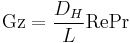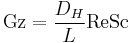Graetz number
In fluid dynamics, the Graetz number, 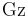 is a dimensionless number that characterises laminar flow in a conduit. The number is defined as:[1]
is a dimensionless number that characterises laminar flow in a conduit. The number is defined as:[1]
where
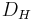 is the diameter in round tubes or hydraulic diameter in arbitrary cross-section ducts
is the diameter in round tubes or hydraulic diameter in arbitrary cross-section ducts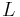 is the length
is the length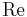 is the Reynolds number and
is the Reynolds number and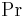 is the Prandtl number.
is the Prandtl number.
This number is useful in determining the thermally developing flow entrance length in ducts. A Graetz number of approximately 1000 or less is the point at which flow would be considered thermally fully developed.[2]
When used in connection with mass transfer the Prandtl number is replaced by the Schmidt number 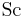 which expresses the ratio of the momentum diffusivity to the mass diffusivity.
which expresses the ratio of the momentum diffusivity to the mass diffusivity.
The quantity is named after the physicist Leo Graetz.
References
- ^ Nellis, G., and Klein, S. (2009) "Heat Transfer" (Cambridge), page 663.
- ^ Shah, R. K., and Sekulic, D. P. (2003) "Fundamentals of Heat Exchanger Design" (John Wiley and Sons), page 503.
|
|||||