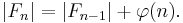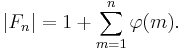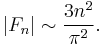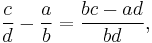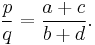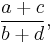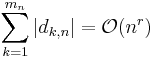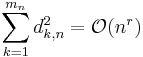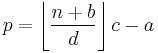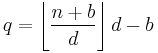Farey sequence
In mathematics, the Farey sequence of order n is the sequence of completely reduced fractions between 0 and 1 which, when in lowest terms, have denominators less than or equal to n, arranged in order of increasing size.
Each Farey sequence starts with the value 0, denoted by the fraction 0⁄1, and ends with the value 1, denoted by the fraction 1⁄1 (although some authors omit these terms).
A Farey sequence is sometimes called a Farey series, which is not strictly correct, because the terms are not summed.
Contents |
Examples
The Farey sequences of orders 1 to 8 are :
- F1 = {0⁄1, 1⁄1}
- F2 = {0⁄1, 1⁄2, 1⁄1}
- F3 = {0⁄1, 1⁄3, 1⁄2, 2⁄3, 1⁄1}
- F4 = {0⁄1, 1⁄4, 1⁄3, 1⁄2, 2⁄3, 3⁄4, 1⁄1}
- F5 = {0⁄1, 1⁄5, 1⁄4, 1⁄3, 2⁄5, 1⁄2, 3⁄5, 2⁄3, 3⁄4, 4⁄5, 1⁄1}
- F6 = {0⁄1, 1⁄6, 1⁄5, 1⁄4, 1⁄3, 2⁄5, 1⁄2, 3⁄5, 2⁄3, 3⁄4, 4⁄5, 5⁄6, 1⁄1}
- F7 = {0⁄1, 1⁄7, 1⁄6, 1⁄5, 1⁄4, 2⁄7, 1⁄3, 2⁄5, 3⁄7, 1⁄2, 4⁄7, 3⁄5, 2⁄3, 5⁄7, 3⁄4, 4⁄5, 5⁄6, 6⁄7, 1⁄1}
- F8 = {0⁄1, 1⁄8, 1⁄7, 1⁄6, 1⁄5, 1⁄4, 2⁄7, 1⁄3, 3⁄8, 2⁄5, 3⁄7, 1⁄2, 4⁄7, 3⁄5, 5⁄8, 2⁄3, 5⁄7, 3⁄4, 4⁄5, 5⁄6, 6⁄7, 7⁄8, 1⁄1}
History
- The history of 'Farey series' is very curious — Hardy & Wright (1979) Chapter III[1]
- ... once again the man whose name was given to a mathematical relation was not the original discoverer so far as the records go. — Beiler (1964) Chapter XVI[2]
Farey sequences are named after the British geologist John Farey, Sr., whose letter about these sequences was published in the Philosophical Magazine in 1816. Farey conjectured, without offering proof, that each new term in a Farey sequence expansion is the mediant of its neighbours. Farey's letter was read by Cauchy, who provided a proof in his Exercises de mathématique, and attributed this result to Farey. In fact, another mathematician, Charles Haros, had published similar results in 1802 which were not known either to Farey or to Cauchy.[2] Thus it was a historical accident that linked Farey's name with these sequences.
Properties
Sequence length
The Farey sequence of order n contains all of the members of the Farey sequences of lower orders. In particular Fn contains all of the members of Fn−1, and also contains an additional fraction for each number that is less than n and coprime to n. Thus F6 consists of F5 together with the fractions 1⁄6 and 5⁄6. The middle term of a Farey sequence Fn is always 1⁄2, for n > 1.
From this, we can relate the lengths of Fn and Fn−1 using Euler's totient function φ(n) :
Using the fact that |F1| = 2, we can derive an expression for the length of Fn :
The asymptotic behaviour of |Fn| is :
Farey neighbours
Fractions which are neighbouring terms in any Farey sequence are known as a Farey pair and have the following properties.
If a⁄b and c⁄d are neighbours in a Farey sequence, with a⁄b < c⁄d, then their difference c⁄d − a⁄b is equal to 1⁄bd. Since
this is equivalent to saying that
- bc − ad = 1.
Thus 1⁄3 and 2⁄5 are neighbours in F5, and their difference is 1⁄15.
The converse is also true. If
- bc − ad = 1
for positive integers a,b,c and d with a < b and c < d then a⁄b and c⁄d will be neighbours in the Farey sequence of order max(b,d).
If p⁄q has neighbours a⁄b and c⁄d in some Farey sequence, with
- a⁄b < p⁄q < c⁄d
then p⁄q is the mediant of a⁄b and c⁄d — in other words,
This follows easily from the previous property, since if bp-aq = qc-pd = 1, then bp+pd = qc+aq, p(b+d)=q(a+c), p/q = (a+c)/(b+d)
It follows that if a⁄b and c⁄d are neighbours in a Farey sequence then the first term that appears between them as the order of the Farey sequence is increased is
which first appears in the Farey sequence of order b + d.
Thus the first term to appear between 1⁄3 and 2⁄5 is 3⁄8, which appears in F8.
The Stern-Brocot tree is a data structure showing how the sequence is built up from 0 (= 0⁄1) and 1 (= 1⁄1), by taking successive mediants.
Fractions that appear as neighbours in a Farey sequence have closely related continued fraction expansions. Every fraction has two continued fraction expansions — in one the final term is 1; in the other the final term is greater than 1. If p⁄q, which first appears in Farey sequence Fq, has continued fraction expansions
- [0; a1, a2, …, an − 1, an, 1]
- [0; a1, a2, …, an − 1, an + 1]
then the nearest neighbour of p⁄q in Fq (which will be its neighbour with the larger denominator) has a continued fraction expansion
- [0; a1, a2, …, an]
and its other neighbour has a continued fraction expansion
- [0; a1, a2, …, an − 1]
Thus 3⁄8 has the two continued fraction expansions [0; 2, 1, 1, 1] and [0; 2, 1, 2], and its neighbours in F8 are 2⁄5, which can be expanded as [0; 2, 1, 1]; and 1⁄3, which can be expanded as [0; 2, 1].
Ford circles
There is an interesting connection between Farey sequence and Ford circles.
For every fraction p/q (in its lowest terms) there is a Ford circle C[p/q], which is the circle with radius 1/(2q2) and centre at (p/q, 1/(2q2)). Two Ford circles for different fractions are either disjoint or they are tangent to one another—two Ford circles never intersect. If 0 < p/q < 1 then the Ford circles that are tangent to C[p/q] are precisely the Ford circles for fractions that are neighbours of p/q in some Farey sequence.
Thus C[2/5] is tangent to C[1/2], C[1/3], C[3/7], C[3/8] etc.
Riemann hypothesis
Farey sequences are used in two equivalent formulations of the Riemann hypothesis. Suppose the terms of 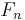 are
are 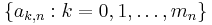 . Define
. Define 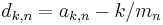 , in other words
, in other words 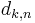 is the difference between the kth term of the nth Farey sequence, and the kth member of a set of the same number of points, distributed evenly on the unit interval. Franel and Landau proved that the two statements that
is the difference between the kth term of the nth Farey sequence, and the kth member of a set of the same number of points, distributed evenly on the unit interval. Franel and Landau proved that the two statements that
for any r > 1/2, and that
for any r > −1, are equivalent to the Riemann hypothesis.
Next term
A surprisingly simple algorithm exists to generate the terms in either traditional order (ascending) or non-traditional order (descending). The algorithm computes each successive entry in terms of the previous two entries using the mediant property given above. If a/b and c/d are the two given entries, and p/q is the unknown next entry, then c/d = (a + p)/(b + q). c/d is in lowest terms, so there is an integer k such that kc = a + p and kd = b + q, giving p = kc − a and q = kd − b. The value of k must give a value of p/q which is as close as possible to c/d, which implies that k must be as large as possible subject to kd − b ≤ n, so k is the greatest integer ≤ (n + b)/d. In other words, k = (n+b)/d, and
This is implemented in Python as:
def farey( n, asc=True ): """Python function to print the nth Farey sequence, either ascending or descending.""" if asc: a, b, c, d = 0, 1, 1 , n # (*) else: a, b, c, d = 1, 1, n-1 , n # (*) print "%d/%d" % (a,b) while (asc and c <= n) or (not asc and a > 0): k = int((n + b)/d) a, b, c, d = c, d, k*c - a, k*d - b print "%d/%d" % (a,b)
Brute-force searches for solutions to Diophantine equations in rationals can often take advantage of the Farey series (to search only reduced forms). The lines marked (*) can also be modified to include any two adjacent terms so as to generate terms only larger (or smaller) than a given term.[3]
References
- ^ Hardy, G.H. & Wright, E.M. (1979) An Introduction to the Theory of Numbers (Fifth Edition). Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-853171-0
- ^ a b Beiler, Albert H. (1964) Recreations in the Theory of Numbers (Second Edition). Dover. ISBN 0-486-21096-0. Cited in Farey Series, A Story at Cut-the-Knot
- ^ Norman Routledge, "Computing Farey Series," The Mathematical Gazette, Vol. 92 (No. 523), 55–62 (March 2008).
Further reading
- Ronald L. Graham, Donald E. Knuth, and Oren Patashnik, Concrete Mathematics: A Foundation for Computer Science, 2nd Edition (Addison-Wesley, Boston, 1989); in particular, Sec. 4.5 (pp. 115–123), Bonus Problem 4.61 (pp. 150, 523–524), Sec. 4.9 (pp. 133–139), Sec. 9.3, Problem 9.3.6 (pp. 462–463). ISBN 0201558025.
- Linas Vepstas. The Minkowski Question Mark, GL(2,Z), and the Modular Group. http://linas.org/math/chap-minkowski.pdf reviews the isomorphisms of the Stern-Brocot Tree.
- Linas Vepstas. Symmetries of Period-Doubling Maps. http://linas.org/math/chap-takagi.pdf reviews connections between Farey Fractions and Fractals.
- Scott B. Guthery, A Motif of Mathematics: History and Application of the Mediant and the Farey Sequence, (Docent Press, Boston, 2010). ISBN 1453810579.
External links
- Alexander Bogomolny. Farey series and Stern-Brocot Tree at Cut-the-Knot
- Weisstein, Eric W., "Stern-Brocot Tree" from MathWorld.
- Farey Sequence from The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences.