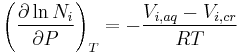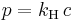Solubility
Solubility is the property of a solid, liquid, or gaseous chemical substance called solute to dissolve in a solid, liquid, or gaseous solvent to form a homogeneous solution of the solute in the solvent. The solubility of a substance fundamentally depends on the used solvent as well as on temperature and pressure. The extent of the solubility of a substance in a specific solvent is measured as the saturation concentration where adding more solute does not increase the concentration of the solution.
Most often, the solvent is a liquid, which can be a pure substance or a mixture.[1] One may also speak of solid solution, but rarely of solution in a gas (see vapor-liquid equilibrium instead).
The extent of solubility ranges widely, from infinitely soluble (fully miscible[2] ) such as ethanol in water, to poorly soluble, such as silver chloride in water. The term insoluble is often applied to poorly or very poorly soluble compounds.
Under certain conditions, the equilibrium solubility can be exceeded to give a so-called supersaturated solution, which is metastable.[3]
Solubility is not to be confused with the ability to dissolve or liquefy a substance, because the solution might occur not only because of dissolution but also because of a chemical reaction. For example, zinc is insoluble in hydrochloric acid, but does dissolve in it by chemical reaction into zinc chloride and hydrogen, where zinc chloride is then soluble in hydrochloric acid. Solubility does not also depend on particle size or other kinetic factors; given enough time, even large particles will eventually dissolve.
IUPAC definition
According to an IUPAC definition[4], solubility is the analytical composition of a saturated solution expressed as a proportion of a designated solute in a designated solvent. Solubility may be stated in units of concentration, molality, mole fraction, mole ratio, and other units.
Molecular view
Solubility occurs under dynamic equilibrium, which means that solubility results from the simultaneous and opposing processes of dissolution and phase joining (e.g., precipitation of solids). The solubility equilibrium occurs when the two processes proceed at a constant rate.
The term solubility is also used in some fields where the solute is altered by solvolysis. For example, many metals and their oxides are said to be "soluble in hydrochloric acid," whereas the aqueous acid degrades the solid to irreversibly give soluble products. It is also true that most ionic solids are degraded by polar solvents, but such processes are reversible. In those cases where the solute is not recovered upon evaporation of the solvent, the process is referred to as solvolysis. The thermodynamic concept of solubility does not apply straightforwardly to solvolysis.
When a solute dissolves, it may form several species in the solution. For example, an aqueous suspension of ferrous hydroxide, Fe(OH)2, will contain the series [Fe(H2O)6 − x(OH)x](2 − x)+ as well as other oligomeric species. Furthermore, the solubility of ferrous hydroxide and the composition of its soluble components depends on pH. In general, solubility in the solvent phase can be given only for a specific solute that is thermodynamically stable, and the value of the solubility will include all the species in the solution (in the example above, all the iron-containing complexes).
Factors affecting solubility
Solubility is defined for specific phases. For example, the solubility of aragonite and calcite in water are expected to differ, even though they are both polymorphs of calcium carbonate and have the same chemical formula.
The solubility of one substance in another is determined by the balance of intermolecular forces between the solvent and solute, and the entropy change that accompanies the solvation. Factors such as temperature and pressure will alter this balance, thus changing the solubility.
Solubility may also strongly depend on the presence of other species dissolved in the solvent, for example, complex-forming anions (ligands) in liquids. Solubility will also depend on the excess or deficiency of a common ion in the solution, a phenomenon known as the common-ion effect. To a lesser extent, solubility will depend on the ionic strength of solutions. The last two effects can be quantified using the equation for solubility equilibrium.
For a solid that dissolves in a redox reaction, solubility is expected to depend on the potential (within the range of potentials under which the solid remains the thermodynamically stable phase). For example, solubility of gold in high-temperature water is observed to be almost an order of magnitude higher when the redox potential is controlled using a highly-oxidizing Fe3O4-Fe2O3 redox buffer than with a moderately-oxidizing Ni-NiO buffer.[5]
Solubility (metastable) also depends on the physical size of the crystal or droplet of solute (or, strictly speaking, on the specific or molar surface area of the solute). For quantification, see the equation in the article on solubility equilibrium. For highly defective crystals, solubility may increase with the increasing degree of disorder. Both of these effects occur because of the dependence of solubility constant on the Gibbs energy of the crystal. The last two effects, although often difficult to measure, are of practical importance. For example, they provide the driving force for precipitate aging (the crystal size spontaneously increasing with time).
Temperature
The solubility of a given solute in a given solvent typically depends on temperature. For many solids dissolved in liquid water, the solubility increases with temperature up to 100 °C.[6] In liquid water at high temperatures, (e.g., that approaching the critical temperature), the solubility of ionic solutes tends to decrease due to the change of properties and structure of liquid water; the lower dielectric constant results in a less polar solvent.
Gaseous solutes exhibit more complex behavior with temperature. As the temperature is raised, gases usually become less soluble in water (to minimum, which is below 120 °C for most permanent gases[7]), but more soluble in organic solvents.[6]
The chart shows solubility curves for some typical solid inorganic salts (temperature is in degrees Celsius).[8] Many salts behave like barium nitrate and disodium hydrogen arsenate, and show a large increase in solubility with temperature. Some solutes (e.g., NaCl in water) exhibit solubility that is fairly independent of temperature. A few, such as cerium(III) sulfate, become less soluble in water as temperature increases. This temperature dependence is sometimes referred to as "retrograde" or "inverse" solubility. Occasionally, a more complex pattern is observed, as with sodium sulfate, where the less soluble decahydrate crystal loses water of crystallization at 32 °C to form a more soluble anhydrous phase.
The solubility of organic compounds nearly always increases with temperature. The technique of recrystallization, used for purification of solids, depends on a solute's different solubilities in hot and cold solvent. A few exceptions exist, such as certain cyclodextrins.[9]
Pressure
For condensed phases (solids and liquids), the pressure dependence of solubility is typically weak and usually neglected in practice. Assuming an ideal solution, the dependence can be quantified as:
where the index i iterates the components, Ni is the mole fraction of the ith component in the solution, P is the pressure, the index T refers to constant temperature, Vi,aq is the partial molar volume of the ith component in the solution, Vi,cr is the partial molar volume of the ith component in the dissolving solid, and R is the universal gas constant.[10]
The pressure dependence of solubility does occasionally have practical significance. For example, precipitation fouling of oil fields and wells by calcium sulfate (which decreases its solubility with decreasing pressure) can result in decreased productivity with time.
Solubility of gases
Henry's law is used to quantify the solubility of gases in solvents. The solubility of a gas in a solvent is directly proportional to the partial pressure of that gas above the solvent. This relationship is written as:
where kH is a temperature-dependent constant (for example, 769.2 L·atm/mol for dioxygen (O2) in water at 298 K), p is the partial pressure (atm), and c is the concentration of the dissolved gas in the liquid (mol/L).
The solubility of gases is sometimes also quantified using Bunsen solubility coefficient.
In the presence of small bubbles, the solubility of the gas does not depend on the bubble radius in any other way than through the effect of the radius on pressure (i.e., the solubility of gas in the liquid in contact with small bubbles is increased due to pressure increase by Δp = 2γ/r; see Young–Laplace equation).[11]
Polarity
A popular aphorism used for predicting solubility is "like dissolves like".[12] This statement indicates that a solute will dissolve best in a solvent that has a similar chemical structure to itself. This view is simplistic, but it is a useful rule of thumb. The overall solvation capacity of a solvent depends primarily on its polarity.[13] For example, a very polar (hydrophilic) solute such as urea is very soluble in highly polar water, less soluble in fairly polar methanol, and practically insoluble in non-polar solvents such as benzene. In contrast, a non-polar or lipophilic solute such as naphthalene is insoluble in water, fairly soluble in methanol, and highly soluble in non-polar benzene.[14]
The solubility is favored by entropy of mixing and depends on enthalpy of dissolution and the hydrophobic effect.
Synthetic chemists often exploit differences in solubilities to separate and purify compounds from reaction mixtures, using the technique of liquid-liquid extraction.
Rate of dissolution
Dissolution is not always an instantaneous process. It is fast when salt and sugar dissolve in water but much slower for a tablet of aspirin or a large crystal of hydrated copper(II) sulfate. These observations are the consequence of two factors: the rate of solubilization (in kg/s) is related to the solubility product and the surface area of the material. The speed at which a solid dissolves may depend on its crystallinity or lack thereof in the case of amorphous solids and the surface area (crystallite size) and the presence of polymorphism. Many practical systems illustrate this effect, for example in designing methods for controlled drug delivery. Critically, the dissolution rate may depend on the presence of mixing and other factors that determine the degree of undersaturation in the liquid solvent film immediately adjacent to the solid solute crystal. In some cases, solubility equilibria can take a long time to establish (hours, days, months, or many years; depending on the nature of the solute and other factors). In practice, it means that the amount of solute in a solution is not always determined by its thermodynamic solubility, but may depend on kinetics of dissolution (or precipitation).
The rate of dissolution and solubility should not be confused as they are different concepts, kinetic and thermodynamic, respectively. The solubilization kinetics, as well as apparent solubility can be improved after complexation of an active ingredient with cyclodextrin. This can be used in the case of drug with poor solubility.[15]
Quantification of solubility
Solubility is commonly expressed as a concentration, either by mass (g of solute per kg of solvent, g per dL (100mL) of solvent, molarity, molality, mole fraction, or other similar descriptions of concentration. The maximum equilibrium amount of solute that can dissolve per amount of solvent is the solubility of that solute in that solvent under the specified conditions. The advantage of expressing solubility in this manner is its simplicity, while the disadvantage is that it can strongly depend on the presence of other species in the solvent (for example, the common ion effect).
Solubility constants are used to describe saturated solutions of ionic compounds of relatively low solubility (see solubility equilibrium). The solubility constant is a special case of an equilibrium constant. It describes the balance between dissolved ions from the salt and undissolved salt. The solubility constant is also "applicable" (i.e., useful) to precipitation, the reverse of the dissolving reaction. As with other equilibrium constants, temperature can affect the numerical value of solubility constant. The solubility constant is not as simple as solubility, however the value of this constant is generally independent of the presence of other species in the solvent.
The Flory-Huggins solution theory is a theoretical model describing the solubility of polymers. The Hansen Solubility Parameters and the Hildebrand solubility parameters are empirical methods for the prediction of solubility. It is also possible to predict solubility from other physical constants such as the enthalpy of fusion.
The partition coefficient (Log P) is a measure of differential solubility of a compound in a hydrophobic solvent (octanol) and a hydrophilic solvent (water). The logarithm of these two values enables compounds to be ranked in terms of hydrophilicity (or hydrophobicity).
Applications
Solubility is of fundamental importance in a large number of scientific disciplines and practical applications, ranging from ore processing, to the use of medicines, and the transport of pollutants.
Solubility is often said to be one of the "characteristic properties of a substance," which means that solubility is commonly used to describe the substance, to indicate a substance's polarity, to help to distinguish it from other substances, and as a guide to applications of the substance. For example, indigo is described as "insoluble in water, alcohol, or ether but soluble in chloroform, nitrobenzene, or concentrated sulfuric acid".
Solubility of a substance is useful when separating mixtures. For example, a mixture of salt (sodium chloride) and silica may be separated by dissolving the salt in water, and filtering off the undissolved silica. The synthesis of chemical compounds, by the milligram in a laboratory, or by the ton in industry, both make use of the relative solubilities of the desired product, as well as unreacted starting materials, byproducts, and side products to achieve separation.
Another example of this is the synthesis of benzoic acid from phenylmagnesium bromide and dry ice. Benzoic acid is more soluble in an organic solvent such as dichloromethane or diethyl ether, and when shaken with this organic solvent in a separatory funnel, will preferentially dissolve in the organic layer. The other reaction products, including the magnesium bromide, will remain in the aqueous layer, clearly showing that separation based on solubility is achieved. This process, known as liquid-liquid extraction, is an important technique in synthetic chemistry.
Solubility of ionic compounds in water
Some ionic compounds (salts) dissolve in water, which arises because of the attraction between positive and negative charges (see: solvation). For example, the salt's positive ions (e.g. Ag+) attract the partially-negative oxygens in H2O. Likewise, the salt's negative ions (e.g. Cl−) attract the partially-positive hydrogens in H2O. Note: oxygen is partially-negative because it is more electronegative than hydrogen, and vice-versa (see: chemical polarity).
- AgCl(s) Ag+(aq) + Cl−(aq)
However, there is a limit to how much salt can be dissolved in a given volume of water. This amount is given by the solubility product, Ksp. This value depends on the type of salt (AgCl vs. NaCl, for example), temperature, and the common ion effect.
One can calculate the amount of AgCl that will dissolve in 1 liter of water, some algebra is required.
- Ksp = [Ag+] × [Cl−] (definition of solubility product)
- Ksp = 1.8 × 10−10 (from a table of solubility products)
[Ag+] = [Cl−], in the absence of other silver or chloride salts,
- [Ag+]2 = 1.8 × 10−10
- [Ag+] = 1.34 × 10−5
The result: 1 liter of water can dissolve 1.34 × 10−5 moles of AgCl(s) at room temperature. Compared with other types of salts, AgCl is poorly soluble in water. In contrast, table salt (NaCl) has a higher Ksp and is, therefore, more soluble.
| Soluble | Insoluble |
|---|---|
| Group I and NH4+ compounds | Carbonates (Except Group I, NH4+ and uranyl compounds) |
| Nitrates | Sulfites (Except Group I and NH4+ compounds) |
| Acetates (Ethanoates) (Except Ag+ compounds) | Phosphates (Except Group I and NH4+ compounds) |
| Chlorides (Chlorates and Perchlorates), bromides and iodides (Except Ag+, Pb2+, Cu+ and Hg22+) | Hydroxides and oxides (Except Group I, NH4+, Ba2+, Sr2+ and Tl+) |
| Sulfates (Except Ag+, Pb2+, Ba2+, Sr2+ and Ca2+) | Sulfides (Except Group I, Group II and NH4+ compounds) |
Solubility of organic compounds
The principle outlined above under polarity, that like dissolves like, is the usual guide to solubility with organic systems. For example, petroleum jelly will dissolve in gasoline because both petroleum jelly and gasoline are non-polar hydrocarbons. It will not, on the other hand, dissolve in ethyl alcohol or water, since the polarity of these solvents is too high. Sugar will not dissolve in gasoline, since sugar is too polar in comparison with gasoline. A mixture of gasoline and sugar can therefore be separated by filtration, or extraction with water.
Solubility in non-aqueous solvents
Most publicly available solubility values are those for solubility in water.[16] The reference also lists some for non-aqueous solvents. Solubility data for non-aqueous solvents is currently being collected via an open notebook science crowdsourcing project.[17][18]
Solid solution
This term is often used in the field of metallurgy to refer to the extent that an alloying element will dissolve into the base metal without forming a separate phase. The solubility line (or curve) is the line (or lines) on a phase diagram that give the limits of solute addition. That is, the lines show the maximum amount of a component that can be added to another component and still be in solid solution. In the solid's crystalline structure, the 'solute' element can either take the place of the matrix within the lattice (a substitutional position, for example: chromium in iron) or take a place in a space between the lattice points (an interstitial position, for example: carbon in iron).
In microelectronic fabrication, solid solubility refers to the maximum concentration of impurities one can place into the substrate.
Incongruent dissolution
Many substances dissolve congruently; i.e., the composition of the solid and the dissolved solute stoichiometrically match. However, some substances may dissolve incongruently, whereby the composition of the solute in solution does not match that of the solid. This solubilization is accompanied by alteration of the "primary solid" and possibly formation of a secondary solid phase. However, in general, some primary solid also remains and a complex solubility equilibrium establishes. For example, dissolution of albite may result in formation of gibbsite.[19]
- NaAlSi3O8(s) + H+ + 7H2O = Na+ + Al(OH)3(s) + 3H4SiO4.
In this case, the solubility of albite is expected to depend on the solid-to-solvent ratio. This kind of solubility is of great importance in geology, where it results in formation of metamorphic rocks.
See also
- Biopharmaceutics Classification System
- Dühring's rule
- Fajans-Paneth-Hahn Law
- Flexible SPC water model
- Hot water extraction
- Hydrotrope
- Raoult's law
- Simulations Plus
- Solubility equilibrium
- Solubilization
- Apparent molar property
References
- ^ Yuen, C. (2003)). Element, Compound and Mixture.
- ^ Clugston M. and Fleming R. (2000). Advanced Chemistry (1st ed.). Oxford: Oxford Publishing. p. 108.
- ^ "Cancerweb.ncl.ac.uk: from Online Medical Dictionary, University of Newcastle Upon Tyne". http://cancerweb.ncl.ac.uk/cgi-bin/omd?metastable.
- ^ IUPAC. Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book"). Compiled by A. D. McNaught and A. Wilkinson. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford (1997). XML on-line corrected version: http://goldbook.iupac.org (2006-) created by M. Nic, J. Jirat, B. Kosata; updates compiled by A. Jenkins. ISBN 0-9678550-9-8. doi:10.1351/goldbook. Entry: Solubility.
- ^ I.Y. Nekrasov (1996). Geochemistry, Mineralogy and Genesis of Gold Deposits. Taylor & Francis. pp. 135–136. ISBN 9789054107231. http://books.google.ca/books?id=HUWRZecignoC&pg=PA135#PPA135,M1.
- ^ a b John W. Hill, Ralph H. Petrucci, General Chemistry, 2nd edition, Prentice Hall, 1999.
- ^ P. Cohen, ed (1989). The ASME handbook on Water Technology for Thermal Power Systems. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers. p. 442.
- ^ Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (27th ed.). Cleveland, Ohio: Chemical Rubber Publishing Co.. 1943.
- ^ Salvatore Filippone, Frank Heimanna and André Rassat (2002). "A highly water-soluble 2+1 b-cyclodextrin–fullerene conjugate". Chem. Commun. 2002: 1508–1509. doi:10.1039/b202410a.
- ^ E.M.Gutman (1994). Mechanochemistry of Solid Surfaces. World Scientific Publishing Co..
- ^ G.W. Greenwood (1969). "The Solubility of Gas Bubbles". Journal of Material Science 4: 320–322. doi:10.1007/BF00550401.
- ^ Kenneth J. Williamson (1994). Macroscale and Microscale Organic Experiments (2nd ed.). Lexington, Mass.: D. C, Heath. p. 40. ISBN 0669194298.
- ^ The solvent polarity is defined as its solvation power according to Reichardt
- ^ Merck Index (7th ed.). Merck & Co.. 1960.
- ^ Gil A, Chamayou A, Leverd E, Bougaret J, Baron M, Couarraze G (2004). "Evolution of the interaction of a new chemical entity, eflucimibe, with gamma-cyclodextrin during kneading process". Eur. J. Pharm. Sciences 23: 123–129. doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2004.06.002.
- ^ "NIST solubility database". http://srdata.nist.gov/solubility/casNO.aspx.
- ^ "ONS Solubility challenge". http://onschallenge.wikispaces.com/.
- ^ "Solubility of Vanillin in various non-aqueous solvents". http://oru.edu/cccda/sl/solubility/allsolvents.php?solute=vanillin.
- ^ O.M.Saether & P. de Caritat, ed (1997). Geochemical processes, weathering and groundwater recharge in catchments. Rotterdam: Taylor & Francis. p. 6. ISBN 9054106417.
External links
- VCClab.org, "ALOGPS" free interactive calculation of aqueous solubility of compounds at Virtual Computational Chemistry Laboratory using several algorithms.
- ACDlabs.com? ACD/Solubility DB aqueous solubility prediction
- Simulations-plus.com, S+Sw, an aqueous solubility prediction model.
|
||||||||||||||