Fried parameter
The Fried parameter[1] or Fried's coherence length (commonly written as 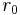 ) measures the optical quality of the atmosphere. This parameter is usually expressed in centimeters and corresponds to an area over which the rms wavefront aberration is less than 1 radian. As such,
) measures the optical quality of the atmosphere. This parameter is usually expressed in centimeters and corresponds to an area over which the rms wavefront aberration is less than 1 radian. As such, 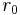 indicates the size of a telescope which can just operate at the diffraction limit. Any larger and resolution will be seeing-limited, any smaller and it will be limited by the telescope itself.
indicates the size of a telescope which can just operate at the diffraction limit. Any larger and resolution will be seeing-limited, any smaller and it will be limited by the telescope itself.
Although not explicitly written in his article, Fried's parameter is usually written as
where 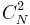 is the strength of turbulence versus altitude,
is the strength of turbulence versus altitude, 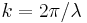 is the angular Wavenumber, and
is the angular Wavenumber, and 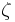 is the angle of the telescope, measured from zenith.
is the angle of the telescope, measured from zenith.
Typical values for 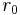 are 10 cm for average seeing and 20 cm for good to excellent seeing on the best sites. The seeing-limited angular resolution is
are 10 cm for average seeing and 20 cm for good to excellent seeing on the best sites. The seeing-limited angular resolution is 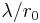 . Since almost all professional telescopes have diameter
. Since almost all professional telescopes have diameter 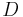 larger than
larger than 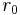 , they employ adaptive optics to correct the aberrations and get diffraction limited images, with resolution of
, they employ adaptive optics to correct the aberrations and get diffraction limited images, with resolution of 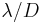 . Because
. Because 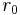 varies with wavelength as
varies with wavelength as 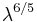 , it is usually specified at
, it is usually specified at 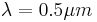
See also
References
- ^ Fried, D. L. (October 1966). "Optical Resolution Through a Randomly Inhomogeneous Medium for Very Long and Very Short Exposures". Journal of the Optical Society of America 56 (10): 1372–1379. Bibcode 1966JOSA...56.1372F. doi:10.1364/JOSA.56.001372. http://www.opticsinfobase.org/abstract.cfm?id=53167.
- ^ Hardy, Johw W. (1998). Adaptive optics for astronomical telescopes. Oxford University Press. p. 92. ISBN 0195090195. http://openlibrary.org/works/OL2633873W/Adaptive_optics_for_astronomical_telescopes.
![r_0 = \left [ 0.423 \, k^2 \, \sec \zeta \int_{\mathrm{Path}} C_n^2(z) \, dz \right ]^{-3/5}.](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/8fd846f308c0a3bdeedb7700d82f79f3.png)