
Aryabhata, in his treatise Aryabhatiya, is known to have used a similar but more complex system to represent astronomical numbers. But there is not definitive evidence whether the Ka-ṭa-pa-yā-di System originated from Āryabhaṭa numeration.[5]
Geographical spread of the use
Almost all evidences of the use of Ka-ṭa-pa-yā-di System is from south India, especially Kerala. Not much is known about its use in North India. However, on Sanskrit astrolabe discovered in north India, the degrees of the altitude are marked in the Kaṭapayādi system. It is now preserved in the Sarasvathy Bhavan Library of Sampurnanand Sanskrit University, Varanasi.[1]
The use of the Ka-ṭa-pa-yā-di system is not confined to India. Some Pali chronograms based on the Ka-ṭa-pa-yā-di system have been discovered from Burma.[6]
Rules and practices
Following verse found in Śaṅkaravarman's Sadratnamāla explains the mechanism of the system.[7][8]
नज्ञावचश्च शून्यानि संख्या: कटपयादय:|
मिश्रे तूपान्त्यहल् संख्या न च चिन्त्यो हलस्वर:||
Transiliteration
nanyāvacaśca śūnyāni saṃkhyāḥ kaṭapayādayaḥ
miśre tūpāntyahal saṃkhyā na ca cintyo halasvaraḥ
Translation: na (न), nya (ञ) and a (अ)-s i.e. vowels represent zero. The (nine) integers are represented by consonant group beginning with ka, ṭa, pa, ya. In a conjunct consonant, the last of the consonants alone will count. A consonant without vowel is to be ignored.
Explanation
The assignment of letters to the numerals are as per the following arrangement.
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ka क ക | kha ख ഖ | ga ग ഗ | gha घ ഘ | nga ङ ങ | ca च ച | cha छ ഛ | ja ज ജ | jha झ ഝ | nya ञ ഞ |
| ṭa ट ട | ṭha ठ ഠ | ḍa ड ഡ | ḍha ढ ഢ | ṇa ण ണ | ta त ത | tha थ | da द ദ | dha ध ധ | na न ന |
| pa प പ | pha फ ഫ | ba ब ബ | bha भ ഭ | ma म മ | - | - | - | - | - |
| ya य യ | ra र ര | la ल ല | va व വ | śha श ശ | sha ष ഷ | sa स സ | ha ह ഹ | - | - |
- Consonants have numerals assigned as per the above table. For example, ba (ब) is always three 3 whereas 5 can be represented by either nga (ङ) or ṇa (ण) or ma (म) or śha (श).
- All stand-alone vowels like a (अ) and ṛ (ऋ) are assigned to zero 0.
- In case of a conjuct, consonants attached to a non-vowel will not be valueless. For example, kya (क्या) is formed by k (क्) + ya (य) + a (अ). The only consonant standing with a vowel is ya (य). So the corresponding numeral for kya (क्या) will be 1.
- There is no way of representing Decimal separator in the system.
- Indians used the Hindu-Arabic numeral system for numbering, traditionally written in increasing place values from left to right. This is as per the rule aṅkānām vāmato gati (अङ्कानाम् वामतो गति) which means numbers go from left to right.[9]
Variations
- The Dravidian consonant, ḷ (Malayalam: ള, Devanagari: ळ), of the Dravidian languages of south India is employed in works using the Kaṭapayādi System, like the Madhava's sine table.
- Some practicers doesn't map the stand-alone vowels to zero. But considers as valueless.
Usage
Mathematics and Astronomy
- Madhava's sine table constructed by 14th century Kerala mathematician-astronomer Madhava of Sangamagrama, employs the Kaṭapayādi system to enlist the trigonometric sines of various angles.
- Karanapaddhati, written in the 15th century, has the following śloka for the value of pi (π)
- അനൂനനൂന്നാനനനുന്നനിത്യൈ-
- സ്സമാഹതാശ്ചക്രകലാവിഭക്താഃ
- ചണ്ഡാംശുചന്ദ്രാധമകുംഭിപാലൈര്-
- വ്യാസസ്തദര്ദ്ധം ത്രിഭമൗര്വിക സ്യാത്
- Transiliteration
vyāsastadarddhaṃ tribhamaurvika syāt
- anūnanūnnānananunnanityai
- ssmāhatāścakra kalāvibhaktoḥ
- caṇḍāṃśucandrādhamakuṃbhipālair
- It gives the circumference of a circle of diameter, anūnanūnnānananunnanityai (10,000,000,000) as caṇḍāṃśucandrādhamakuṃbhipālair (31415926536)
- Sankaravarman's Sadratnamala uses the Kaṭapayādi system. A famous verse found in Sadratnamala is
- भद्राम्बुद्धिसिद्धजन्मगणितश्रद्धा स्म यद् भूपगी:
- Transiliteration
- bhadrāṃbuddhisiddhajanmagaṇitaśraddhā sma yad bhūpagīḥ
- Splitting the consonants gives,
| भ bha | द् d | रा rā | म् ṃ | बु ba | द् d | धि dh | सि sa | द् d | ध dha | ज ja | न् n | म ma | ग ga | णि ṇa | त ta | श् ṣ | र ra | द् d | धा dha | स् s | म ma | य ya | द् d | भू bha | प pa | गि gi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | - | 2 | - | 3 | - | 9 | 7 | - | 9 | 8 | - | 5 | 3 | 5 | 6 | - | 2 | - | 9 | - | 5 | 1 | - | 4 | 1 | 3 |
- Reversing the digits to modern day usage of descending order of decimal places, we get 314159265358979324 which is the value of pi (π) to 17 decimal places, except the last digit might be rounded off to 4.
Carnatic music
- The melakarta ragas of the Carnatic music is named so that the first two syllables of the name will give its number. This system is sometimes called the Ka-ta-pa-ya-di sankhya. The Swaras 'Sa' and 'Pa' are fixed, and here is how to get the other swaras from the melakarta number.
- Melakartas 1 through 36 have Ma1 and those from 37 through 72 have Ma2.
- The other notes are derived by noting the (integral part of the) quotient and remainder when one less than the melakarta number is divided by 6.
- 'Ri' and 'Ga' positions: the raga will have:
- Ri1 and Ga1 if the quotient is 0
- Ri1 and Ga2 if the quotient is 1
- Ri1 and Ga3 if the quotient is 2
- Ri2 and Ga2 if the quotient is 3
- Ri2 and Ga3 if the quotient is 4
- Ri3 and Ga3 if the quotient is 5
- 'Da' and 'Ni' positions: the raga will have:
- Da1 and Ni1 if remainder is 0
- Da1 and Ni2 if remainder is 1
- Da1 and Ni3 if remainder is 2
- Da2 and Ni2 if remainder is 3
- Da2 and Ni3 if remainder is 4
- Da3 and Ni3 if remainder is 5
- See swaras in Carnatic music for details on above notation.
Examples
The katapayadi scheme associates dha 9 and ra
9 and ra 2, hence the raga's melakarta number is 29 (92 reversed). Now 29
2, hence the raga's melakarta number is 29 (92 reversed). Now 29 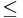 36, hence Dheerasankarabharanam has Ma1. Divide 28 (1 less than 29)by 6, the quotient is 4 and the remainder 4. Therefore, this raga has Ri2, Ga3 (quotient is 4) and Da2, Ni3 (remainder is 4). Therefore, this raga's scale is Sa Ri2 Ga3 Ma1 Pa Da2 Ni3 SA.
36, hence Dheerasankarabharanam has Ma1. Divide 28 (1 less than 29)by 6, the quotient is 4 and the remainder 4. Therefore, this raga has Ri2, Ga3 (quotient is 4) and Da2, Ni3 (remainder is 4). Therefore, this raga's scale is Sa Ri2 Ga3 Ma1 Pa Da2 Ni3 SA.
- Raga MechaKalyani
From the coding scheme Ma  5, Cha
5, Cha  6. Hence the raga's melakarta number is 65 (56 reversed). 65 is greater than 36. So MechaKalyani has Ma2. Since the raga's number is greater than 36 subtract 36 from it. 65-36=29. 28 (1 less than 29) divided by 6 : quotient=4, remainder=4. Ri2 Ga3 occurs. Da2 Ni3 occurs. So MechaKalyani has the notes Sa Ri2 Ga3 Ma2 Pa Da2 Ni3 SA.
6. Hence the raga's melakarta number is 65 (56 reversed). 65 is greater than 36. So MechaKalyani has Ma2. Since the raga's number is greater than 36 subtract 36 from it. 65-36=29. 28 (1 less than 29) divided by 6 : quotient=4, remainder=4. Ri2 Ga3 occurs. Da2 Ni3 occurs. So MechaKalyani has the notes Sa Ri2 Ga3 Ma2 Pa Da2 Ni3 SA.
- Exception for Simhendramadhyamam
You can see that, as per the above calculation we should get Sa  7, Ha
7, Ha  8 giving the number 87 instead of 57 for Simhendramadhyamam. This should be ideally Sa
8 giving the number 87 instead of 57 for Simhendramadhyamam. This should be ideally Sa  7, Ma
7, Ma  5 giving the number 57. So it is believed that the name should be written as Sihmendramadhymam (As in the case of Brahmana in Sanskrit).
5 giving the number 57. So it is believed that the name should be written as Sihmendramadhymam (As in the case of Brahmana in Sanskrit).
Representation of dates
Important dates were remembered by converting them using Kaṭapayādi system. These dates are generally represented as number of days since the start of Kali Yuga. It is sometimes called kalidina sankhya.
- The Malayalam calendar known as kollavarsham (Malayalam: കൊല്ലവര്ഷം) was adopted in Kerala beginning from 825 CE, revamping some existing calendars. This date is remembered as āchārya vāgbhadā, converted using Kaṭapayādi into 1434160 days since the start of Kali Yuga.[10]
- Narayaniyam, written by Melpathur Narayana Bhattathiri, ends with the line, āyurārogyasaukhyam (ആയുരാരോഗ്യസൌഖ്യം) which means long-life, health and happiness.[11]
| In Malayalam | ആയുരാരോഗ്യസൌഖ്യം |
|---|---|
| In Devanagari | आयुरारोग्यसौख्यम् |
| In IAST | āyurārogyasaukhyam |
| Value as per Kaṭapayādi | 1712210 |
- This number is the time at which the work was completed represented as number of days since the start of Kali Yuga as per the Malayalam calendar.
Others
- Some people use the Kaṭapayādi system in naming newborns.[12][13]
- The following verse compiled in Malayalam by Koduṅṅallur Kuññikkuṭṭan Taṃpurān using Kaṭapayādi is the number of days in the months of Gregorian Calendar.
- പലഹാരേ പാലു നല്ലൂ, പുലര്ന്നാലോ കലക്കിലാം
- ഇല്ലാ പാലെന്നു ഗോപാലന് - ആംഗ്ലമാസദിനം ക്രമാല്
- Transiliteration
- palahāre pālu nallū, pularnnālo kalakkilāṃ
- illā pālennu gopālan - āṃgḷamāsadinaṃ kramāl
- Translation: Milk is best for breakfast, when it is morning, it should be stirred. But Gopālan says there is no milk - the number of days of English months in order.
- Converting pairs of letters using Kaṭapayādi yields - pala (പല) is 31, hāre (ഹാരേ) is 28, pālu പാലു = 31, nallū (നല്ലൂ) is 30, pular (പുലര്) is 31, nnālo (ന്നാലോ) is 30, kala (കല) is 31, kkilāṃ (ക്കിലാം) is 31, illā (ഇല്ലാ) is 30, pāle (പാലെ) is 31, nnu go (ന്നു ഗോ) is 30, pālan (പാലന്) is 31.
See also
- Kerala school of astronomy and mathematics
- Madhava's sine table
- Katapayadi sankhya
- Bhutasamkhya system
- Aryabhata numeration
Further reading
A.A. Hattangadi, Explorations in Mathematics, Universities Press (India) Pvt. Ltd., Hyderabad (2001) ISBN 81 7371 387 1 [6]
References
- ^ a b Sreeramamula Rajeswara Sarma (1999), Kaṭapayādi Notation on a Sanskrit Astrolabe [1]
- ^ J J O'Connor; E F Robertson (November 2000). "Sankara Narayana". School of Mathematics and Statistics, University of St Andrews, Scotland. http://www-history.mcs.st-and.ac.uk/Biographies/Sankara.html. Retrieved 1 January 2010.
- ^ Usenet Discussion. "Aryabhatta's numerical encoding". http://www-wireless.usenet-replayer.com/data/humanities/language/sanskrit/4154.html. Retrieved 1 January 2010.
- ^ Plofker, Kim (2008). Mathematics in India. Princeton University Press. pp. 384. ISBN 978-0-691-12067-6.
- ^ J. F. Fleet (Apr., 1912). "The Ka-ta-pa-ya-di Notation of the Second Arya-Siddhanta". The Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland (Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland): 459–462. http://www.jstor.org/stable/25190035.
- ^ J.F. Fleet (Jul., 1911). "The Katapayadi System of Expressing Numbers". The Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland (Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland): 788–794. http://www.jstor.org/stable/25189917. Retrieved 2 January 2010.
- ^ Sarma, K.V. (2001). "Sadratnamala of Sankara Varman". Indian Journal of History of Science (Indian National Academy of Science, New Delhi) 36 (3–4 (Supplement)): 1–58. [2]
- ^ Anand Raman, The Ancient Katapayadi Formula and the Modern Hashing Method [3]
- ^ Aryabhatta's Numerical Encoding
- ^ Francis Zimmerman, 1989, Lilavati, gracious lady of arithmetic - India - A Mathematical Mystery Tour [4]
- ^ Dr. C Krishnan Namboodiri, Chekrakal Illam, Calicut, Namboothiti.com Dr. C Krishnan Namboodiri. ""Katapayaadi" or "Paralpperu"". Namboothiri Websites Trust. http://www.namboothiri.com/articles/katapayaadi.htm. Retrieved 1 January 2010.
- ^ Visti Larsen, Choosing the auspicious name
- ^ [5]
|
|||||||||||||||||