Haploid-relative-risk
Haploid-relative-risk (HRR) is a family based method for determining gene allele association to a disease. Nuclear families with one affected child are sampled using the parental haplotypes not transmitted as a control. While similar to genotype relative risk (RR), HRR provides a solution to the problem of population stratification by only sampling within family trios. HRR method was first proposed by Rubinstein in 1981 then detailed in 1987 by Rubinstein and Falk [1] and is an important tool in genetic association studies.
The original method proposed by Falk and Rubinstien fell under scrutiny in 1989, when Ott showed the equivalence of HRR to the classical RR method[2] demonstrating the HRR holds only when there is zero chance of recombination between disease locus and its markers.[3] This led to the adoption of the transmission disequilibrium test as the more commonly used method for association linkage; Yet, when the recombination factor for a gene marker and its locus are >0 there is no tendency for false positives seen.[4]
While HRR method has been shown as an effective means of avoiding population stratification another family based associations test known as transmission disequilibrium test[5] or, TDT is more commonly used because of its more simplified algorithms. Some research uses both HRR and TDT for there ability to complement each other since one result my give no association while the other will. A positive association result from both TDT and HRR means there is strong evidence that a link exists and vise verse. For example, both HRR and TDT methods were used in a study looking for polymorphism in D2 and D3 dopamine receptor in association with schizophrenia and found no linkage in both tests;[6] showing absolutely no possible association.
Calculation
This model represents a case which there is a single locus where all genotypes may lead to expression of the allele in its the most simplified definition. Under these parameters an disequilibrium linkage more than 50% means there is a possible link to the gene allele and inheritance.
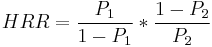
Gives the HHR which can be estimated by
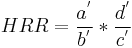
a' denotes the observed frequency of children who are positive for the gene allele H.
b' denotes the observed frequency of children who are negative for the gene allele H.
c' is the observed frequency of families with at least one transmitted parental marker allele H.
d' is the observed frequency of families with no transmitted parental marker allele H.
P1 is the probability this child is positive for the allele of interest H.
P2 is the probability that at least one of the nontransmitted parental marker alleles equals the allele of interest H.
H is the allele of interest. [7]
References
- ^ Falk CT, Rubinstein P (1987) "Haplotype relative risks: and easy reliable way to construct a proper control sample for risk calculations". Ann Hum Genet 51:227-233
- ^ Woolf B (1955) "On estimating the relation between blood group and disease". Ann Human Genet 19:251-253
- ^ Ott J (1989) statistical properties of the haplotype relative risk. Genetic Epidemiol 6:127-130
- ^ Knapp,Seuchter,Baur (1987) "The haplotype-relative-risk" (HRR) method for analysis of association in nuclear families. Am J Hum Genet 52:1085-10093,1993
- ^ a b c Spielman RS, McGinnis RE, Ewens WJ (Mar 1993). "Transmission test for linkage disequilibrium: the insulin gene region and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM)". Am J Hum Genet. 52 (3): 506–16. PMID 8447318.
- ^ Ambròsio, Kennedy, Macciardi, macoedo, Valente, Dourado, oliveria, Carlos, Pato (2004)"Family association study between DRD2 and DRD3 gene polymorphisms and schizophrenia in a portuguese population". Psychiatry Research 125:185-191
- ^ Knapp,Seuchter,Baur (1987) "The haplotype-relative-risk (HRR) method for analysis of association in nuclear families". Am J Hum Genet 52:1085-10093,1993