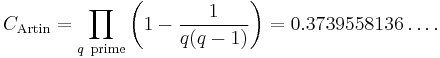Artin's conjecture on primitive roots
In number theory, Artin's conjecture on primitive roots states that a given integer a which is not a perfect square and not −1 is a primitive root modulo infinitely many primes p. The conjecture also ascribes an asymptotic density to these primes. This conjectural density equals Artin's constant or a rational multiple thereof.
The conjecture was made by Emil Artin to Helmut Hasse on September 27, 1927, according to the latter's diary. Although significant progress has been made, the conjecture is still unresolved. In fact, there is no a single value of a for which Artin's conjecture is proved.
Contents |
Formulation
Let a be an integer which is not a perfect square and not −1. Write a = a0b2 with a0 square-free. Denote by S(a) the set of prime numbers p such that a is a primitive root modulo p. Then
- S(a) has a positive asymptotic density inside the set of primes. In particular, S(a) is infinite.
- Under the conditions that a is not a perfect power and that a0 is not congruent to 1 modulo 4, this density is independent of a and equals Artin's constant which can be expressed as an infinite product
Similar conjectural product formulas [1] exist for the density when a does not satisfy the above conditions. In these cases, the conjectural density is always a rational multiple of CArtin.
Example
For example, take a = 2. The conjecture claims that the set of primes p for which 2 is a primitive root has the above density CArtin. The set of such primes is (sequence A001122 in OEIS)
- S(2) = {3, 5, 11, 13, 19, 29, 37, 53, 59, 61, 67, 83, 101, 107, 131, 139, 149, 163, 173, 179, 181, 197, 211, 227, 269, 293, 317, 347, 349, 373, 379, 389, 419, 421, 443, 461, 467, 491, ...}.
It has 38 elements smaller than 500 and there are 95 primes smaller than 500. The ratio (which conjecturally tends to CArtin) is 38/95 = 2/5 = 0.4.
Proof attempts
In 1967, Hooley published a conditional proof for the conjecture, assuming certain cases of the Generalized Riemann hypothesis.[2] In 1984, R. Gupta and M. Ram Murty showed unconditionally that Artin's conjecture is true for infinitely many a using sieve methods.[3] Roger Heath-Brown improved on their result and showed unconditionally that there are at most two exceptional prime numbers a for which Artin's conjecture fails.[4] This result is not constructive, as far as the exceptions go. For example, it follows from the theorem of Heath-Brown that one out of 3, 5, and 7 is a primitive root modulo p for infinitely many p. But the proof does not provide us with a way of computing which one.
See also
- Brown–Zassenhaus conjecture
- Cyclic number (group theory)
References
- ^ Gerard P. Michon (2006-06-15). "Artin's Constant". Numericana. http://www.numericana.com/answer/constants.htm#artin.
- ^ Hooley, Christopher (1967). "On Artin's conjecture". J. Reine Angew. Math. 225: 209–220.
- ^ Gupta, Rajiv; Murty, M. Ram (1984). "A remark on Artin's conjecture". Invent. Math. 78 (1): 127–130. doi:10.1007/BF01388719.
- ^ Heath-Brown, D. R. (1986). "Artin's conjecture for primitive roots". Quart. J. Math. Oxford Ser. 37 (1): 27–38. doi:10.1093/qmath/37.1.27.