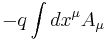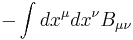Kalb–Ramond field
In theoretical physics in general and string theory in particular, the Kalb–Ramond field, also known as the NS-NS B-field, is a quantum field that transforms as a two-form i.e. an antisymmetric tensor field with two indices.[1]
It generalizes the electromagnetic potential but it has two indices instead of one. This difference is related to the fact that the electromagnetic potential is integrated over one-dimensional worldlines of particles to obtain one of its contributions to the action while the Kalb–Ramond field must be integrated over the two-dimensional worldsheet of the string. In particular, while the action for a charged particle moving in an electromagnetic potential is given by
that for a string coupled to the Kalb–Ramond field has the form
This term in the action implies that the fundamental string of string theory is a source of the NS-NS B-field much like charged particles are sources of the electromagnetic field.
The Kalb–Ramond field appears, together with the metric tensor and dilaton, as a set of massless excitations of a closed string.
See also
References
- ^ Michael Kalb and P. Ramond (1974). "Classical direct interstring action". Phys. Rev. D 9 (8): 2273–2284. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.9.2273.