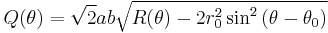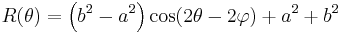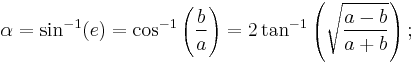Ellipse
In geometry, an ellipse (from Greek ἔλλειψις elleipsis, a "falling short") is a plane curve that results from the intersection of a cone by a plane in a way that produces a closed curve. Circles are special cases of ellipses, obtained when the cutting plane is orthogonal to the cone's axis. An ellipse is also the locus of all points of the plane whose distances to two fixed points add to the same constant.
Ellipses are closed curves and are the bounded case of the conic sections, the curves that result from the intersection of a circular cone and a plane that does not pass through its apex; the other two (open and unbounded) cases are parabolas and hyperbolas. Ellipses arise from the intersection of a right circular cylinder with a plane that is not parallel to the cylinder's main axis of symmetry. Ellipses also arise as images of a circle under parallel projection and the bounded cases of perspective projection, which are simply intersections of the projective cone with the plane of projection. It is also the simplest Lissajous figure, formed when the horizontal and vertical motions are sinusoids with the same frequency.
Elements of an ellipse
An ellipse is a smooth closed curve which is symmetric about its horizontal and vertical axes. The distance between antipodal points on the ellipse, or pairs of points whose midpoint is at the center of the ellipse, is maximum along the major axis or transverse diameter, and a minimum along the perpendicular minor axis or conjugate diameter.[1]
The semi-major axis (denoted by a in the figure) and the semi-minor axis (denoted by b in the figure) are one half of the major and minor axes, respectively. These are sometimes called (especially in technical fields) the major and minor semi-axes,[2][3] the major and minor semiaxes,[4][5] or major radius and minor radius.[6][7][8][9]
The foci of the ellipse are two special points F1 and F2 on the ellipse's major axis and are equidistant from the center point. The sum of the distances from any point P on the ellipse to those two foci is constant and equal to the major axis ( PF1 + PF2 = 2a ). Each of these two points is called a focus of the ellipse.
Refer to the lower Directrix section of this article for a second equivalent construction of an ellipse.
The eccentricity of an ellipse, usually denoted by ε or e, is the ratio of the distance between the two foci, to the length of the major axis or e = 2f/2a = f/a. For an ellipse the eccentricity is between 0 and 1 (0<e<1). When the eccentricity is 0 the foci coincide with the center point and the figure is a circle. As the eccentricity tends toward 1, the ellipse gets a more elongated shape. It tends towards a line segment (see below) if the two foci remain a finite distance apart and a parabola if one focus is kept fixed as the other is allowed to move arbitrarily far away.
The distance ae from a focal point to the centre is called the linear eccentricity of the ellipse (f = ae).
Drawing ellipses
Pins-and-string method
An ellipse can be drawn using two drawing pins, a length of string, and a pencil:
- Push the pins into the paper at two points, which will become the ellipse's foci. Tie the string into a loose loop around the two pins. Pull the loop taut with the pen's tip, so as to form a triangle. Move the pen around, while keeping the string taut, and its tip will trace out an ellipse. Using two pegs and a rope, this procedure is traditionally used by gardeners to outline an elliptical flower bed; thus it is called the gardener's ellipse.
If the ellipse is to be inscribed within a specified rectangle,[diagram needed] tangent to its four sides at their midpoints, one must first determine the position of the foci and the length of the string loop:
- Let A,B,C,D be the corners of the rectangle, in clockwise order, with A-B being one of the long sides. Draw a circle centered on A, whose radius is the short side A-D. From corner B draw a tangent to the circle. The length L of this tangent is the distance between the foci. This length L can be calculated with the Pythagorean theorem. As the tangent is at a right angles to the radius at the intersect of the tangent with the circle L equals square root ((A-B)squared - (A-D)squared) i.e. square root of the long side of the rectangle squared minus short side squared. Draw a horizontal line through the center of the rectangle. This will be the major axis of the ellipse. Place the foci on the major axis, at distance L/2 from the center.
To adjust the length of the string loop, insert a pin at one focus, and the second pin at the opposite side of the rectangle on the major axis. Loop the string around the two pins and tie it taut. Move the second pin to the other focus. Then draw the ellipse as above; it should fit snugly in the original rectangle. Unfortunately strings tend to be elastic so if you push harder on the pencil stretching the string more you will get a bigger ellipse, pushing less it will be smaller. It may take a few tries to push just hard enough to make the ellipse fit the rectangle. The string method was developed by James Clerk Maxwell, the discoverer of the electromagnetic nature of light, at age 12.
Other methods
An ellipse can also be drawn using a ruler, a set square, and a pencil:
- Draw two perpendicular lines M,N on the paper; these will be the major and minor axes of the ellipse. Mark three points A, B, C on the ruler. A->C being the length of the major axis and B->C the length of the minor axis. With one hand, move the ruler on the paper, turning and sliding it so as to keep point A always on line N, and B on line M. With the other hand, keep the pencil's tip on the paper, following point C of the ruler. The tip will trace out an ellipse.
The trammel of Archimedes or ellipsograph is a mechanical device that implements this principle. The ruler is replaced by a rod with a pencil holder (point C) at one end, and two adjustable side pins (points A and B) that slide into two perpendicular slots cut into a metal plate.[10] The mechanism can be used with a router to cut ellipses from board material. The mechanism is also used in a toy called the "nothing grinder".
Approximations to ellipses
An ellipse of low eccentricity can be represented reasonably accurately by a circle with its centre offset. With the exception of Mercury, all the planets have an orbit whose minor axis differs from the major axis by less than half of one percent. To draw the orbit with a pair of compasses the centre of the circle should be offset from the focus by an amount equal to the eccentricity multiplied by the radius.
Mathematical definitions and properties
In Euclidean geometry
Definition
In Euclidean geometry, an ellipse is usually defined as the bounded case of a conic section, or as the set of points such that the sum of the distances to two fixed points is constant. The equivalence of these two definitions can be proved using the Dandelin spheres.
Equations
The equation of an ellipse whose major and minor axes coincide with the Cartesian axes is 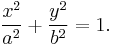
Focus
The distance from the center C to either focus is f = ae, which can be expressed in terms of the major and minor radii:
Eccentricity
The eccentricity of the ellipse (commonly denoted as either e or 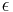 ) is
) is
(where again a and b are one-half of the ellipse's major and minor axes respectively, and f is the focal distance) or, as expressed in terms using the flattening factor 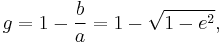
Directrix
Each focus F of the ellipse is associated with a line parallel to the minor axis called a directrix. Refer to the illustration on the right. The distance from any point P on the ellipse to the focus F is a constant fraction of that point's perpendicular distance to the directrix resulting in the equality, e=PF/PD. The ratio of these two distances is the eccentricity of the ellipse. This property (which can be proved using the Dandelin spheres) can be taken as another definition of the ellipse.
Besides the well known ratio e=f/a, it is also true that e=a/d.
Circular directrix
The ellipse can also be defined as the set of points that are equidistant from one focus and a particular circle, the directrix circle, that is centered on the other focus. The radius of the directrix circle is greater than the distance between the center of this circle and the focus; thus, the focus is inside the directrix circle, as is the entire ellipse.
Ellipse as hypotrochoid
The ellipse is a special case of the hypotrochoid when R = 2r.
Area
The area enclosed by an ellipse is πab, where (as before) a and b are one-half of the ellipse's major and minor axes respectively.
If the ellipse is given by the implicit equation 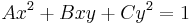 , then the area is
, then the area is 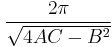 .
.
Circumference
The circumference 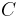 of an ellipse is:
of an ellipse is:
where again e is the eccentricity and where the function 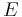 is the complete elliptic integral of the second kind.
is the complete elliptic integral of the second kind.
The exact infinite series is:
or
For computational purposes a much faster series where the denominators vanish at a rate 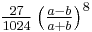 is given by:[11]
is given by:[11]
A good approximation is Ramanujan's:
and a better approximation is
For the special case where the minor axis is half the major axis, these become:
or, as an estimate of the better approximation,
The most accurate single-line formula is a modification of Ramanujan's approximation:[12]
![C\approx\pi (a%2Bb)\left[ 1%2B\frac{3h}{10%2B\sqrt{4-3h}}%2B\frac{{{h}^{6.67}}}{2376%2B7968\left( 1-h \right)}%2B\left( \frac{4}{\pi }-\frac{275}{216} \right){{h}^{43}} \right]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/970b3717599ed8487122debb8a5d39fd.png)
where 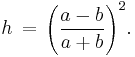
More generally, the arc length of a portion of the circumference, as a function of the angle subtended, is given by an incomplete elliptic integral.
The inverse function, the angle subtended as a function of the arc length, is given by the elliptic functions.
Chords
The midpoints of a set of parallel chords of an ellipse are collinear.[13]:p.147
In projective geometry
In projective geometry, an ellipse can be defined as the set of all points of intersection between corresponding lines of two pencils of lines which are related by a projective map. By projective duality, an ellipse can be defined also as the envelope of all lines that connect corresponding points of two lines which are related by a projective map.
This definition also generates hyperbolae and parabolae. However, in projective geometry every conic section is equivalent to an ellipse. A parabola is an ellipse that is tangent to the line at infinity Ω, and the hyperbola is an ellipse that crosses Ω.
An ellipse is also the result of projecting a circle, sphere, or ellipse in three dimensions onto a plane, by parallel lines. It is also the result of conical (perspective) projection of any of those geometric objects from a point O onto a plane P, provided that the plane Q that goes through O and is parallel to P does not cut the object. The image of an ellipse by any affine map is an ellipse, and so is the image of an ellipse by any projective map M such that the line M−1(Ω) does not touch or cross the ellipse.
In analytic geometry
General ellipse
In analytic geometry, the ellipse is defined as the set of points 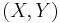 of the Cartesian plane that, in non-degenerate cases, satisfy the implicit equation[14][15]
of the Cartesian plane that, in non-degenerate cases, satisfy the implicit equation[14][15]
provided 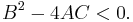
To distinguish the degenerate cases from the non-degenerate case, let ∆ be the determinant of the 3×3 matrix [A, B/2, D/2 ; B/2, C, E/2 ; D/2, E/2, F ]: that is, ∆ = (AC - B2/4)F + BED/4 - CD2/4 - AE2/4. Then the ellipse is a non-degenerate real ellipse if and only if C∆<0. If C∆>0 we have an imaginary ellipse, and if ∆=0 we have a point ellipse.[16]:p.63
Canonical form
Let 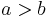 . By a proper choice of coordinate system, the ellipse can be described by the canonical implicit equation
. By a proper choice of coordinate system, the ellipse can be described by the canonical implicit equation
Here 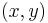 are the point coordinates in the canonical system, whose origin is the center
are the point coordinates in the canonical system, whose origin is the center 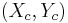 of the ellipse, whose
of the ellipse, whose  -axis is the unit vector
-axis is the unit vector 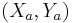 coinciding with the major axis, and whose
coinciding with the major axis, and whose 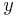 -axis is the perpendicular vector
-axis is the perpendicular vector 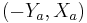 coinciding with the minor axis. That is,
coinciding with the minor axis. That is, 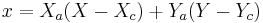 and
and 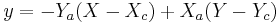 .
.
In this system, the center is the origin 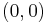 and the foci are
and the foci are 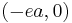 and
and 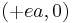 .
.
Any ellipse can be obtained by rotation and translation of a canonical ellipse with the proper semi-diameters. Translation of an ellipse centered at 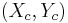 is expressed as
is expressed as
Moreover, any canonical ellipse can be obtained by scaling the unit circle of 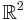 , defined by the equation
, defined by the equation
by factors a and b along the two axes.
For an ellipse in canonical form, we have
The distances from a point 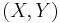 on the ellipse to the left and right foci are
on the ellipse to the left and right foci are 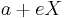 and
and 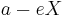 , respectively.
, respectively.
In trigonometry
General parametric form
An ellipse in general position can be expressed parametrically as the path of a point 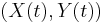 , where
, where
as the parameter t varies from 0 to 2π. Here 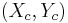 is the center of the ellipse, and
is the center of the ellipse, and 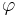 is the angle between the
is the angle between the  -axis and the major axis of the ellipse.
-axis and the major axis of the ellipse.
Parametric form in canonical position
For an ellipse in canonical position (center at origin, major axis along the X-axis), the equation simplifies to
Note that the parameter t (called the eccentric anomaly in astronomy) is not the angle of 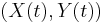 with the X-axis.
with the X-axis.
Formulae connecting a tangential angle  , the angle anchored at the ellipse's center
, the angle anchored at the ellipse's center 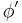 (called also the polar angle from the ellipse center), and the parametric angle t[17] are[18][19][20]:
(called also the polar angle from the ellipse center), and the parametric angle t[17] are[18][19][20]:
Polar form relative to center
In polar coordinates, with the origin at the center of the ellipse and with the angular coordinate 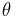 measured from the major axis, the ellipse's equation is
measured from the major axis, the ellipse's equation is
Polar form relative to focus
If instead we use polar coordinates with the origin at one focus, with the angular coordinate 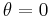 still measured from the major axis, the ellipse's equation is
still measured from the major axis, the ellipse's equation is
where the sign in the denominator is negative if the reference direction 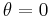 points towards the center (as illustrated on the right), and positive if that direction points away from the center.
points towards the center (as illustrated on the right), and positive if that direction points away from the center.
In the slightly more general case of an ellipse with one focus at the origin and the other focus at angular coordinate  , the polar form is
, the polar form is
The angle 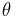 in these formulas is called the true anomaly of the point. The numerator
in these formulas is called the true anomaly of the point. The numerator 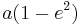 of these formulas is the semi-latus rectum of the ellipse, usually denoted
of these formulas is the semi-latus rectum of the ellipse, usually denoted 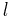 . It is the distance from a focus of the ellipse to the ellipse itself, measured along a line perpendicular to the major axis.
. It is the distance from a focus of the ellipse to the ellipse itself, measured along a line perpendicular to the major axis.
General polar form
The following equation on the polar coordinates (r, θ) describes a general ellipse with semidiameters a and b, centered at a point (r0, θ0), with the a axis rotated by φ relative to the polar axis:
where
Angular eccentricity
The angular eccentricity 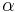 is the angle whose sine is the eccentricity e; that is,
is the angle whose sine is the eccentricity e; that is,
Degrees of freedom
An ellipse in the plane has five degrees of freedom (the same as a general conic section), defining its position, orientation, shape, and scale. In comparison, circles have only three degrees of freedom (position and scale), while parabolae have four. Said another way, the set of all ellipses in the plane, with any natural metric (such as the Hausdorff distance) is a five-dimensional manifold. These degrees can be identified with, for example, the coefficients A,B,C,D,E of the implicit equation, or with the coefficients Xc, Yc, φ, a, b of the general parametric form.
Ellipses in physics
Elliptical reflectors and acoustics
If the water's surface is disturbed at one focus of an elliptical water tank, the circular waves created by that disturbance, after being reflected by the walls, will converge simultaneously to a single point — the second focus. This is a consequence of the total travel length being the same along any wall-bouncing path between the two foci.
Similarly, if a light source is placed at one focus of an elliptic mirror, all light rays on the plane of the ellipse are reflected to the second focus. Since no other smooth curve has such a property, it can be used as an alternative definition of an ellipse. (In the special case of a circle with a source at its center all light would be reflected back to the center.) If the ellipse is rotated along its major axis to produce an ellipsoidal mirror (specifically, a prolate spheroid), this property will hold for all rays out of the source. Alternatively, a cylindrical mirror with elliptical cross-section can be used to focus light from a linear fluorescent lamp along a line of the paper; such mirrors are used in some document scanners.
Sound waves are reflected in a similar way, so in a large elliptical room a person standing at one focus can hear a person standing at the other focus remarkably well. The effect is even more evident under a vaulted roof shaped as a section of a prolate spheroid. Such a room is called a whisper chamber. The same effect can be demonstrated with two reflectors shaped like the end caps of such a spheroid, placed facing each other at the proper distance. Examples are the National Statuary Hall at the United States Capitol (where John Quincy Adams is said to have used this property for eavesdropping on political matters), at an exhibit on sound at the Museum of Science and Industry in Chicago, in front of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Foellinger Auditorium, and also at a side chamber of the Palace of Charles V, in the Alhambra.
Planetary orbits
In the 17th century, Johannes Kepler discovered that the orbits along which the planets travel around the Sun are ellipses with the Sun at one focus, in his first law of planetary motion. Later, Isaac Newton explained this as a corollary of his law of universal gravitation.
More generally, in the gravitational two-body problem, if the two bodies are bound to each other (i.e., the total energy is negative), their orbits are similar ellipses with the common barycenter being one of the foci of each ellipse. The other focus of either ellipse has no known physical significance. Interestingly, the orbit of either body in the reference frame of the other is also an ellipse, with the other body at one focus.
Keplerian elliptical orbits are the result of any radially directed attraction force whose strength is inversely proportional to the square of the distance. Thus, in principle, the motion of two oppositely charged particles in empty space would also be an ellipse. (However, this conclusion ignores losses due to electromagnetic radiation and quantum effects which become significant when the particles are moving at high speed.)
For elliptical orbits, useful relations involving the eccentricity, 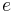 are:
are:
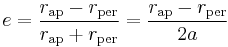
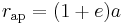
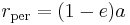
where:
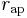 is radius at apoapsis (i.e., the farthest distance).
is radius at apoapsis (i.e., the farthest distance).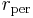 is radius at periapsis (the closest distance).
is radius at periapsis (the closest distance).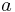 is the length of the semi-major axis.
is the length of the semi-major axis.
In addition, the semimajor axis 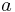 is the arithmetic mean of
is the arithmetic mean of 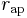 and
and 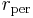 , or
, or 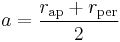 , and the semiminor axis
, and the semiminor axis 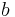 is the geometric mean of
is the geometric mean of 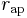 and
and 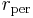 , or
, or 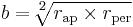 .
.
Also the semi-latus rectum (the distance from a focus to a point on the ellipse along a line parallel to the minor axis) is the harmonic mean of 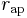 and
and 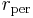 , or
, or 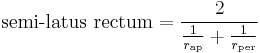 .
.
Harmonic oscillators
The general solution for a harmonic oscillator in two or more dimensions is also an ellipse. Such is the case, for instance, of a long pendulum that is free to move in two dimensions; of a mass attached to a fixed point by a perfectly elastic spring; or of any object that moves under influence of an attractive force that is directly proportional to its distance from a fixed attractor. Unlike Keplerian orbits, however, these "harmonic orbits" have the center of attraction at the geometric center of the ellipse, and have fairly simple equations of motion.
Phase visualization
In electronics, the relative phase of two sinusoidal signals can be compared by feeding them to the vertical and horizontal inputs of an oscilloscope. If the display is an ellipse, rather than a straight line, the two signals are out of phase.
Elliptical gears
Two non-circular gears with the same elliptical outline, each pivoting around one focus and positioned at the proper angle, will turn smoothly while maintaining contact at all times. Alternatively, they can be connected by a link chain or timing belt, or in the case of a bicycle the main chainring may be elliptical, or an ovoid similar to an ellipse in form. Such elliptical gears may be used in mechanical equipment to produce variable angular speed or torque from a constant rotation of the driving axle, or in the case of a bicycle to allow a varying crank rotation speed with inversely varying mechanical advantage.
Elliptical bicycle gears make it easier for the chain to slide off the cog when changing gears.[21]
An example gear application would be a device that winds thread onto a conical bobbin on a spinning machine. The bobbin would need to wind faster when the thread is near the apex than when it is near the base.[22]
Optics
In a material that is optically anisotropic (birefringent), the refractive index depends on the direction of the light. The dependency can be described by an index ellipsoid. (If the material is optically isotropic, this ellipsoid is a sphere.)
Ellipses in statistics and finance
In statistics, a random vector (X, Y) is jointly elliptically distributed if its iso-density contours — loci of equal values of the density function — are ellipses. The concept extends to an arbitrary number of elements of the random vector, in which case in general the iso-density contours are ellipsoids. A special case is the multivariate normal distribution. The elliptical distributions are important in finance because if rates of return on assets are jointly elliptically distributed then all portfolios can be characterized completely by their mean and variance — that is, any two portfolios with identical mean and variance of portfolio return have identical distributions of portfolio return.[23][24]
Ellipses in computer graphics
Drawing an ellipse as a graphics primitive is common in standard display libraries, such as the MacIntosh QuickDraw API, and Direct2D on Windows. Jack Bresenham at IBM is most famous for the invention of 2D drawing primitives, including line and circle drawing, using only fast integer operations such as addition and branch on carry bit. M. L. V. Pitteway extended Bresenham's algorithm for lines to conics in 1967.[25] Another efficient generalization to draw ellipses was invented in 1984 by Jerry Van Aken (IEEE CG&A, Sept. 1984).
In 1970 Danny Cohen presented at the "Computer Graphics 1970" conference in England a linear algorithm for drawing ellipses and circles. In 1971, L. B. Smith published similar algorithms for all conic sections and proved them to have good properties.[26] These algorithms need only a few multiplications and additions to calculate each vector.
It is beneficial to use a parametric formulation in computer graphics because the density of points is greatest where there is the most curvature. Thus, the change in slope between each successive point is small, reducing the apparent "jaggedness" of the approximation.
Drawing with Bezier spline paths
Multiple Bezier splines may also be used to draw an ellipse to sufficient accuracy, since any ellipse may be construed as an affine transformation of a circle. The spline methods used to draw a circle may be used to draw an ellipse, since the constituent Bezier curves will behave appropriately under such transformations.
Line segment as a type of degenerate ellipse
A line segment is a degenerate ellipse with semi-minor axis = 0 and eccentricity = 1, and with the focal points at the ends.[27] Although the eccentricity is 1 this is not a parabola. A radial elliptic trajectory is a non-trivial special case of an elliptic orbit, where the ellipse is a line segment.
Ellipses in Optimization Theory
It is sometimes useful to find the minimum bounding ellipse on a set of points. The Ellipsoid method is quite useful for attacking this problem
See also
- Apollonius of Perga, the classical authority
- Cartesian oval, a generalization of the ellipse
- Circumconic and inconic
- Conic section
- Ellipsoid, a higher dimensional analog of an ellipse
- Elliptic coordinates, an orthogonal coordinate system based on families of ellipses and hyperbolae
- Elliptical distribution, in statistics
- Elliptic partial differential equation
- Great ellipse
- Hyperbola
- Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion
- Matrix representation of conic sections
- n-ellipse, a generalization of the ellipse for n foci
- Oval
- Parabola
- Proofs involving the ellipse
- Spheroid, the ellipsoids obtained by rotating an ellipse about its major or minor axis.
- Superellipse, a generalization of an ellipse that can look more rectangular or more "pointy"
- True, eccentric, and mean anomaly
References
- Charles D. Miller, Margaret L. Lial, David I. Schneider: Fundamentals of College Algebra. 3rd Edition Scott Foresman/Little 1990. ISBN 0-673-38638-4, page 381
- Coxeter, H. S. M.: Introduction to Geometry. 2nd ed. New York: Wiley, pp. 115–119, 1969.
- Ellipse at the Encyclopedia of Mathematics (Springer)
- Ellipse at Planetmath
- Weisstein, Eric W., "Ellipse" from MathWorld.
Notes
- ^ Haswell, Charles Haynes (1920). Mechanics' and Engineers' Pocket-book of Tables, Rules, and Formulas. Harper & Brothers. http://books.google.com/books?id=Uk4wAAAAMAAJ&pg=RA1-PA381&zoom=3. Retrieved 2007-04-09.
- ^ John Herschel (1842) A Treatise on Astronomy, page 256
- ^ John Lankford (1996), History of Astronomy: An Encyclopedia, page 194
- ^ V. Prasolov and V. Tikhomirov (2001), Geometry, page 80
- ^ Donald Fenna (2006), Cartographic science: a compendium of map projections, with derivations, page 24
- ^ Autocad release 13: command reference, page 216
- ^ David Salomon (2006), Curves and surfaces for computer graphics, page 365
- ^ CRC Press (2004), The CRC handbook of mechanical engineering, page 11-8
- ^ The Mathematical Association of America (1976), The American Mathematical Monthly, vol. 83, page 207
- ^ H.T. Brown Five hundred and seven mechanical movements Brown & Brown (1881) pages 40-41 section 152 [1] from (from this Google book)
- ^ Cetin Hakimoglu-Brown iamned.com math page
- ^ Thomas Blankenhorn Online Ellipse Circumference Calculator
- ^ Chakerian, G. D. "A Distorted View of Geometry." Ch. 7 in Mathematical Plums (R. Honsberger, editor). Washington, DC: Mathematical Association of America, 1979.
- ^ Larson, Ron; Hostetler, Robert P.; Falvo, David C. (2006). Precalculus with Limits. Cengage Learning. p. 767. ISBN 0-618-66089-5. http://books.google.com/books?id=yMdHnyerji8C., Chapter 10, p. 767
- ^ Young, Cynthia Y. (2010). Precalculus. John Wiley and Sons. p. 831. ISBN 0-471-75684-9. http://books.google.com/books?id=9HRLAn326zEC., Chapter 9, p. 831
- ^ Lawrence, J. Dennis, A Catalog of Special Plane Curves, Dover Publ., 1972.
- ^ If the ellipse is illustrated as a meridional one for the earth, the tangential angle is equal to geodetic latitude, the angle
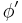 is the geocentric latitude, and parametric angle t is a parametric (or reduced) latitude of auxiliary circle
is the geocentric latitude, and parametric angle t is a parametric (or reduced) latitude of auxiliary circle - ^ Ellipse at MathWorld, derived from formula (58)
- ^ Auxiliary circle and various ellipse formulas
- ^ J. Meeus - Astronomical Algorithms, chap. 10 (The Earth's Globe), p. 78, Willmann-Bell, Inc, 1991
- ^ David Drew. "Elliptical Gears". [2]
- ^ G.B. Grant A Treatise on Gear Wheels Philadelphia Gear Works (1906) p. 72 Google books
- ^ Chamberlain, G. 1983."A characterization of the distributions that imply mean-variance utility functions", Journal of Economic Theory 29, 185-201.
- ^ Owen, J., and Rabinovitch, R. 1983. "On the class of elliptical distributions and their applications to the theory of portfolio choice", Journal of Finance 38, 745-752.
- ^ Pitteway, M.L.V., Algorithm for drawing ellipses or hyperbolae with a digital plotter, "Computer Journal, Vol 10 1967 pp282-289
- ^ Smith, L.B., Drawing ellipses, hyperbolae or parabolae with a fixed number of points, "Computer Journal, Volume 14, 1971, pp 81-86
- ^ [3]
External links
- Video: How to draw Ellipse
- Apollonius' Derivation of the Ellipse at Convergence
- Ellipse & Hyperbola Construction - Two interactive applets showing how to trace the curves of the ellipse and hyperbola. (Requires Java.)
- The Shape and History of The Ellipse in Washington, D.C. by Clark Kimberling
- Collection of animated ellipse demonstrations. Ellipse, axes, semi-axes, area, perimeter, tangent, foci.
- Weisstein, Eric W., "Ellipse as hypotrochoid" from MathWorld.
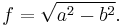
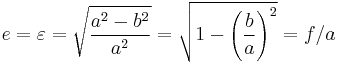
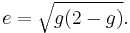
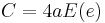
![C = 2\pi a \left[{1 - \left({1\over 2}\right)^2e^2 - \left({1\cdot 3\over 2\cdot 4}\right)^2{e^4\over 3} - \left({1\cdot 3\cdot 5\over 2\cdot 4\cdot 6}\right)^2{e^6\over5} - \cdots}\right]\,\!](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/4ccf6f26b9798ea144f1fe636a828924.png)
![C = 2\pi a \left[1 - \sum_{n=1}^\infty {e^{2n}\over 2n - 1} \prod_{m=1}^n \left({ 2m-1 \over 2m}\right)^2\right] \,\!](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/1a5c4de5c4f916cbee1cf9c1870e028c.png)
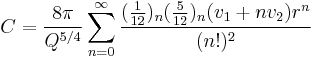
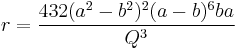
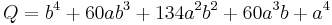
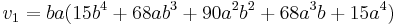
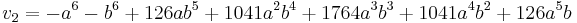
![C \approx \pi \left[3(a%2Bb) - \sqrt{(3a%2Bb)(a%2B3b)}\right]= \pi \left[3(a%2Bb)-\sqrt{10ab%2B3(a^2%2Bb^2)}\right]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/98fe993c7427f52b03ef3a53a9d0b331.png)
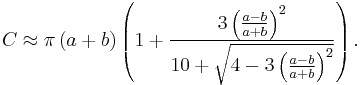
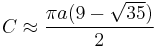
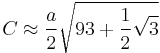
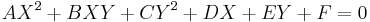
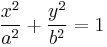
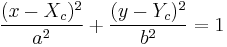
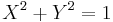
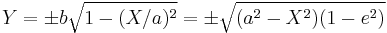
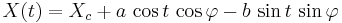
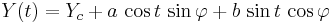
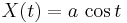
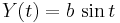
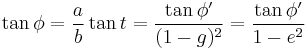
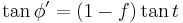
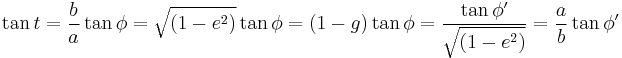
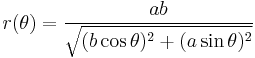
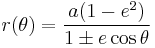
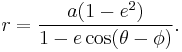
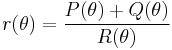
![P(\theta )=r_0 \left[\left(b^2-a^2\right) \cos \left(\theta %2B\theta _0-2 \varphi
\right)%2B\left(a^2%2Bb^2\right) \cos \left(\theta -\theta_0\right)\right]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/a86d2309f2c44d6c8a6e708fa177e3a1.png)