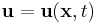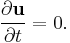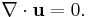Flow velocity
In fluid dynamics the flow velocity, or velocity field, of a fluid is a vector field which is used to mathematically describe the motion of a fluid. The length of the flow velocity vector is the flow speed.
Contents |
Definition
The flow velocity u of a fluid is a vector field
which gives the velocity of an element of fluid at a position 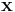 and time
and time 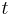 .
.
The flow speed q is the length of the flow velocity vector[1]
and is a scalar field.
Uses
The flow velocity of a fluid effectively describes everything about the motion of a fluid. Many physical properties of a fluid can be expressed mathematically in terms of the flow velocity. Some common examples follow:
Steady flow
The flow of a fluid is said to be steady if 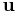 does not vary with time. That is if
does not vary with time. That is if
Incompressible flow
A fluid is incompressible if the divergence of 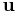 is zero:
is zero:
That is, if 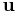 is a solenoidal vector field.
is a solenoidal vector field.
Irrotational flow
A flow is irrotational if the curl of 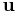 is zero:
is zero:
That is, if 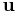 is an irrotational vector field.
is an irrotational vector field.
Vorticity
The vorticity, 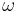 , of a flow can be defined in terms of its flow velocity by
, of a flow can be defined in terms of its flow velocity by
Thus in irrotational flow the vorticity is zero.
The velocity potential
If an irrotational flow occupies a simply-connected fluid region then there exists a scalar field  such that
such that
The scalar field  is called the velocity potential for the flow. (See Irrotational vector field.)
is called the velocity potential for the flow. (See Irrotational vector field.)
Notes and references
- ^ Courant, R.; Friedrichs, K.O. (1977) (5th ed.), Springer, ISBN 0387902325, p. 24