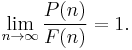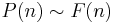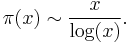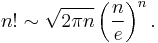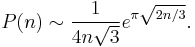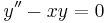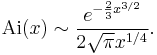Asymptotic formula
In mathematics, an asymptotic formula for a quantity (function or expression) depending on natural numbers, or on a variable taking real numbers as values, is a function of natural numbers, or of a real variable, whose values are nearly equal to the values of the former when both are evaluated for the same large values of the variable. An asymptotic formula for a quantity is a function which is asymptotically equivalent to the former.
More generally, an asymptotic formula is "a statement of equality between two functions which is not a true equality but which means the ratio of the two functions approaches 1 as the variable approaches some value, usually infinity".[1]
Contents |
Definition
Let P(n) be a quantity or function depending on n which is a natural number. A function F(n) of n is an asymptotic formula for P(n) if P(n) is asymptotically equivalent toF(n), that is, if
This is symbolically denoted by
Examples
Prime number theorem
For a real number x, let π (x) denote the number of prime numbers less than or equal to x. The classical prime number theorem gives an asymptotic formula for π (x):
Stirling's formula
Stirling's approximation formula is a well known asymptotic formula for the following quantity:
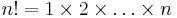 .
.
The asymptotic formula is
Asymptotic formula for the partition function
For a positive integer n, the partition function P(n), sometimes also denoted p(n), gives the number of ways of writing the integer n as a sum of positive integers, where the order of addends is not considered significant.[2] Thus, for example, P(4) = 5. G.H. Hardy and Srinivasa Ramanujan in 1918 obtained the following asymptotic formula for P(n)[2]:
Asymptotic formula for Airy function
The Airy function Ai(x) which is a solution of the differential equation
and which has many applications in physics, has the following asymptotic formula:
See also
References
- ^ "Sci-Tech Dictionary: asymptotic formula". http://www.answers.com/topic/asymptotic-formula. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ^ a b Weisstein, Eric W. "Partition Function P." From MathWorld--A Wolfram Web Resource. http://mathworld.wolfram.com/PartitionFunctionP.html