Dolev-Yao model
The Dolev-Yao model is a formal model used to prove properties of interactive protocols.
Contents |
The network
The network is represented by a set of abstract machines that can exchange messages. These messages consist of formal terms.
The adversary
The adversary in this model can overhear, intercept, and synthesise any message and is only limited by the constraints of the cryptographic methods used. In other words: "the attacker carries the message."
This omnipotence has been very difficult to model and many threat models simplify it, as, for example, the attacker in ubiquitous computing.
The algebraic model
Cryptographic primitives are modeled by abstract operators. For example, asymmetric encryption for a user  is represented by the encryption function
is represented by the encryption function 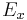 and the decryption function
and the decryption function 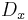 . Their main properties are that their composition is the identity function (
. Their main properties are that their composition is the identity function (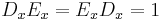 ) and that an encrypted message
) and that an encrypted message 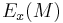 reveals nothing about
reveals nothing about  . Unlike in the real world, the adversary can neither manipulate the encryption's bit representation nor guess the key.
. Unlike in the real world, the adversary can neither manipulate the encryption's bit representation nor guess the key.
See also
References
- Dolev, D.; Yao, A. C. (1983), "On the security of public key protocols", IEEE trans. on Information Theory IT-29: 198–208, http://www.cs.huji.ac.il/~dolev/pubs/dolev-yao-ieee-01056650.pdf
- Backes, Michael; Pfitzmann, Birgit; Waidner, Michael (2006), "Soundness Limits of Dolev-Yao Models", Workshop on Formal and Computational Cryptography (FCC'06), affiliated with ICALP'06, http://www.infsec.cs.uni-saarland.de/~backes/papers/backes06soundness.html
- "Secure Transaction Protocol Analysis: Models and Applications", Lecture Notes in Computer Science / Programming and Software Engineering, 2008, http://books.google.com/books?id=IMIuV_tUYfMC&printsec=frontcover&dq=secure+transaction+protocol+analysis+models+applications&source=bl&ots=7iqJoLjEmJ&sig=8SSMmTl8djd4St90QW6zlYPzcDA&hl=en&ei=OPMNTavHIIrmvQP1qLXLDQ&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=3&ved=0CC8Q6AEwAg#v=onepage&q&f=false