Base (topology)
In mathematics, a base (or basis) B for a topological space X with topology T is a collection of open sets in T such that every open set in T can be written as a union of elements of B. We say that the base generates the topology T. Bases are useful because many properties of topologies can be reduced to statements about a base generating that topology, and because many topologies are most easily defined in terms of a base which generates them.
Contents |
Simple properties of bases
Two important properties of bases are:
- The base elements cover X.
- Let B1, B2 be base elements and let I be their intersection. Then for each x in I, there is a base element B3 containing x and contained in I.
If a collection B of subsets of X fails to satisfy either of these, then it is not a base for any topology on X. (It is a subbase, however, as is any collection of subsets of X.) Conversely, if B satisfies both of the conditions 1 and 2, then there is a unique topology on X for which B is a base; it is called the topology generated by B. (This topology is the intersection of all topologies on X containing B.) This is a very common way of defining topologies. A sufficient but not necessary condition for B to generate a topology on X is that B is closed under intersections; then we can always take B3 = I above.
For example, the collection of all open intervals in the real line forms a base for a topology on the real line because the intersection of any two open intervals is itself an open interval or empty. In fact they are a base for the standard topology on the real numbers.
However, a base is not unique. Many bases, even of different sizes, may generate the same topology. For example, the open intervals with rational endpoints are also a base for the standard real topology, as are the open intervals with irrational endpoints, but these two sets are completely disjoint and both properly contained in the base of all open intervals. In contrast to a basis of a vector space in linear algebra, a base need not be maximal; indeed, the only maximal base is the topology itself. In fact, any open sets in the space generated by a base may be safely added to the base without changing the topology. The smallest possible cardinality of a base is called the weight of the topological space.
An example of a collection of open sets which is not a base is the set S of all semi-infinite intervals of the forms (−∞, a) and (a, ∞), where a is a real number. Then S is not a base for any topology on R. To show this, suppose it were. Then, for example, (−∞, 1) and (0, ∞) would be in the topology generated by S, being unions of a single base element, and so their intersection (0,1) would be as well. But (0, 1) clearly cannot be written as a union of the elements of S. Using the alternate definition, the second property fails, since no base element can "fit" inside this intersection.
Given a base for a topology, in order to prove convergence of a net or sequence it is sufficient to prove that it is eventually in every set in the base which contains the putative limit.
Objects defined in terms of bases
- The order topology is usually defined as the topology generated by a collection of open-interval-like sets.
- The metric topology is usually defined as the topology generated by a collection of open balls.
- A second-countable space is one that has a countable base.
- The discrete topology has the singletons as a base.
Theorems
- For each point x in an open set U, there is a base element containing x and contained in U.
- A topology T2 is finer than a topology T1 if and only if for each x and each base element B of T1 containing x, there is a base element of T2 containing x and contained in B.
- If B1,B2,...,Bn are bases for the topologies T1,T2,...,Tn, then the set product B1 × B2 × ... × Bn is a base for the product topology T1 × T2 × ... × Tn. In the case of an infinite product, this still applies, except that all but finitely many of the base elements must be the entire space.
- Let B be a base for X and let Y be a subspace of X. Then if we intersect each element of B with Y, the resulting collection of sets is a base for the subspace Y.
- If a function f:X → Y maps every base element of X into an open set of Y, it is an open map. Similarly, if every preimage of a base element of Y is open in X, then f is continuous.
- A collection of subsets of X is a topology on X if and only if it generates itself.
- B is a basis for a topological space X if and only if the subcollection of elements of B which contain x form a local base at x, for any point x of X.
Base for the closed sets
Closed sets are equally adept at describing the topology of a space. There is, therefore, a dual notion of a base for the closed sets of a topological space. Given a topological space X, a base for the closed sets of X is a family of closed sets F such that any closed set A is an intersection of members of F.
Equivalently, a family of closed sets forms a base for the closed sets if for each closed set A and each point x not in A there exists an element of F containing A but not containing x.
It is easy to check that F is a base for the closed sets of X if and only if the family of complements of members of F is a base for the open sets of X.
Let F be a base for the closed sets of X. Then
- ∩F = ∅
- For each F1 and F2 in F the union F1 ∪ F2 is the intersection of some subfamily of F (i.e. for any x not in F1 or F2 there is an F3 in F containing F1 ∪ F2 and not containing x).
Any collection of subsets of a set X satisfying these properties forms a base for the closed sets of a topology on X. The closed sets of this topology are precisely the intersections of members of F.
In some cases it is more convenient to use a base for the closed sets rather than the open ones. For example, a space is completely regular if and only if the zero sets form a base for the closed sets. Given any topological space X, the zero sets form the base for the closed sets of some topology on X. This topology will be finest completely regular topology on X coarser than the original one. In a similar vein, the Zariski topology on An is defined by taking the zero sets of polynomial functions as a base for the closed sets.
Weight and Character
We shall work with Notions established in (Engelking 1977, pp. 12, 127--128). Fix 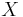 a topological Space. We define the Weight as
a topological Space. We define the Weight as 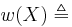 the minimum Cardinality of a Basis; we define the network Weight as
the minimum Cardinality of a Basis; we define the network Weight as 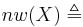 the minimum Cardinality of a Network; the Character of a Point
the minimum Cardinality of a Network; the Character of a Point 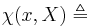 the minimum Cardinality of a Neighbourhood Basis for
the minimum Cardinality of a Neighbourhood Basis for 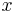 in
in 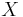 ; and the Character of
; and the Character of 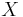 to be
to be 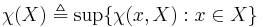 .
.
Here, a Network is a family 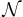 of sets, for which, for all Points
of sets, for which, for all Points 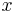 and open Neighbourhoods
and open Neighbourhoods 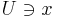 , there is a
, there is a 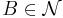 for which
for which 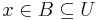 .
.
The point of computing the Character and Weight is useful to be able to tell what sort of Bases and local Bases can exist. We have following Facts:
- obviously
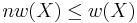 .
. - if
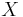 is discrete, then
is discrete, then 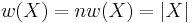 .
. - if
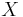 is hausdorff, then
is hausdorff, then 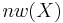 is finite iff
is finite iff 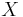 is finite discrete.
is finite discrete. - if
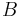 a Basis of
a Basis of 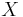 then there is a Basis
then there is a Basis 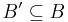 of Size
of Size 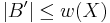 .
. - if
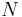 a Neighbourhood Basis for
a Neighbourhood Basis for 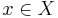 then there is a Neighbourhood Basis
then there is a Neighbourhood Basis 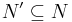 of Size
of Size 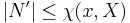 .
. - if
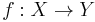 is a continuous surjection, then
is a continuous surjection, then 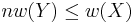 . (Simply consider the
. (Simply consider the 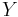 -Network
-Network 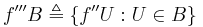 for each Basis
for each Basis 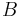 of
of 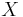 .)
.) - if
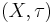 is hausdorff, then there exists a weaker hausdorff Topology
is hausdorff, then there exists a weaker hausdorff Topology 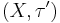 so that
so that 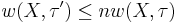 . So a forteori, if
. So a forteori, if 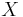 is also compact, then such Topologies coincide and hence we have, combined with the first Fact,
is also compact, then such Topologies coincide and hence we have, combined with the first Fact, 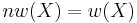 .
. - if
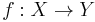 a continuous surjective map from a compact metrisable Space to an hausdorff Space, then
a continuous surjective map from a compact metrisable Space to an hausdorff Space, then 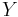 is compact metrisable.
is compact metrisable.
The last Fact comes from the Fact that 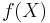 is compact hausdorff, and hence
is compact hausdorff, and hence 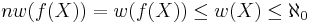 (since compact metrisable Spaces are necessarily second countable); as well as the Fact that compact hausdorff Spaces are metrisable exactly in case they are second countable. (An Application of this, for instance, is that every Path in an hausdorff Space is compact metrisable.)
(since compact metrisable Spaces are necessarily second countable); as well as the Fact that compact hausdorff Spaces are metrisable exactly in case they are second countable. (An Application of this, for instance, is that every Path in an hausdorff Space is compact metrisable.)
Increasing Chains of Open Sets
Using the above given Notation, suppose that 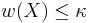 some infinite Cardinal. Then there does not exist a strictly increasing Sequence of open Sets (equivalently strictly decreasing Sequence of closed Sets) of Length
some infinite Cardinal. Then there does not exist a strictly increasing Sequence of open Sets (equivalently strictly decreasing Sequence of closed Sets) of Length 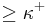 .
.
To see this (without the Axiom of Choice), fix 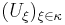 a Basis of open Sets. And suppose per contra, that
a Basis of open Sets. And suppose per contra, that 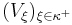 were a strictly increasing Sequence of open Sets. This means
were a strictly increasing Sequence of open Sets. This means 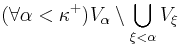 is non-empty. If
is non-empty. If 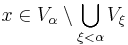 , we may utilise the Basis to find some
, we may utilise the Basis to find some 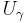 with
with 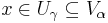 . In this way we may well-define a Map,
. In this way we may well-define a Map, 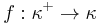 mapping each
mapping each 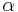 to the least
to the least 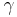 for which
for which 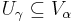 and meets
and meets 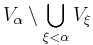 . This Map can be seen to be injective. (For otherwise there would be
. This Map can be seen to be injective. (For otherwise there would be 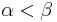 with
with 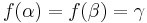 , say, which would further imply
, say, which would further imply 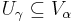 but also meets
but also meets 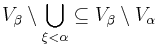 which is a Contradiction.) But this would go to show that
which is a Contradiction.) But this would go to show that 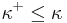 , a Contradiction.
, a Contradiction.
See also
References
- Engelking, Ryszard (1977). General Topology. PWN, Warsaw.
- James Munkres (1975) Topology: a First Course. Prentice-Hall.
- Willard, Stephen (1970) General Topology. Addison-Wesley. Reprinted 2004, Dover Publications.