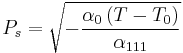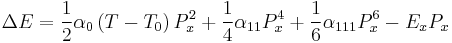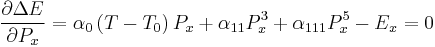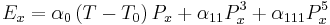Ferroelectricity
Ferroelectricity is a property of certain materials which possess a spontaneous electric polarization that can be reversed by the application of an external electric field.[1][2] The term is used in analogy to ferromagnetism, in which a material exhibits a permanent magnetic moment. Ferromagnetism was already known when ferroelectricity was discovered in 1920 in Rochelle salt by Valasek.[3] Thus, the prefix ferro, meaning iron, was used to describe the property despite the fact that most ferroelectric materials do not contain iron.
Contents |
Polarization
Most materials are polarized linearly by an external electric field; nonlinearities are insignificant. This is called dielectric polarization (see figure). Some materials, known as paraelectric materials, demonstrate a more pronounced nonlinear polarization (see figure). The electric permittivity, corresponding to the slope of the polarization curve, is thereby a function of the external electric field. In addition to being nonlinear, ferroelectric materials demonstrate a spontaneous (zero field) polarization (see figure). The distinguishing feature of ferroelectrics is that the direction of the spontaneous polarization can be reversed by an applied electric field, yielding a hysteresis loop.
Typically, materials demonstrate ferroelectricity only below a certain phase transition temperature, called the Curie temperature, Tc, and are paraelectric above this temperature.
Applications
The nonlinear nature of ferroelectric materials can be used to make capacitors with tunable capacitance. Typically, a ferroelectric capacitor simply consists of a pair of electrodes sandwiching a layer of ferroelectric material. The permittivity of ferroelectrics is not only tunable but commonly also very high in absolute value, especially when close to the phase transition temperature. Because of this, ferroelectric capacitors are small in physical size compared to dielectric (non-tunable) capacitors of similar capacitance.
The spontaneous polarization of ferroelectric materials implies a hysteresis effect which can be used as a memory function, and ferroelectric capacitors are indeed used to make ferroelectric RAM[4] for computers and RFID cards. In these applications thin films of ferroelectric materials are typically used, as this allows the field required to switch the polarization to be achieved with a moderate voltage. However, when using thin films a great deal of attention needs to be paid to the interfaces, electrodes and sample quality for devices to work reliably.[5]
Ferroelectric materials are required by symmetry considerations to be also piezoelectric and pyroelectric. The combined properties of memory, piezoelectricity, and pyroelectricity make ferroelectric capacitors very useful, e.g. for sensor applications. Ferroelectric capacitors are used in medical ultrasound machines (the capacitors generate and then listen for the ultrasound ping used to image the internal organs of a body), high quality infrared cameras (the infrared image is projected onto a two dimensional array of ferroelectric capacitors capable of detecting temperature differences as small as millionths of a degree Celsius), fire sensors, sonar, vibration sensors, and even fuel injectors on diesel engines.
Another idea of recent interest is the ferroelectric tunnel junction (FTJ) in which a contact made up by nanometer-thick ferroelectric film placed between metal electrodes.[6] The thickness of the ferroelectric layer is small enough to allow tunneling of electrons. The piezoelectric and interface effects as well as the depolarization field may lead to a giant electroresistance (GER) switching effect.
Yet another hot topic is multiferroics, where researchers are looking for ways to couple magnetic and ferroelectric ordering within a material or heterostructure; there are several recent reviews on this topic.[7]
Materials
The internal electric dipoles of a ferroelectric material are coupled to the material lattice so anything that changes the lattice will change the strength of the dipoles (in other words, a change in the spontaneous polarization). The change in the spontaneous polarization results in a change in the surface charge. This can cause current flow in the case of a ferroelectric capacitor even without the presence of an external voltage across the capacitor. Two stimuli that will change the lattice dimensions of a material are force and temperature. The generation of a surface charge in response to the application of an external stress to a material is called piezoelectricity. A change in the spontaneous polarization of a material in response to a change in temperature is called pyroelectricity.
Ferroelectric phase transitions are often characterized as either displacive (such as BaTiO3) or order-disorder (such as NaNO2), though often phase transitions will demonstrate elements of both behaviors. In barium titanate, a typical ferroelectric of the displacive type, the transition can be understood in terms of a polarization catastrophe, in which, if an ion is displaced from equilibrium slightly, the force from the local electric fields due to the ions in the crystal increases faster than the elastic-restoring forces. This leads to an asymmetrical shift in the equilibrium ion positions and hence to a permanent dipole moment. The ionic displacement in barium titanate concerns the relative position of the titanium ion within the oxygen octahedral cage. In lead titanate, another key ferroelectric material, although the structure is rather similar to barium titanate the driving force for ferroelectricity is more complex with interactions between the lead and oxygen ions also playing an important role. In an order-disorder ferroelectric, there is a dipole moment in each unit cell, but at high temperatures they are pointing in random directions. Upon lowering the temperature and going through the phase transition, the dipoles order, all pointing in the same direction within a domain.
An important ferroelectric material for applications is lead zirconate titanate (PZT), which is part of the solid solution formed between ferroelectric lead titanate and anti-ferroelectric lead zirconate. Different compositions are used for different applications; for memory applications, PZT closer in composition to lead titanate is preferred, whereas piezoelectric applications make use of the diverging piezoelectric coefficients associated with the morphotropic phase boundary that is found close to the 50/50 composition.
Ferroelectric crystals often show several transition temperatures and domain structure hysteresis, much as do ferromagnetic crystals. The nature of the phase transition in some ferroelectric crystals is still not well understood.
In 1974 R.B. Meyer used symmetry arguments to predict ferroelectric liquid crystals[8], and the prediction could immediately be verified by several observations of behavior connected to ferroelectricity in smectic liquid-crystal phases that are chiral and tilted. The technology allows the building of flat-screen monitors. Mass production began in 1994 by Canon. However, the costs were too high, and the production was shut down 1999 (or before) after big losses.
In 2010 David Field found that prosaic films of chemicals such as nitrous oxide or propane exhibited ferroelectric properties. This new class of ferroelectric materials may have wide ranging applications in device and nano-technology and also influence the electrical nature of dust in the interstellar medium.
Theory
Based on Ginzburg–Landau theory, the free energy of a ferroelectric material, in the absence of an electric field and applied stress may be written as a Taylor expansion in terms of the order parameter, P. If a sixth order expansion is used (i.e. 8th order and higher terms truncated), the free energy is given by:
where Px, Py, and Pz are the components of the polarization vector in the x, y, and z directions respectively, and the coefficients, 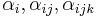 must be consistent with the crystal symmetry. To investigate domain formation and other phenomena in ferroelectrics, these equations are often used in the context of a phase field model. Typically, this involves adding a gradient term, an electrostatic term and an elastic term to the free energy. The equations are then discretized onto a grid using the finite difference method and solved subject to the constraints of Gauss's law and Linear elasticity.
must be consistent with the crystal symmetry. To investigate domain formation and other phenomena in ferroelectrics, these equations are often used in the context of a phase field model. Typically, this involves adding a gradient term, an electrostatic term and an elastic term to the free energy. The equations are then discretized onto a grid using the finite difference method and solved subject to the constraints of Gauss's law and Linear elasticity.
In all known ferroelectrics, 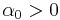 and
and 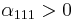 . These coefficients may be obtained experimentally or from ab-initio simulations. For ferroelectrics with a first order phase transition,
. These coefficients may be obtained experimentally or from ab-initio simulations. For ferroelectrics with a first order phase transition, 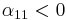 and
and 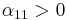 for a second order phase transition.
for a second order phase transition.
The spontaneous polarization, Ps of a ferroelectric for a cubic to tetragonal phase transition may be obtained by considering the 1D expression of the free energy which is:
This free energy has the shape of a double well potential with two free energy minima at 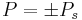 , where Ps is the spontaneous polarization. At these two minima, the derivative of the free energy is zero, i.e.:
, where Ps is the spontaneous polarization. At these two minima, the derivative of the free energy is zero, i.e.:
Since Px = 0 corresponds to a free energy maxima in the ferroelectric phase, the spontaneous polarization, Ps, is obtained from the solution of the equation:
which is:
and elimination of solutions yielding a negative square root (for either the first or second order phase transitions) gives:
If 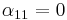 , using the same approach as above, the spontaneous polarization may be obtained as:
, using the same approach as above, the spontaneous polarization may be obtained as:
The hysteresis loop (Px versus Ex) may be obtained from the free energy expansion by adding an additional electrostatic term, Ex Px, as follows:
Plotting Ex as a function of Px and reflecting the graph about the 45 degree line gives an 'S' shaped curve. The central part of the 'S' corresponds to a free energy local maximum (since 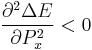 ). Elimination of this region, and connection of the top and bottom portions of the 'S' curve by vertical lines at the discontinuities gives the hysteresis loop.
). Elimination of this region, and connection of the top and bottom portions of the 'S' curve by vertical lines at the discontinuities gives the hysteresis loop.
See also
|
Physics |
Lists |
References
- ^ Werner Känzig (1957). "Ferroelectrics and Antiferroelectrics". In Frederick Seitz, T. P. Das, David Turnbull, E. L. Hahn. Solid State Physics. 4. Academic Press. p. 5. ISBN 0126077045. http://books.google.com/?id=7yFWuc_YL3UC&pg=PA5&dq=ferroelectricity.
- ^ M. Lines & A. Glass (1979). Principles and applications of ferroelectrics and related materials. Clarendon Press, Oxford. ISBN 0198512864.
- ^ See J. Valasek (1920). "Piezoelectric and allied phenomena in Rochelle salt". Physical Review 15: 537. and J. Valasek (1921). "Piezo-Electric and Allied Phenomena in Rochelle Salt". Physical Review 17 (4): 475. Bibcode 1921PhRv...17..475V. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.17.475.
- ^ J.F. Scott (2000). Ferroelectric Memories. Springer. ISBN 3540663878.
- ^ M. Dawber, K.M. Rabe, J.F. Scott (2005). "Physics of thin-film ferroelectric oxides". Reviews of Modern Physics 77 (4): 1083. arXiv:cond-mat/0503372. Bibcode 2005RvMP...77.1083D. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.77.1083.
- ^ M.Ye. Zhuravlev, R.F. Sabirianov, S.S. Jaswal, E.Y. Tsymbal (2005). "Giant Electroresistance in Ferroelectric Tunnel Junctions". Physical Review Letters 94 (24): 246802–4. arXiv:cond-mat/0502109. Bibcode 2005PhRvL..94x6802Z. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.94.246802.
- ^ R. Ramesh, N.A Spaldin (2007). "Multiferroics: Progress and prospects in thin films". Nature Materials 6 (1): 21. Bibcode 2007NatMa...6...21R. doi:10.1038/nmat1805.W. Eerenstein, N.D. Mathur, J.F. Scott (2006). "Multiferroic and magnetoelectric materials". Nature 442 (7104): 759. Bibcode 2006Natur.442..759E. doi:10.1038/nature05023., N.A. Spaldin, M. Fiebig (2005). Science 309: 391–2. doi:10.1126/science.1113357. M. Fiebig (2005). Journal of Physics D -Applied Physics 38: R123.
- ^ Noel A. Clark, Sven Torbjörn Lagerwall (1980). "Submicrosecond Bistable Electro-Optic Switching in Liquid Crystals". Applied Physics Letters 36 (11): 899. Bibcode 1980ApPhL..36..899C. doi:10.1063/1.91359.
Further reading
- A. S. Sidorkin (2006). Domain Structure in Ferroelectrics and Related Materials. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 1904602142.
- Karin M Rabe, Jean-Marc Triscone, Charles H Ahn (2007). Physics of Ferroelectrics: A modern perspective. Springer. ISBN 3540345914.
- Julio A. Gonzalo (2006). Effective Field Approach to Phase Transitions and Some Applications to Ferroelectrics. World Scientific. ISBN 9812568751.
External links
|
|
|||||
![\begin{array} {ll}
\Delta E= & \frac{1}{2}\alpha_0\left(T-T_0\right)\left(P_x^2%2BP_y^2%2BP_z^2\right)%2B
\frac{1}{4}\alpha_{11}\left(P_x^4%2BP_y^4%2BP_z^4\right)\\
& %2B\frac{1}{2}\alpha_{12}\left(P_x^2 P_y^2%2BP_y^2 P_z^2%2BP_z^2P_x^2\right)\\
& %2B\frac{1}{6}\alpha_{111}\left(P_x^6%2BP_y^6%2BP_z^6\right)\\
& %2B\frac{1}{2}\alpha_{112}\left[P_x^4\left(P_y^2%2BP_z^2\right)
%2BP_y^4\left(P_x^2%2BP_z^2\right)%2BP_z^4\left(P_x^2%2BP_y^2\right)\right]\\
& %2B\frac{1}{2}\alpha_{123}P_x^2P_y^2P_z^2
\end{array}](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/378616b66face7926c2a4677a4b9c070.png)
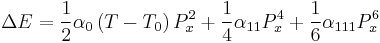
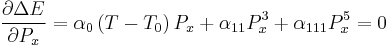
![P_x \left[ \alpha_0\left(T-T_0\right)%2B\alpha_{11}P_x^2%2B\alpha_{111}P_x^4\right]=0](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/7aff57cef7abc1c57e4fc2687a034a3c.png)
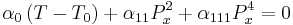
![P_s^2=\frac{1}{2\alpha_{111}}\left[-\alpha_{11}\pm\sqrt{\alpha_{11}^2-4\alpha_0\alpha_{111}\left(T-T_0\right)}\right]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/21a40a2c58bc7a1690b3d22bcb49cf93.png)
![P_s=\sqrt{\frac{1}{2\alpha_{111}}\left[-\alpha_{11}%2B\sqrt{\alpha_{11}^2-4\alpha_0\alpha_{111}\left(T-T_0\right)}\right]}](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/0eae5d6d9f9bbf53fbcfae60c776ff38.png)