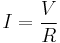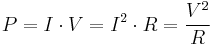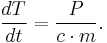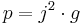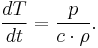Electrosurgery
| Electrosurgery | |
|---|---|
| Intervention | |
A surgeon using (monopolar) electrosurgical coagulation in the excision of a lipoma. |
|
| MeSH | D004598 |
Electrosurgery is the application of a high-frequency electric current to biological tissue as a means to cut, coagulate, desiccate, or fulgurate tissue.[1][2][3][4][5][6][7] (These terms are used in specific ways for this methodology—see below). Its benefits include the ability to make precise cuts with limited blood loss. Electrosurgical devices are frequently used during surgical operations helping to prevent blood loss in hospital operating rooms or in outpatient procedures.[8]
In electrosurgical procedures, the tissue is heated by an electric current. Although electrical devices may be used for the cauterization of tissue in some applications, electrosurgery is usually used to refer to a quite different method than electrocautery. The latter uses heat conduction from a probe heated to a glowing temperature by a direct current (much in the manner of a soldering iron). This may be accomplished by direct current from dry-cells in a penlight-type device. Electrosurgery, by contrast, uses alternating current to directly heat the tissue itself. When this results in destruction of small blood vessels and halting of bleeding, it is technically a process of electrocoagulation, although "electrocautery" is sometimes loosely and nontechnically used to describe it.
Often electrosurgery is mistakenly referred to as diathermy. Unlike Ohmic heating by electric current passing through the conductive tissue in conventional electrosurgery, diathermy means dielectric heating, produced by rotation of molecular dipoles in high frequency alternating electric field. This effect is most widely used in microwave ovens which operate at gigahertz frequencies.
Electrosurgery is commonly used in dermatological, gynecological, cardiac, plastic, ocular, spine, ENT, maxillofacial, orthopedic, urological, neuro- and general surgical procedures as well as certain dental procedures.
Electrosurgery is performed using an electrosurgical generator (also referred to as power supply or waveform generator) and a handpiece including one or several electrodes, sometimes referred to as an RF Knife. The apparatus when used for cutting or coagulation in surgery is still often referred to informally by surgeons as a "Bovie," after the inventor.
History
Development of the first commercial electrosurgical device is credited to William T. Bovie, who developed the first electrosurgical device while employed at Harvard University.[8][9] The first use of an electrosurgical generator in an operating room occurred on October 1, 1926 at Peter Bent Brigham Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts. The operation—removal of a mass from a patient’s head—was performed by Harvey Cushing.[10] The low powered Hyfrecator for office use was introduced in 1940.
Tissue heating by electric current
When voltage is applied across the material it produces electric field which exerts force on charged particles. A flow of free charge carriers – electrons and ions - is called electric current. In metals and semiconductors the charge carriers are primarily electrons, whereas in liquids the charge is carried predominantly by ions. Electrical conduction in biological tissues is primarily due to the conductivity of the interstitial fluids, and thus is predominantly ionic. Transition between the electronic and ionic conduction is governed by electrochemical processes at the electrode–electrolyte interface. Value of electric current, I, is determined by the applied voltage, V, and material’s resistance, R, according to Ohm's law:
Electric current of a constant polarity is referred to as direct current (DC). A current of alternating polarity is referred to as alternating current (AC). Its frequency is measured in cycles per second or hertz (Hz).
Current flowing through a resistor causes the generation of Joule heating. In other words, the resistance of the tissue converts the electric energy of the voltage source into heat (thermal energy) which causes the tissue temperature to rise. The deposited electric power (energy per time) can be calculated using:
where P represents the electric power, typically measured in watts.
In absence of heat conduction, the rate of temperature rise, dT/dt, in a heated object is proportional to the deposited power P, and inversely proportional to which is in turn proportional to the mass m of the object and its specific heat capacity c:
Larger amount of heat is required to increase the temperature of a heavier object. Thus when heat is generated in a small region of an object, the temperature of that localized region will rise much faster than if the same amount of heat is evenly dispersed over the entire object.
Current density, j is a measure of the concentration of electric current. A higher current density results in a higher concentration of Joule heating. Power density generated by electric current in the material, p is proportional to the square of the current density, and to the material's resistivity, g:
In absence of heat conduction, the rate of local temperature rise is proportional to the power density, p, produced in that region of tissue, and inversely proportional to its specific heat capacity and density 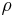 [11].
[11].
Electrical stimulation of neural and muscle cells
Neural and muscle cells are electrically-excitable, i.e. they can be stimulated by electric current. In human patients such stimulation may cause acute pain, muscle spasms, and even cardiac arrest. Sensitivity of the nerve and muscle cells to electric field is due to the voltage-gated ion channels present in their cell membranes. Stimulation threshold does not vary much at low frequencies (so called rheobase-constant level). However, the threshold starts increasing with decreasing duration of a pulse (or a cycle) when it drops below a characteristic minimum (so called chronaxie). Typically, chronaxie of neural cells is in the range of 0.1–10 ms, so the sensitivity to electrical stimulation (inverse of the stimulation threshold) decreases with increasing frequency in the kHz range and above. (Note that frequency of the alternating electric current is an inverse of the duration of a single cycle). To minimize the effects of muscle and neural stimulation, electrosurgical equipment typically operates in the radio frequency (RF) range of 100 kHz to 5 MHz.
Operation at higher frequencies also helps minimizing the amount of hydrogen and oxygen generated by electrolysis of water. This is especially important consideration for applications in liquid medium in closed compartments, where generation of gas bubbles may interfere with the procedure. For example, bubbles produced during an operation inside an eye may obscure a field of view.
Common electrode configurations for ground-return-pad devices
There are several commonly used electrode configurations or circuit topologies:
In bipolar configuration the voltage is applied to the patient using a pair of similarly-sized electrodes. For example, special forceps, with one tine connected to one pole of the AC generator and the other tine connected to the other pole of the generator. When a piece of tissue is held by the forceps, a high frequency electric current flows from one to the other forceps tine, heating the intervening tissue.
In monopolar configuration the patient is attached to the return electrode, a relatively large metal plate or a flexible metalized plastic pad which is connected to the return electrode of the AC source. The surgeon uses a pointed electrode to make contact with the tissue. The electric current flows from the active electrode, through the body to the return electrode, and then back to the electrosurgical generator. Since electric current spreads from the pointed electrode as it enters the body the current density is rapidly (quadratically) decreasing with distance from the electrode. Since the rate of heating is proportional to the square of current density, the heating occurs in a very localized region, only near the probe tip. On an extremity such as a finger, there is limited cross-sectional area for the return current to spread across, which might result in higher current density and some heating throughout the volume of the extremity.
There is also a common intermediate configuration, when both electrodes are located on the same probe, but the return electrode is much larger than the active one. Since current density is higher in front of the smaller electrode, the heating and associated tissue effects take place only (or primarily) in front of the active electrode, and exact position of the return electrode on tissue is not critical. Sometimes such configuration is called sesquipolar, even though the origin of this term in Latin (sesqui) means a ratio of 1.5 [12].
Dedicated non-ground-return machines
Relatively low-powered high frequency electrosurgery can be performed on conscious outpatients with no return electrode at all [13]. Safely Operating at low currents with no return electrode is possible, because at the medium RF frequencies (usually 100 - 500 kHz) that the machines generate, the self-capacitance of the patient's body (which is between the patient's body and the machine's return potential or ground) is large enough to allow the resulting displacement current to act as a return path.
One example of such a machine is called a hyfrecator. This term began in 1940 as a Birtcher Corporation brandname Hyfrecator® for "High Frequency Eradicator", but now serves generically to describe a general class of single-electrode, non-isolated (earth-referenced) low-powered electrosurgical machines intended mainly for office use. An accidental additional return path through an earth-ground provides a danger of a burn at a site far away from the probe electrode, and for this reason single-electrode devices are used only on conscious patients who would be aware of such complications, and only on carefully insulated tables.
In such a setting, hyfrecators are not used to cut tissue, but to destroy relatively small lesions, and also to stop bleeding in surgical incisions made by blade instruments under local anesthesia.
Electrosurgical modalities
In cutting mode electrode touches the tissue, and sufficiently high power density is applied to vaporize its water content. Since water vapor is not conductive under normal cirumstances, electric current cannot flow through the vapor layer. Energy delivery beyond the vaporization threshold can continue if sufficiently high voltage is applied (> +/-200 V) [11] to ionize vapor and convert it into a conductive plasma. Vapor and fragments of the overheated tissue are ejected, forming a crater [14]. Electrode surfaces intended to be used for cutting often feature a finer wire or wire loop, as opposed to a more flat blade with a rounded surface.
Coagulation is performed using waveforms with lower average power, generating heat insufficient for explosive vaporization, but producing a thermal coagulum instead.
Electrosurgical desiccation occurs when the electrode touches the tissue open to air, and the amount of generated heat is lower than that required for cutting. The tissue surface and some of the tissue more deep to the probe dries out and forms a coagulum (a dry patch of dead tissue). This technique may be used for treating nodules under the skin where minimal damage to the skin surface is desired.
In fulguration mode, the electrode is held away from the tissue, so that when the air gap between the electrode and the tissue is ionized, an electric arc discharge develops. In this approach the burning to the tissue is more superficial, because the current is spread over the tissue area larger than the tip of electrode.[15] Under these conditions, superficial skin charring or carbonization is seen over a wider area than when operating in contact with the probe, and this technique is therefore used for very superficial or protrusive lesions such as skin tags. Ionization of an air gap requires voltage in the kV range.
Besides the thermal effects in tissue, electric field can produce pores in the cellular membranes - a phenomenon called electroporation. This effect may affect cells beyond the range of thermal damage.
Wet field electrosurgery
There are wet and dry field electrosurgical devices. Wet field devices operate in a saline solution, or in an open wound. Heating is as a result of an alternating current that passes between two electrodes. Heating is usually greatest where the current density is highest. Therefore it is usually the smallest or sharpest electrode that generates the most heat.
Cut/Coag Most wet field electrosurgical systems operate in two modes: "Cut" causes a small area of tissue to be vaporized, and "Coag" causes the tissue to "dry" (in the sense of bleeding being stopped). "Dried" tissues are killed (and will later slough or be replaced by fibrotic tissue) but they are temporarily physically intact after electrosurgical application. The depth of tissue death is typically a few millimeters near the contact of the electrode.
Cut If the voltage level is high enough, the heat generated can generates a vapour pocket. The vapour pocket typically reaches temperatures of approximately 400 degrees Celsius, which vaporizes and explodes a small section of soft tissue, resulting in an incision.
Coag When the system is operating in "coag mode" the voltage output is usually lower than in cut mode and less power is delivered. This therefore generates less heat and a vapour pocket is not generated. Tissue remains grossly intact, but cells are destroyed at the point of contact, and smaller vessels are destroyed and sealed, stopping capillary and small-arterial bleeding.
Electrosurgical waveforms
Different waveforms can be used for different electrosurgical procedures. For cutting, a continuous single frequency sine wave is often employed. Rapid tissue heating leads to explosive vaporization of interstitial fluid. If the voltage is sufficiently high (> 400 V peak-to-peak)[11] the vapor sheath is ionized, forming conductive plasma. Electric current continues to flow from the metal electrode through the ionized gas into the tissue. Rapid overheating of tissue results in its vaporization, fragmentation and ejection of fragments, allowing for tissue cutting[11]. In applications of a continuous wave the heat diffusion typically leads to formation of a significant thermal damage zone at the edges of the lesion. Open circuit voltage in electrosurgical waveforms is typically in the range of 300–10,000 V peak-to-peak.
Higher precision can be achieved with pulsed waveforms [11][14]. Using bursts of several tens of microseconds in duration the tissue can be cut, while the size of the heat diffusion zone does not exceed the cellular scale. Heat accumulation during repetitive application of bursts can also be avoided if sufficient delay is provided between the bursts, allowing the tissue to cool down [14]. The proportion of ON time to OFF time can be varied to allow control of the heating rate. A related parameter, duty cycle, is defined as the ratio of the ON time to the period (the time of a single ON-OFF cycle). In the terminology of electrical engineering, this process of altering an amplitude of a periodic waveform is called modulation.
For coagulation, the average power is typically reduced below the threshold of cutting. Typically, sine wave is turned on and off in a rapid succession. The overall effect is a slower heating process, which causes tissue to coagulate. In simple coagulation/cutting mode machines, the lower duty cycle typical of coagulation mode is usually heard by the ear as a lower frequency and a rougher tone than the higher frequency tone typical of cutting mode with the same equipment.
Many modern electrosurgical generators provide sophisticated waveforms with power adjusted in real time, based on changes of the tissue impedance.
Prevention of unintended burns in patients
For high power surgical uses during anesthesia the monopolar modality relies on a good electrical contact between a large area of the body (typically at least the entire back of the patient) and the return electrode or pad (also known as dispersive pad or patient plate). Severe burns (3rd degree) can occur if contact with the return electrode is insufficient, or when a patient comes into contact with metal objects serving as an unintended (capacitative) leakage path to Earth-ground.
To prevent unintended burns, the skin is cleaned and a conductive gel is used to enhance contact with the return electrode. Proper electrical grounding practices must be followed in the electrical wiring of the building. It is also recommended to use a modern electrosurgical unit that includes a return electrode monitoring system that continuously tests for reliable and safe patient contact. These systems interrogate the impedance of a split or dual-pad return electrode and will alarm out, disabling further generator output in case of fault. Prior generators relied on single pad return electrodes and thus had no means of verifying safe patient connection. Return electrodes should always have full contact with the skin and be placed on the same side of the body and close to the body part where the procedure is occurring.
If there is any metal in the body of the patient, the return electrode is placed on the opposite side of the body from the metal and be placed between the metal and the operation site. This prevents current from passing selectively through metal on the way to the return electrode. For example, for a patient who has had a right sided hip replacement who is scheduled for surgery, the return electrode is placed on the left side of the body on the lateral side of the lower abdomen, which places the return electrode between the location of the metal and the surgical site and on the opposite side from the metal. If there is metal on both sides of the body, the return electrode is placed between the metal and the procedure site when possible. Common return electrode locations include lateral portions of the outer thighs, abdomen, back, or shoulder blades.[8]
The use of the bipolar option does not require the placement of a return electrode because the current only passes between tines of the forceps or other bipolar output device.
Electrosurgery should only be performed by a physician who has received specific training in this field and who is familiar with the techniques used to prevent burns.
Notes
- ^ Hainer BL, "Fundamentals of electrosurgery", Journal of the American Board of Family Practice, 4(6):419-26, 1991 Nov-Dec.
- ^ Electrosurgery for the Skin, Barry L. Hainer M.D., Richard B. Usatine, M.D., American Family Physician (Journal of the American Academy of Family Physicians), 2002 Oct 1;66(7):1259-66.
- ^ A Simple Guide to the Hyfrecator 2000 Schuco International (London) Ltd.
- ^ Boughton RS, Spencer SK, "Electrosurgical fundamentals", J Am Acad Dermatol, 1987 Apr;16(4):862-7.
- ^ Bouchier G, "The fundamentals of electro-surgery. High frequency current generators", Cah Prothese, 1980 Jan;8(29):95-106. In French.
- ^ Oringer MJ, "Fundamentals of electrosurgery", J Oral Surg Anesth Hosp Dent Serv, 1960 Jan;18:39-49.
- ^ Reidenbach HD, "Fundamentals of bipolar high-frequency surgery", Endosc Surg Allied Technol, 1993 Apr;1(2):85-90.
- ^ a b c McCauley, Genard (2003). "Understanding Electrosurgery". Aaron Medical. http://www.aaronmed.com/Images/UNDERSTANDINGLIT.pdf. Retrieved 2011-07-13.
- ^ Pollack, SV; Carruthers, A; Grekin, RC (2000). "The History of Electrosurgery". Dermatologic Surgery 26 (10): 904–8.
- ^ Bovie, WT; Cushing, H (1928). "Electrosurgery as an aid to the removal of intracranial tumors with a preliminary note on a new surgical-current generator". Surg Gynecol Obstet 47: 751–84.
- ^ a b c d e On Mechanisms of Interaction in Electrosurgery. New Journal of Physics. 10: 123022 (2008).
- ^ US Patent 3987795. Electrosurgical devices having sesquipolar electrode structures incorporated therein
- ^ see page 6
- ^ a b c Electrosurgery with Cellular Precision. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 55(2):838-841 (2008)
- ^ Electrosurgery for the Skin. Barry L. Hainer M.D., Richard B. Usatine, M.D., American Family Physician (Journal of the American Academy of Family Physicians), 2002 Oct 1;66(7):1259-66. See illustration.
See also
- Electrosurgery (Dentistry)
- Cryosurgery
- Laser surgery
- Electrocautery
- Dielectric heating
- microwave minimaze procedure
- Harmonic scalpel
External links
- A Simple Guide to the Hyfrecator 2000, Richard J Motley, Schuco International Ltd. a primer for low-powered outpatient dermatological devices, such as the Hyfrecator 2000 device.
- Electrosurgery for the Skin, Barry L. Hainer M.D., Richard B. Usatine, M.D., American Family Physician (Journal of the American Academy of Family Physicians), 2002 Oct 1;66(7):1259-66.
- Electrosurgical Generator Testing Online Journal of he Biomedical Engineering Association of Ireland (BEAI), May 1997.
- Update on Electrosurgery, Judith Lee, Contributing Editor, Outpatient Surgery Magazine, February, 2002.