Current ratio
The current ratio is a financial ratio that measures whether or not a firm has enough resources to pay its debts over the next 12 months. It compares a firm's current assets to its current liabilities. It is expressed as follows:
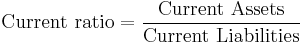
For example, if WXY Company's current assets are $50,000,000 and its current liabilities are $40,000,000, then its current ratio would be $50,000,000 divided by $40,000,000, which equals 1.25. It means that for every dollar the company owes in the short term it has $1.25 available in assets that can be converted to cash in the short term. A current ratio of assets to liabilities of 2:1 is usually considered to be acceptable (i.e., your current assets are twice your current liabilities).[1]
The current ratio is an indication of a firm's market liquidity and ability to meet creditor's demands. Acceptable current ratios vary from industry to industry. If a company's current ratio is in this range, then it is generally considered to have good short-term financial strength. If current liabilities exceed current assets (the current ratio is below 1), then the company may have problems meeting its short-term obligations. If the current ratio is too high, then the company may not be efficiently using its current assets or its short-term financing facilities. This may also indicate problems in working capital management.
Low values for the current or quick ratios (values less than 1) indicate that a firm may have difficulty meeting current obligations. Low values, however, do not indicate a critical problem. If an organization has good long-term prospects, it may be able to borrow against those prospects to meet current obligations. Some types of businesses usually operate with a current ratio less than one. For example, if inventory turns over much more rapidly than the accounts payable become due, then the current ratio will be less than one (this is true for McDonalds). This can allow a firm to operate with a low current ratio.
If all other things were equal, a creditor, who is expecting to be paid in the next 12 months, would consider a high current ratio to be better than a low current ratio, because a high current ratio means that the company is more likely to meet its liabilities which fall due in the next 12 months.