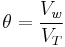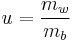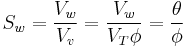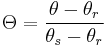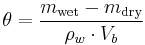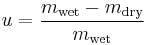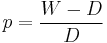Water content
Water content or moisture content is the quantity of water contained in a material, such as soil (called soil moisture), rock, ceramics, fruit, or wood. Water content is used in a wide range of scientific and technical areas, and is expressed as a ratio, which can range from 0 (completely dry) to the value of the materials' porosity at saturation. It can be given on a volumetric or mass (gravimetric) basis.
Volumetric water content, θ, is defined mathematically as:
where 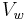 is the volume of water and
is the volume of water and 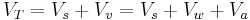 is the total volume (that is soil volume + water volume + air space).
is the total volume (that is soil volume + water volume + air space).
Gravimetric water content[1] is expressed by mass (weight) as follows:
where  is the mass of water and
is the mass of water and 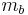 is the bulk mass. The bulk mass is taken as the total mass, except for geotechnical and soil science applications where oven-dried soil (
is the bulk mass. The bulk mass is taken as the total mass, except for geotechnical and soil science applications where oven-dried soil (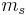 , see the diagram) is conventionally used as
, see the diagram) is conventionally used as 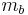 .
.
To convert gravimetric water content to volumetric water, multiply the gravimetric water content by the bulk specific gravity of the material.
Contents |
Other definitions
Degree of saturation
In soil mechanics and petroleum engineering, the term water saturation or degree of saturation, 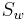 is used, defined as
is used, defined as
where 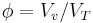 is the porosity and
is the porosity and 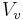 is the volume of void or pore space.
is the volume of void or pore space.
Values of Sw can range from 0 (dry) to 1 (saturated). In reality, Sw never reaches 0 or 1 - these are idealizations for engineering use.
Normalized volumetric water content
The normalized water content, 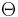 , (also called effective saturation or
, (also called effective saturation or 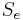 ) is a dimensionless value defined by van Genuchten[2] as:
) is a dimensionless value defined by van Genuchten[2] as:
where 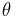 is the volumetric water content;
is the volumetric water content; 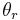 is the residual water content, defined as the water content for which the gradient
is the residual water content, defined as the water content for which the gradient 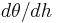 becomes zero; and,
becomes zero; and, 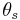 is the saturated water content, which is equivalent to porosity,
is the saturated water content, which is equivalent to porosity,  .
.
Measurement
Direct methods
Water content can be directly measured using a known volume of the material, and a drying oven. Volumetric water content, θ, is calculated[3] using:
where
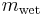 and
and 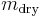 are the masses of the sample before and after drying in the oven;
are the masses of the sample before and after drying in the oven;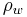 is the density of water; and
is the density of water; and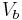 is the volume of the sample before drying the sample.
is the volume of the sample before drying the sample.
For materials that change in volume with water content, such as coal, the water content, u, is expressed in terms of the mass of water per unit mass of the moist specimen:
However, geotechnics requires the moisture content to be expressed as a percentage of the sample's dry weight i.e. % moisture content = 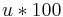
- Where
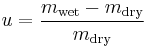
For wood, the convention is to report moisture content on oven-dry basis (i.e. generally drying sample in an oven set at 105 deg Celsius for 24 hours). In wood drying, this is an important concept.
Laboratory methods
Other methods that determine water content of a sample include chemical titrations (for example the Karl Fischer titration), determining mass loss on heating (perhaps in the presence of an inert gas), or after freeze drying. In the food industry the Dean-Stark method is also commonly used.
From the Annual Book of ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) Standards, the total evaporable moisture content in Aggregate (C 566) can be calculated with the formula:
where 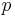 is the fraction of total evaporable moisture content of sample,
is the fraction of total evaporable moisture content of sample, 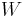 is the mass of the original sample, and
is the mass of the original sample, and 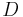 is mass of dried sample.
is mass of dried sample.
Geophysical methods
There are several geophysical methods available that can approximate in situ soil water content. These methods include: time-domain reflectometry (TDR), neutron probe, frequency domain sensor, capacitance probe, electrical resistivity tomography, ground penetrating radar (GPR), and others that are sensitive to the physical properties of water .[4] Geophysical sensors are often used to monitor soil moisture continuously in agricultural and scientific applications.
Satellite remote sensing method
Satellite microwave remote sensing is used to estimate soil moisture based on the large contrast between the dielectric properties of wet and dry soil. The microwave radiation is not sensitive to atmospheric variables, and can penetrate through clouds. Also, microwave signal can penetrate, to a certain extent, the vegetation canopy and retrieve information from ground surface [1]. The data from microwave remote sensing satellite such as: WindSat, AMSR-E, RADARSAT, ERS-1-2, Metop/ASCAT are used to estimate surface soil moisture [2].
Classification and uses
Moisture may be present as adsorbed moisture at internal surfaces and as capillary condensed water in small pores. At low relative humidities, moisture consists mainly of adsorbed water. At higher relative humidities, liquid water becomes more and more important, depending on the pore size. In wood-based materials, however, almost all water is adsorbed at humidities below 98% RH.
In biological applications there can also be a distinction between physisorbed water and "free" water — the physisorbed water being that closely associated with and relatively difficult to remove from a biological material. The method used to determine water content may affect whether water present in this form is accounted for. For a better indication of "free" and "bound" water, the water activity of a material should be considered.
Water molecules may also be present in materials closely associated with individual molecules, as "water of crystallization", or as water molecules which are static components of protein structure.
Earth and agricultural sciences
In soil science, hydrology and agricultural sciences, water content has an important role for groundwater recharge, agriculture, and soil chemistry. Many recent scientific research efforts have aimed toward a predictive-understanding of water content over space and time. Observations have revealed generally that spatial variance in water content tends to increase as overall wetness increases in semiarid regions, to decrease as overall wetness increases in humid regions, and to peak under intermediate wetness conditions in temperature regions .[5]
There are four standard water contents that are routinely measured and used, which are described in the following table:
| Name | Notation | Suction pressure (J/kg or kPa) |
Typical water content (vol/vol) |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saturated water content | θs | 0 | 0.2–0.5 | Fully saturated soil, equivalent to effective porosity |
| Field capacity | θfc | −33 | 0.1–0.35 | Soil moisture 2–3 days after a rain or irrigation |
| Permanent wilting point | θpwp or θwp | −1500 | 0.01–0.25 | Minimum soil moisture at which a plant wilts |
| Residual water content | θr | −∞ | 0.001–0.1 | Remaining water at high tension |
And lastly the available water content, θa, which is equivalent to:
- θa ≡ θfc − θpwp
which can range between 0.1 in gravel and 0.3 in peat.
Agriculture
When a soil gets too dry, plant transpiration drops because the water is becoming increasingly bound to the soil particles by suction. Below the wilting point plants are no longer able to extract water. At this point they wilt and cease transpiring altogether. Conditions where soil is too dry to maintain reliable plant growth is referred to as agricultural drought, and is a particular focus of irrigation management. Such conditions are common in arid and semi-arid environments.
Some agriculture professionals are beginning to use environmental measurements such as soil moisture to schedule irrigation. This method is referred to as smart irrigation or soil cultivation.
Groundwater
In saturated groundwater aquifers, all available pore spaces are filled with water (volumetric water content = porosity). Above a capillary fringe, pore spaces have air in them too.
Most soils have a water content less than porosity, which is the definition of unsaturated conditions, and they make up the subject of vadose zone hydrogeology. The capillary fringe of the water table is the dividing line between saturated and unsaturated conditions. Water content in the capillary fringe decreases with increasing distance above the phreatic surface.
One of the main complications which arises in studying the vadose zone, is the fact that the unsaturated hydraulic conductivity is a function of the water content of the material. As a material dries out, the connected wet pathways through the media become smaller, the hydraulic conductivity decreasing with lower water content in a very non-linear fashion.
A water retention curve is the relationship between volumetric water content and the water potential of the porous medium. It is characteristic for different types of porous medium. Due to hysteresis, different wetting and drying curves may be distinguished.
See also
- Humidity, "water content" in air
- Moisture
- Moisture analysis
- Soil moisture sensors
- Water activity
- Water retention curve
References
- ^ T. William Lambe & Robert V. Whitman (1969). "Chapter 3: Description of an Assemblage of Particles". Soil Mechanics (First ed.). John Wiley & Sons, Inc.. p. 553. ISBN 471-51192-7.
- ^ van Genuchten, M.Th. (1980). "A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils". Soil Science Society of America Journal 44 (5): 892–898. doi:10.2136/sssaj1980.03615995004400050002x. http://hydro.nevada.edu/courses/gey719/vg.pdf.
- ^ Dingman, S.L. (2002). "Chapter 6, Water in soils: infiltration and redistribution". Physical Hydrology (Second ed.). Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Prentice-Hall, Inc.. p. 646. ISBN 0-13-099695-5.
- ^ F. Ozcep, M. Asci, O. Tezel, T. Yas, N. Alpaslan, D. Gundogdu (2005). "Relationships Between Electrical Properties (in Situ) and Water Content (in the Laboratory) of Some Soils in Turkey". Geophysical Research Abstracts 7. http://www.cosis.net/abstracts/EGU05/08470/EGU05-J-08470.pdf.
- ^ Lawrence, J. E., and G. M. Hornberger (2007). "Soil moisture variability across climate zones". Geophys. Res. Lett. 34 (L20402): L20402. Bibcode 2007GeoRL..3420402L. doi:10.1029/2007GL031382.
|
|||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||