Encephalization
|
Encephalization is defined as the amount of brain mass exceeding that related to an animal's total body mass. Quantifying an animal's encephalization has been argued to be directly related to that animal's level of intelligence. Aristotle wrote in 335 B.C. "Of all the animals, man has the brain largest in proportion to his size."[1] Also, in 1871, Charles Darwin wrote in his book The Descent of Man: "No one, I presume, doubts that the large proportion which the size of man's brain bears to his body, compared to the same proportion in the gorilla or orang, is closely connected with his mental powers."[2]
In 2004, Dennis Bramble and Daniel Lieberman proposed that early Homo were scavengers that used stone tools to harvest meat off carcasses and to open bones. They proposed that humans specialized in long-distance running to compete with other scavengers in reaching carcasses.[3] It has been suggested that such an adaptation ensured a food supply that made large brains possible.
More encephalized species tend to have longer spinal shock duration.
Encephalization may also refer to the tendency for a species toward larger brains through evolutionary time. Anthropological studies indicate that bipedalism preceded encephalization in the human evolutionary lineage after divergence from the chimpanzee lineage. Compared to the chimpanzee brain, the human brain is larger and certain brain regions have been particularly altered during human evolution.[4] Most brain growth of chimpanzees happens before birth while most human brain growth happens after birth.[5]
Encephalization quotient
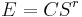
In Snell's equation of simple allometry[6] "E" is the weight of the brain, "C" is the cephalization factor and "S" is body weight and "r" is the exponential constant. The exponential constant for primates is 0.28[6] and either 0.56 or 0.66 for mammals in general.[7]
The "Encephalization Quotient" (EQ) is the ratio of "C" over the expected value for "C" of an animal of given weight "S".[7]
| Species | EQ[7] | Species | EQ[7] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Human | 7.44 | Cat | 1.00 |
| Dolphin | 5.31 | Horse | 0.86 |
| Chimpanzee | 2.49 | Sheep | 0.81 |
| Rhesus Monkey | 2.09 | Mouse | 0.50 |
| Elephant | 1.87 | Rat | 0.40 |
| Whale | 1.76 | Rabbit | 0.40 |
| Dog | 1.17 |
See also
References
- ^ Russell, Stuart and Norvig, Peter (2003), Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, Upper Saddle River, N.J.: Prentice Hall/Pearson Education, ISBN 0-13-790395-2
- ^ Darwin, Charles (1981 reprint of 1871 edition), The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex, Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press, p. 145, ISBN 0-691-02369-7 See also quote, p.60, in online text of earlier reprint of second (1874) edition.
- ^ Bramble DM, Lieberman DE (November 2004), "Endurance running and the evolution of Homo" (PDF), Nature 432 (7015): 345–52, doi:10.1038/nature03052, PMID 15549097, http://www.clas.ufl.edu/users/krigbaum/proseminar/Bramble_Leib_2004_nature.pdf.
- ^ See Figures 1 and 2 of Bradbury J (March 2005), "Molecular insights into human brain evolution", PLoS Biol. 3 (3): e50, doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0030050, PMC 1065704, PMID 15760271, http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1065704.
- ^ see: Heterochrony
- ^ a b Williams, M.F. (April 2002), "Primate encephalization and intelligence", Medical Hypotheses 58 (4): 284–290, doi:10.1054/mehy.2001.1516, PMID 12027521, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6WN2-45WYMG6-9&_coverDate=04%2F30%2F2002&_alid=345187568&_rdoc=1&_fmt=&_orig=search&_qd=1&_cdi=6950&_sort=d&view=c&_acct=C000050221&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=10&md5=cb9acecb46bd950701b34eb5bb5e94ee
- ^ a b c d Serendip. Thinking about brain size. Retrieved May 21, 2011, http://serendip.brynmawr.edu/bb/kinser/Int3.html
Further reading
- Allman, John Morgan (1999), Evolving Brains, New York: Scientific American Library, ISBN 0-7167-5076-7
- Foley, R.A; Lee, P.C; Widdowson, E. M.; Knight, C. D.; Jonxis, J. H. P. (1991), "Ecology and energies of encephalization in hominid evolution", Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 334: 223–232, doi:10.1098/rstb.1991.0111
- Jerison H.J. (1976), "Paleoneurology and the evolution of the mind", Scientific American 234 (1): 90–101, doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0176-90.
- Ann E. Russon & David R. Begun, ed. (2004), The Evolution of Thought: Evolutionary Origins of Great Ape Intelligence, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-78335-6, http://books.google.com/?id=e9RgrV7QnhEC&printsec=frontcover&dq=Russon+2004+%22evolution+of+thought%22&cd=2#v=onepage&q&f=false
- Tobias P.V. (1971), The Brain in Hominid Evolution, New York and London: Columbia University Press, ISBN 0231035187
- Carel van Schaik (April 2006), "Why Are Some Animals So Smart?", Scientific American 294 (4): 64–71, doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0406-64, PMID 16596881, http://www.sciam.com/article.cfm?chanID=sa006&articleID=000C1E5D-B9BA-1422-B9BA83414B7F0103 (Also cited in various publications as volume 16, issue 2, pp. 30–37. For example)