Johann Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet
| Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet | |
|---|---|
Johann Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet
|
|
| Born | 13 February 1805 Düren, French Empire |
| Died | 5 May 1859 (aged 54) Göttingen, Hanover |
| Residence | Prussia |
| Nationality | German |
| Fields | Mathematician |
| Institutions | University of Breslau University of Berlin University of Göttingen |
| Alma mater | University of Bonn |
| Doctoral advisor | Simeon Poisson Joseph Fourier |
| Doctoral students | Gotthold Eisenstein Leopold Kronecker Rudolf Lipschitz Carl Wilhelm Borchardt |
| Other notable students | Moritz Cantor Elwin Bruno Christoffel Richard Dedekind Alfred Enneper Eduard Heine Bernhard Riemann Ludwig Schläfli Ludwig von Seidel Wilhelm Weber Julius Weingarten |
| Known for | See full list |
| Notable awards | Pour le Mérite |
Johann Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet (German pronunciation: [ləˈʒœn diʁiˈkleː]; 13 February 1805 – 5 May 1859) was a German mathematician with deep contributions to number theory (including creating the field of analytic number theory), as well as to the theory of Fourier series and other topics in mathematical analysis; he is credited with being one of the first mathematicians to give the modern formal definition of a function.
Contents |
Biography
Early life (1805–22)
Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet was born on 13 February 1805 in a German family in Düren, a town on the left bank of the Rhine which at the time was part of the First French Empire, reverting to Prussia after the Congress of Vienna in 1815. His father Johann Arnold Lejeune Dirichlet was the postmaster, merchant, and city councilor. His paternal grandfather had come to Düren from Richelette, a small community 5 km north east of Liège in Belgium, from which his surname "Lejeune Dirichlet" ("le jeune de Richelette", French for "the youth from Richelette") was derived.[1]
Although his family was not wealthy and he was the youngest of seven children, his parents supported his education. They enrolled him in an elementary school and then private school in hope that he would later become a merchant. The young Dirichlet, who showed a strong interest in mathematics before age 12, convinced his parents to allow him to continue his studies. In 1817 they sent him to the Gymnasium in Bonn under the care of Peter Joseph Elvenich, a student his family knew. In 1820 Dirichlet moved to the Jesuit Gymnasium in Cologne, where his lessons with Georg Ohm helped widen his knowledge in mathematics. He left the gymnasium a year later with only a certificate, as his inability to speak fluent Latin prevented him from earning the Abitur.[1]
Studies in Paris (1822–26)
Dirichlet again convinced his parents to provide further financial support for his studies in mathematics, against their wish for a career in law. As Germany provided little opportunity to study higher mathematics at the time, with only Gauss at the University of Göttingen who was nominally a professor of astronomy and anyway disliked teaching, Dirichlet decided to go to Paris in May 1822. There he attended classes at the Collège de France and at the Faculté des sciences de Paris, learning mathematics from Hachette among others, while undertaking private study of Gauss' Disquisitiones Arithmeticae, a book he kept close for his entire life. In 1823 he was recommended to General Foy, who hired him as a private tutor to teach his children German, the wage finally allowing Dirichlet to become independent from his parents' financial support.[2]
His first original research, comprising part of a proof of Fermat's last theorem for the case 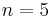 , brought him immediate fame, being the first advance in the theorem since Fermat's own proof of the case
, brought him immediate fame, being the first advance in the theorem since Fermat's own proof of the case 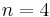 and Euler's proof for
and Euler's proof for 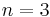 . Adrien-Marie Legendre, one of the referees, soon completed the proof for this case; Dirichlet completed his own proof a short time after Legendre, and a few years later produced a full proof for the case
. Adrien-Marie Legendre, one of the referees, soon completed the proof for this case; Dirichlet completed his own proof a short time after Legendre, and a few years later produced a full proof for the case 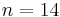 .[3] In June 1825 he was accepted to lecture on his partial proof for the case
.[3] In June 1825 he was accepted to lecture on his partial proof for the case 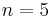 at the French Academy of Sciences, an exceptional feat for a 20 year old student with no degree.[1] His lecture at the Academy has also put Dirichlet in close contact with Fourier and Poisson, who raised his interest in theoretical physics, especially Fourier's analytic theory of heat.
at the French Academy of Sciences, an exceptional feat for a 20 year old student with no degree.[1] His lecture at the Academy has also put Dirichlet in close contact with Fourier and Poisson, who raised his interest in theoretical physics, especially Fourier's analytic theory of heat.
Back to Prussia, Breslau (1825–28)
As General Foy died in November 1825 and he could not find any paying position in France, Dirichlet had to return to Prussia. Fourier and Poisson introduced him to Alexander von Humboldt, who had been called to join the court of King Friedrich Wilhelm III. Humboldt, planning to make Berlin a center of science and research, immediately offered his help to Dirichlet, sending letters in his favour to the Prussian government and to the Prussian Academy of Sciences. Humboldt also secured a recommendation letter from Gauss, who upon reading his memoir on Fermat's theorem wrote with an unusual amount of praise that "Dirichlet showed excellent talent".[4] With the support of Humboldt and Gauss, Dirichlet was offered a teaching position at the University of Breslau (now the University of Wrocław in Poland). However, as he had not passed a doctoral disertation, he submitted his memoir on the Fermat theorem as a thesis to the University of Bonn. Again his lack of fluency in Latin rendered him unable to hold the required public disputation of his thesis; after much discussion, the University decided to bypass the problem by awarding him a honorary doctorate in February 1827. Also, the Minister of education granted him a dispensation for the Latin disputation required for the Habilitation. Dirichlet earned the Habilitation and lectured in the 1827/28 year as a Privatdozent at Breslau.[1]
While in Breslau, Dirichlet continued his number theoretic research, publishing important contributions to the biquadratic reciprocity law which at the time was a focal point of Gauss' research. Alexander von Humboldt took advantage of these new results, which had also drawn enthusiastic praise from Friedrich Bessel, to arrange for him the desired transfer to Berlin. Given Dirichlet's young age (he was 23 years old at the time), Humboldt was only able to get him a trial position at the Prussian Military Academy in Berlin while remaining nominally employed by the University of Breslau. The probation was extended for three years until the position becoming definitive in 1831.
Berlin (1826–1855)
After moving to Berlin, Humboldt introduced Dirichlet to the great salons held by the Mendelssohn family, a distinguished German family headed by banker Abraham Mendelssohn Bartholdy. Their house was a weekly gathering point of the Berlin artists and scientists, including family members Felix Mendelssohn Bartholdy and Fanny Mendelssohn, both famous composers, or painter Wilhelm Hensel (Fanny's husband). Dirichlet showed great interest in Rebecka Mendelssohn, a daughter of Abraham, whom he married in 1832. In 1833 their first son, Walter, was born.
As soon as he came to Berlin, Dirichlet applied to lecture at the University of Berlin, and the Education Minister approved the transfer and in 1831 assigned him to the faculty of philosophy. The faculty required a Habilitation again and although Dirichlet wrote a Habilitationsschrift as needed, he postponed giving the mandatory lecture in Latin for another 20 years, until 1851. For not completing these formal requirements, he remained attached to the faculty with less than full rights, including limited payment, forced him to keep in parallel his teaching position at the Military School. In 1832 Dirichlet became a member of the Prussian Academy of Sciences, the youngest member at only 27 years old.[1]
Dirichlet had a good reputation with students for the clarity of his explanations and enjoyed teaching, especially as his University lectures tended to be on the more advanced topics in which he was doing research: number theory (he was the first German professor to give lectures on number theory), analysis and mathematical physics. He advised the doctoral thesis of several important German mathematicians, as Gotthold Eisenstein, Leopold Kronecker, Rudolf Lipschitz and Carl Wilhelm Borchardt, while being influential in the mathematical formation of many other scientists, including Elwin Bruno Christoffel, Wilhelm Weber, Eduard Heine, Ludwig von Seidel and Julius Weingarten. At the Military Academy Dirichlet managed to introduce differential and integral calculus in the curriculum, significantly raising the level of scientific education there. However, in time he started feeling that his double teaching load, at the Military academy and at the University, started weighing down on the time available for his research.[1]
While in Berlin, Dirichlet kept in contact with other mathematicians. In 1829, during a trip, he met Jacobi, at the time professor of mathematics at Königsberg University. Over the years they kept meeting and corresponding on research matters, in time becoming close friends. In 1839, during a visit to Paris, Dirichlet met Joseph Liouville, the two mathematicians becoming friends, keeping in contact and even visiting each other with the families a few years later. in 1839, Jacobi sent Dirichlet a paper by Ernst Kummer, at the time a school teacher. Realizing Kummer's potential, they helped him get elected in the Berlin Academy and, in 1842, obtained for him a full professor position at the University of Breslau. In 1840 Kummer married Ottilie Mendelssohn, a cousin of Rebecka.
In 1843, when Jacobi fell ill, Dirichlet traveled to Königsberg to help him, then obtained for him the assistance of King Friedrich Wilhelm IV's personal physician. When the medic recommended Jacobi to spend some time in Italy, he joined him on the trip together with his family. They were accompanied to Italy by Ludwig Schläfli, who came as a translator; as he was strongly interested in mathematics, during the trip both Dirichlet and Jacobi lectured him, later Schläfli becoming an important mathematician himself.[1] The Dirichlet family extended their stay in Italy to 1845, their daughter Flora being born there. In 1844, Jacobi moved to Berlin as a royal pensioner, their friendship becoming even closer. In 1846, when the Heidelberg University tried to recruit Dirichlet, Jacobi provided von Humboldt the needed support in order to obtain a doubling of Dirichlet's pay at the University in order to keep him in Berlin; however, even now he wasn't paid a full professor wage and he could not leave the Military Academy.[5]
Holding liberal views, Dirichlet and his family supported the 1848 revolution; he even guarded with a rifle the palace of the Prince of Prussia. After the revolution failed, the Military Academy closed temporarily, causing him a large loss of income. When it reopened, the environment became more hostile to him as the officers he was teaching were naturally reactionary. Also the conservatory press pointed him out, as well as Jacobi and other liberal professors, as "the red contingent of the staff".[1]
In 1849 Dirichlet participated, together with his friend Jacobi, to the jubilee of Gauss' doctorate.
Göttingen (1855–59)
Despite Dirichlet's expertise and the honours he received, and although by 1851 he had finally completed all formal requirements for a full professor, the issue of raising his payment at the University still dragged and he still couldn't leave the Military Academy. In 1855, upon Gauss' death, the University of Göttingen decided to call Dirichlet as his successor. Given the difficulties faced in Berlin, he decided to accept the offer and immediately moved to Göttingen with his family. Kummer was called to follow him as a mathematics professor in Berlin.[2]
Dirichlet enjoyed his time in Göttingen as the lighter teaching load allowed him more time for research and, also, he got in close contact with the new generation of researchers, especially Richard Dedekind and Bernhard Riemann. After moving to Göttingen he was able to obtain a small annual payment for Riemann in order to retain him in the teaching staff there. Dedekind, Riemann, Moritz Cantor and Alfred Enneper, although they had all already earned they PhDs, attended Dirichlet's classes to study with him. Dedekind, who felt that there were significant gaps at the time in his mathematics education, considered that the occasion to study with Dirichlet made him "a new human being".[1] He later edited and published Dirichlet's lectures and other results in number theory under the title Vorlesungen über Zahlentheorie (Lectures on Number Theory).
In the summer of 1858, during a trip to Montreux, Dirichlet suffered a heart attack. On 5 May 1859, he died in Göttingen, several months after the death of his wife Rebecka.[2] Dirichlet's brain is preserved in the department of physiology at the University of Göttingen, along with the brain of Gauss. The Academy in Berlin honored him with a formal memorial speech held by Kummer in 1860, and later ordered the publication of his collected works edited by Kronecker and Lazarus Fuchs.
Mathematics research
Number theory
Number theory was Dirichlet's main research interest,[6] a field in which he found several deep results and in proving them introduced some fundamental tools, many of which were later named after him. In 1837 he published Dirichlet's theorem on arithmetic progressions, using mathematical analysis concepts to tackle an algebraic problem and thus creating the branch of analytic number theory. In proving the theorem, he introduced the Dirichlet characters and L-functions.[7][6] Also, in the article he noted the difference between the absolute and conditional convergence of series and its impact in what was later called the Riemann series theorem. In 1841 he generalized his arithmetic progressions theorem from integers to the ring of Gaussian integers ![\mathbb{Z}[i]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/2a2fc748028420198e13c31eaadb6939.png) .[1]
.[1]
In a couple of papers in 1838 and 1839 he proved the first class number formula, for quadratic forms (later refined by his student Kronecker). The formula, which Jacobi called a result "touching the utmost of human acumen", opened the way for similar results regarding more general number fields.[1] Based on his research of the structure of the unit group of quadratic fields, he proved the Dirichlet unit theorem, a fundamental result in algebraic number theory.[7]
He first used the pigeonhole principle, a basic counting argument, in the proof of a theorem in diophantine approximation, later named after him Dirichlet's approximation theorem. He published important contributions to Fermat's last theorem, for which he proved the cases n = 5 and n = 14, and to the biquadratic reciprocity law.[1] The Dirichlet divisor problem, for which he found the first results, is still an unsolved problem in number theory despite later contributions by other researchers.
Analysis
Inspired by the work of his mentor in Paris, Dirichlet published in 1829 a famous memoir giving the conditions, showing for which functions the convergence of the Fourier series holds. Before Dirichlet's solution, not only Fourier, but also Poisson and Cauchy had tried unsuccessfully to find a rigorous proof of convergence. The memoir pointed out Cauchy's mistake and introduced Dirichlet's test for the convergence of series. It also introduced the Dirichlet function as an example that not any function is integrable (the definite integral was still a developing topic at the time) and, in the proof of the theorem for the Forier series, introduced the Dirichlet kernel and the Dirichlet integral.[8]
Dirichlet also studied the first boundary value problem, for the Laplace equation, proving the unicity of the solution; this type of problem in the theory of partial differential equations was later named the Dirichlet problem after him.[6] In the proof he notably used the principle that the solution is the function that minimizes the so-called Dirichlet energy. Riemann later named this approach the Dirichlet principle, although he knew it had also been used by Gauss and by Lord Kelvin. [1]
Definition of function
While trying to gauge the range of functions for which convergence of the Fourier series can be shown, Dirichlet defines a function by the property that "to any x there corresponds a single finite y", but then restricts his attention to piecewise continuous functions. Based on this, he is credited with introducing the modern concept for a function, as opposed to the older vague understanding of a function as an analytic formula.[1] Imre Lakatos cites Hermann Hankel as the early origin of this attribution, but disputes the claim saying that "there is ample evidence that he had no idea of this concept [...] for instance, when he discusses piecewise continuous functions, he says that at points of discontinuity the function has two values".[9]
Other fields
Dirichlet also worked in mathematical physics, lecturing and publishing research in potential theory (including the Dirichlet problem and Dirichlet priciple mentioned above), the theory of heat and hydrodynamics.[6] He improved on Lagrange's work on conservative systems by showing that the condition for equilibrium is that the potential energy is minimal.[10]
Although he didn't publish much in the field, Dirichlet lectured on probability theory and least squares, introducing some original methods and results, in particular for limit theorems and an improvement of Laplace's method of approximation related to the central limit theorem.[11] The Dirichlet distribution and the Dirichlet process, based on the Dirichlet integral, are named after him.
Honours
Dirichlet was elected as a member of several academies:[12]
- Prussian Academy of Sciences (1832)
- Saint Petersburg Academy of Sciences (1833) – corresponding member
- Göttingen Academy of Sciences (1846)
- French Academy of Sciences (1854) – foreign member
- Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences (1854)
- Royal Belgian Academy of Sciences (1855)
- Royal Society (1855) – foreign member
In 1855 Dirichlet was awarded the civil class medal of the Pour le Mérite order at von Humboldt's recommendation. The Dirichlet crater on the Moon and the 11665 Dirichlet asteroid are named after him.
Selected publications
- Lejeune Dirichlet, J.P.G. (1889). L. Kronecker. ed. Werke. 1. Berlin: Reimer.
- Lejeune Dirichlet, J.P.G. (1897). L. Kronecker, L. Fuchs. ed. Werke. 2. Berlin: Reimer.
- Lejeune Dirichlet, J.P.G.; Richard Dedekind (1863). Vorlesungen über Zahlentheorie. F. Vieweg und sohn.
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Elstrodt, Jürgen (2007). "The Life and Work of Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet (1805–1859)" (PDF). Clay Mathematics Proceedings. http://www.uni-math.gwdg.de/tschinkel/gauss-dirichlet/elstrodt-new.pdf. Retrieved 2007-12-25.
- ^ a b c James, Ioan Mackenzie (2003). Remarkable Mathematicians: From Euler to von Neumann. Cambridge University Press. pp. 103–109. ISBN 978-0521520942.
- ^ Krantz, Steven (2011). The Proof is in the Pudding: The Changing Nature of Mathematical Proof. Springer. pp. 55–58. ISBN 978-0387489087.
- ^ Goldstein, Cathérine; Catherine Goldstein, Norbert Schappacher, Joachim Schwermer (2007). The shaping of arithmetic: after C.F. Gauss's Disquisitiones Arithmeticae. Springer. pp. 204–208. ISBN 978-3540204411.
- ^ Calinger, Ronald (1996). Vita mathematica: historical research and integration with teaching. Cambridge University Press. pp. 156–159. ISBN 978-0883850978.
- ^ a b c d Gowers, Timothy; June Barrow-Green, Imre Leader (2008). The Princeton companion to mathematics. Princeton University Press. pp. 764–765. ISBN 978-0691118802.
- ^ a b Kanemitsu, Shigeru; Chaohua Jia (2002). Number theoretic methods: future trends. Springer. pp. 271–274. ISBN 978-1402010804.
- ^ Bressoud, David M. (2007). A radical approach to real analysis. MAA. pp. 218–227. ISBN 978-0883857472.
- ^ Lakatos, Imre (1976). Proofs and refutations: the logic of mathematical discovery. Cambridge University Press. pp. 151–152. ISBN 978-0521290388.
- ^ Leine, Remco; Nathan van de Wouw (2008). Stability and convergence of mechanical systems with unilateral constraints. Springer. pp. 6. ISBN 978-3540769743.
- ^ Fischer, Hans (February 1994). "Dirichlet's contributions to mathematical probability theory". Historia Mathematica (Elsevier) 21 (1): 39–63. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S031508608471007X. Retrieved 2011-10-18.
- ^ "Obituary notices of deceased fellows". Proceedings of the Royal Society of London (Taylor and Francis) 10: xxxviii–xxxix. 1860.