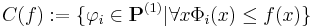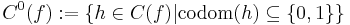Blum axioms
In computational complexity theory the Blum axioms or Blum complexity axioms are axioms which specify desirable properties of complexity measures on the set of computable functions. The axioms were first defined by Manuel Blum in 1967.[1]
Importantly, the Speedup and Gap theorems hold for any complexity measure satisfying these axioms. The most well-known measures satisfying these axioms are those of time (i.e., running time) and space (i.e., memory usage).
Contents |
Definitions
A Blum complexity measure is a tuple 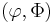 with
with 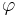 a Gödel numbering of the partial computable functions
a Gödel numbering of the partial computable functions 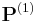 and a computable function
and a computable function
which satisfies the following Blum axioms. We write 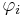 for the i-th partial computable function under the Gödel numbering
for the i-th partial computable function under the Gödel numbering 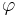 , and
, and 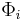 for the partial computable function
for the partial computable function 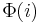 .
.
Examples
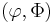 is a complexity measure, if
is a complexity measure, if 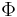 is either the time or the memory (or some suitable combination thereof) required for the computation coded by i.
is either the time or the memory (or some suitable combination thereof) required for the computation coded by i.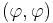 is not a complexity measure, since it fails the second axiom.
is not a complexity measure, since it fails the second axiom.
Notes
A Blum complexity measure is defined using computable functions without any reference to a specific model of computation. In order to make the definition more accessible we rephrase the Blum axioms in terms of Turing machines:
A Blum complexity measure is a function 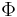 from pairs (Turing machine
from pairs (Turing machine  , input
, input  to
to  ) to the natural numbers union infinity. Furthermore,
) to the natural numbers union infinity. Furthermore, 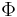 should satisfy the following axioms:
should satisfy the following axioms:
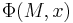 is finite if and only if
is finite if and only if 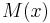 halts
halts- There is an algorithm which, on input
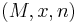 decides if
decides if 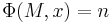
For example, suppose 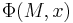 gives the number of time steps that the machine M runs for on input x before halting. The first axiom is clear; the second follows because a universal Turing machine can simulate M on x while counting its steps. If M exceeds n steps, it can halt and reject, so there is no need to determine if M halts on x.
gives the number of time steps that the machine M runs for on input x before halting. The first axiom is clear; the second follows because a universal Turing machine can simulate M on x while counting its steps. If M exceeds n steps, it can halt and reject, so there is no need to determine if M halts on x.
Complexity classes
For a total computable function  complexity classes of computable functions can be defined as
complexity classes of computable functions can be defined as
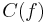 is the set of all computable functions with a complexity less than
is the set of all computable functions with a complexity less than  .
. 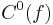 is the set of all boolean-valued functions with a complexity less than
is the set of all boolean-valued functions with a complexity less than  . If we consider those functions as indicator functions on sets,
. If we consider those functions as indicator functions on sets, 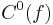 can be thought of as a complexity class of sets.
can be thought of as a complexity class of sets.
References
- ^ Blum, M. (1967). "A Machine-Independent Theory of the Complexity of Recursive Functions". Journal of the ACM 14 (2): 322–336. doi:10.1145/321386.321395.
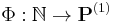
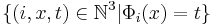 is
is