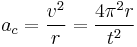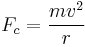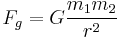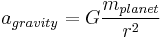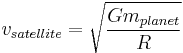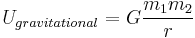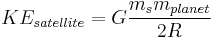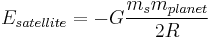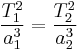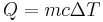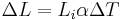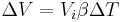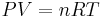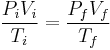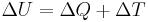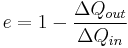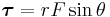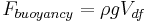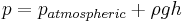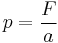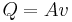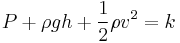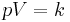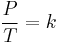Elementary physics formulae
A list of elementary physics formulae commonly appearing in high-school and college introductory physics courses. The list consists primarily of formulas concerning mechanics, showing relations between matter, energy, motion, and force in Euclidean space, under the action of Newtonian mechanics.
Contents |
Meanings of the symbols
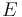 : energy
: energy
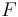 : force
: force
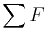 : net force
: net force
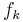 : kinetic friction force
: kinetic friction force
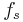 : static friction force
: static friction force
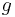 : acceleration due to gravity
: acceleration due to gravity
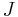 : Impulse
: Impulse
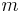 : mass
: mass
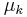 : coefficient of kinetic friction
: coefficient of kinetic friction
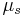 : coefficient of static friction
: coefficient of static friction
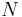 : Normal force to a surface
: Normal force to a surface
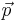 : Momentum
: Momentum
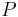 : Power
: Power
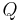 : heat or flowrate
: heat or flowrate
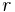 : radius
: radius
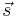 : Distance traveled
: Distance traveled
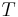 : Period, Temperature
: Period, Temperature
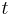 : time
: time
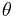 : Angle (see annotations next to each individual formula for details)
: Angle (see annotations next to each individual formula for details)
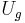 : gravitational potential energy
: gravitational potential energy
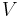 : volume
: volume
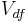 : volume of displaced fluid
: volume of displaced fluid
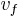 : initial velocity
: initial velocity
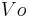 : final velocity
: final velocity
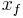 : final position
: final position
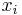 : initial position
: initial position
Dynamics
Like kinematics, dynamics deal with motion, but take into consideration force and mass.
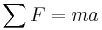 -- Newton's second law
-- Newton's second law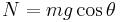 (
(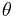 is the angle between the supporting surface and the vertical)
is the angle between the supporting surface and the vertical)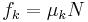 (object moving relative to surface)
(object moving relative to surface)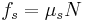 (object not moving relative to surface)
(object not moving relative to surface)
Work, energy and power
Work, energy, and power describes an objects ability to affect nature.
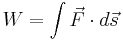 -- definition of mechanical work
-- definition of mechanical work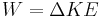
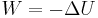
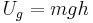
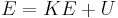
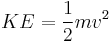
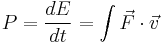
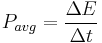
Simple Harmonic Motion
These are mechanics formulae that deal with simple harmonic motion.
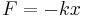 (
(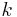 is the spring constant) -- Hooke's law
is the spring constant) -- Hooke's law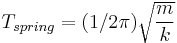
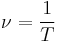
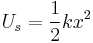 (
(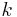 is the spring constant)
is the spring constant)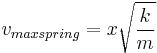
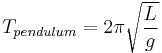 (for a simple pendulum)
(for a simple pendulum)
Momentum
Momentum is the amount of mass moving, in classical mechanics.
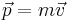 -- definition of momentum
-- definition of momentum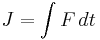 -- definition of impulse
-- definition of impulse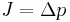
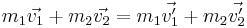 -- conservation of momentum
-- conservation of momentum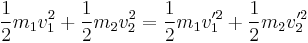 (Note: this is only true for elastic collisions)
(Note: this is only true for elastic collisions)
Uniform circular Motion and Gravitation
An object moving along a circular path at constant speed is in uniform circular motion. In this section, 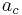 ,
, 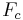 , et cetera, stand for centripetal acceleration and force, respectively.
, et cetera, stand for centripetal acceleration and force, respectively.
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics deal with the energy, motion, and entropy of microscopic particles.
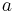 :
: 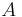 :
: 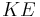 :
: 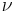 :
: