CAC 40
| CAC 40 | |
|---|---|
| Foundation | 1987 |
| Operator | Euronext |
| Exchanges | Euronext Paris |
| Constituents | 40 |
| Type | Large cap |
| Market cap | €1.031 trillion (end 2009)[1] |
| Weighting method |
Market value-weighted |
| Related indices |
CAC Next 20, CAC Mid 60, CAC Small |
| Website | www.nyse.com/cac40 |
The CAC 40 (French: CAC quarante [kak kaʁɑ̃t]) is a benchmark French stock market index. The index represents a capitalization-weighted measure of the 40 most significant values among the 100 highest market caps on the Paris Bourse (now Euronext Paris). It is one of the main national indices of the pan-European stock exchange group Euronext alongside Brussels' BEL20, Lisbon's PSI-20 and Amsterdam's AEX.
Contents |
History
The CAC 40 takes its name from the Paris Bourse's early automation system Cotation Assistée en Continu (Continuous Assisted Quotation). Its base value of 1,000 was set on 31 December 1987, equivalent to a market capitalisation of 370,437,433,957.70 French francs.[2] In common with many major world stock markets, its all-time high to date (6922.33 points) was reached at the peak of the dot-com bubble in September 2000.[3] In 1 December 2003, the index's weighting system switched from being dependent on total market capitalisation to free float market cap only, in line with other leading indices.[4]
Rules
Selection
The CAC 40 index composition is reviewed quarterly by an independent Index Steering Committee (French: Conseil Scientifique).[2] If any changes are made, they are effected a minimum of two weeks after the review meeting.[2] At each review date, the companies listed on Euronext Paris are ranked according to free float market capitalisation and share turnover over the prior 12 months.[5] From the top 100 companies in this ranking, forty are chosen to enter the CAC 40 such that it is "a relevant benchmark for portfolio management" and "a suitable underlying asset for derivatives products".[5] If a company has more than one class of shares traded on the exchange, only the most actively traded of these will be accepted into the index (generally this will be the ordinary share).[5]
Weighting
The CAC 40 is a market value-weighted index. The number of issued shares (used to calculate the market cap and hence the index weight) of a company is reviewed quarterly, on the third Friday of March, June, September and December.[2] Since December 2003, the index weightings of companies in the index have been capped at 15% at each quarterly index review,[5] but these range freely with share price subsequently. A capping factor is used to limit the weights to 15% (if necessary), and is reviewed annually by the Index Steering Committee on the third Friday of September.[5]
Calculation
The index value I of the CAC 40 index is calculated using the following formula:[5] 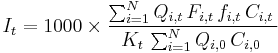 with t the day of calculation; N the number of constituent shares in the index (usually 40); Qi,t the number of shares of company i on day t; Fi,t the free float factor of share i; fi,t the capping factor of share i (exactly 1 for all companies not subject to the 15% cap); Ci,t the price of share i on day t; Qi,0 the number of shares of company i on the index base date; Ci,0 the price of equity i on the index base date; and Kt the "adjustment coefficient for base capitalization" on day t (reflecting the switch from the French franc to the Euro in 1999).
with t the day of calculation; N the number of constituent shares in the index (usually 40); Qi,t the number of shares of company i on day t; Fi,t the free float factor of share i; fi,t the capping factor of share i (exactly 1 for all companies not subject to the 15% cap); Ci,t the price of share i on day t; Qi,0 the number of shares of company i on the index base date; Ci,0 the price of equity i on the index base date; and Kt the "adjustment coefficient for base capitalization" on day t (reflecting the switch from the French franc to the Euro in 1999).
Holdings
Although the CAC 40 is almost exclusively composed of French-domiciled companies, about 45% of its listed shares are owned by foreign investors, more than any other main European index.[6] German, Japanese, American and British investors are amongst the most significant holders of CAC 40 shares. This large percentage is due to the fact that CAC 40 companies are more international, or multinational, than any other European market. CAC 40 companies conduct over two thirds of their business and employ over two thirds of their workforce outside France.[7]
Composition
The index consists of the following companies as of the quarterly update effective 19 December 2011 which saw Legrand replace Suez Environnement.[8]
| Company | ICB Sector | Ticker symbol | Index weighting (%) at 20 December 2011 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accor | hotels | AC | 0.49 |
| Air Liquide | commodity chemicals | AI | 4.64 |
| Alcatel-Lucent | telecommunications equipment | ALU | 0.47 |
| Alstom | industrial machinery | ALO | 0.83 |
| ArcelorMittal | steel | MT | 2.05 |
| AXA | full line insurance | CS | 3.21 |
| BNP Paribas | banks | BNP | 5.01 |
| Bouygues | heavy construction | EN | 0.80 |
| Capgemini | computer services | CAP | 0.65 |
| Carrefour | food retailers and wholesalers | CA | 1.75 |
| Crédit Agricole | banks | ACA | 0.74 |
| EADS | aerospace | EAD | 1.70 |
| EDF | electricity | EDF | 0.90 |
| Essilor | medical supplies | EI | 1.91 |
| France Télécom | fixed line telecommunications | FTE | 3.96 |
| GDF Suez | gas distribution | GSZ | 4.41 |
| Groupe Danone | food products | BN | 4.73 |
| L'Oréal | personal products | OR | 3.41 |
| Lafarge | building materials and fixtures | LG | 0.86 |
| Legrand | electrical components and equipment | LR | 0.94 |
| LVMH | clothing and accessories | MC | 4.84 |
| Michelin | tires | ML | 1.40 |
| Pernod Ricard | distillers and vintners | RI | 2.28 |
| PSA Peugeot Citroën | automobiles | UG | 0.33 |
| PPR | broadline retailers | PP | 1.47 |
| Publicis | media agencies | PUB | 0.83 |
| Renault | automobiles | RNO | 0.88 |
| Safran | aerospace | SAF | 0.90 |
| Saint-Gobain | building materials and fixtures | SGO | 1.99 |
| Sanofi | pharmaceuticals | SAN | 11.14 |
| Schneider Electric | electrical components and equipment | SU | 3.36 |
| Société Générale | banks | GLE | 1.98 |
| STMicroelectronics | semiconductors | STM | 0.48 |
| Technip | oil equipment and services | TEC | 1.22 |
| Total | integrated oil and gas | FP | 14.13 |
| Unibail-Rodamco | real estate investment trusts | UL | 2.14 |
| Vallourec | industrial machinery | VK | 0.79 |
| Veolia Environnement | water | VIE | 0.53 |
| Vinci | heavy construction | DG | 2.60 |
| Vivendi | broadcasting and entertainment | VIV | 3.27 |
See also
References
- ^ "CAC 40 Executive presentation". Euronext. http://www.euronext.com/fic/000/048/501/485014.pdf. Retrieved 2010-03-01.
- ^ a b c d "CAC 40 index profile". Euronext. http://www.euronext.com/editorial/wide/editorial-2667-EN-FR0003500008.html?selectedMep=1. Retrieved 2007-12-03.
- ^ "Investors celebrate stock market boom". BBC News. 31 December 2003. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/business/3359241.stm. Retrieved 2007-12-03.
- ^ "CAC40 shift to free-float weighting: revision of free-float calculation and capping factors" (Press release). Euronext. 5 November 2003. http://www.euronext.com/news/press_release/press_release-1731-EN.html?docid=59760. Retrieved 2007-12-03.
- ^ a b c d e f "Rules for the CAC 40 Index" (PDF). Euronext. January 2009. http://www.euronext.com/fic/000/050/871/508718.pdf. Retrieved 2009-12-17.
- ^ Chirac, Jacques (24 March 2006). "Press conference given by M. Jacques Chirac, President of the Republic, following the European Council (excerpts)". http://www.ambafrance-uk.org/European-Council-Press-conference.html. Retrieved 27 September 2010.
- ^ Lagarde, Christine (6 May 2006). ""France and Globalization": Lecture Given by Mme Christine Lagarde, Minister Delegate for Foreign Trade, to The Ecole des Hautes Etudes Commerciales in Lille (excerpts)". https://pastel.diplomatie.gouv.fr/editorial/actual/ael2/bulletin.gb.asp?liste=20060517.gb.html. Retrieved 2007-12-03.
- ^ "Index Announcement". Euronext. 1 December 2011. http://www.euronext.com/fic/000/068/156/681567.pdf. Retrieved 18 December 2011.
External links
- Official Euronext page for CAC 40 Index
- FCHI: Summary for CAC 40 INDEX - Yahoo! Finance
- Thomson Reuters page for .FCHI
- Bloomberg page for CAC:IND
|
|||||