Aptamer
Aptamers are oligonucleic acid or peptide molecules that bind to a specific target molecule. Aptamers are usually created by selecting them from a large random sequence pool, but natural aptamers also exist in riboswitches. Aptamers can be used for both basic research and clinical purposes as macromolecular drugs. Aptamers can be combined with ribozymes to self-cleave in the presence of their target molecule. These compound molecules have additional research, industrial and clinical applications.
More specifically, aptamers can be classified as:
- DNA or RNA aptamers. They consist of (usually short) strands of oligonucleotides.
- Peptide aptamers. They consist of a short variable peptide domain, attached at both ends to a protein scaffold.
Contents |
Nucleic Acid aptamers
Nucleic acid aptamers are nucleic acid species that have been engineered through repeated rounds of in vitro selection or equivalently, SELEX (systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment) to bind to various molecular targets such as small molecules, proteins, nucleic acids, and even cells, tissues and organisms. Aptamers are useful in biotechnological and therapeutic applications as they offer molecular recognition properties that rival that of the commonly used biomolecule, antibodies. In addition to their discriminate recognition, aptamers offer advantages over antibodies as they can be engineered completely in a test tube, are readily produced by chemical synthesis, possess desirable storage properties, and elicit little or no immunogenicity in therapeutic applications.
In 1990, two labs independently developed the technique of selection: the Gold lab, using the term SELEX for their process of selecting RNA ligands against T4 DNA polymerase; and the Szostak lab, coining the term in vitro selection, selecting RNA ligands against various organic dyes. The Szostak lab also coined the term aptamer (from the Latin, apto, meaning ‘to fit’) for these nucleic acid-based ligands. Two years later, the Szostak lab and Gilead Sciences, independent of one another, used in vitro selection schemes to evolve single stranded DNA ligands for organic dyes and human coagulant, thrombin, respectively. There does not appear to be any systematic differences between RNA and DNA aptamers, save the greater intrinsic chemical stability of DNA.
Interestingly enough, the notion of selection in vitro was actually preceded twenty-plus years prior when Sol Spiegelman used a Qbeta replication system as a way to evolve a self-replicating molecule. In addition, a year before the publishing of in vitro selection and SELEX, Gerald Joyce used a system that he termed ‘directed evolution’ to alter the cleavage activity of a ribozyme.
Since the discovery of aptamers, many researchers have used aptamer selection as a means for application and discovery. In 2001, the process of in vitro selection was automated by the Ellington lab at the University of Texas at Austin, and at SomaLogic, Inc (Boulder, CO), reducing the duration of a selection experiment from six weeks to three days.
While the process of artificial engineering of nucleic acid ligands is highly interesting to biology and biotechnology, the notion of aptamers in the natural world had yet to be uncovered until 2002 when two groups led by Ronald Breaker and Evgeny Nudler discovered a nucleic acid-based genetic regulatory element called a riboswitch that possesses similar molecular recognition properties to the artificially made aptamers. In addition to the discovery of a new mode of genetic regulation, this adds further credence to the notion of an ‘RNA World,’ a postulated stage in time in the origins of life on Earth.
Lately, a concept of smart aptamers, and smart ligands in general, has been introduced. It describes aptamers that are selected with pre-defined equilibrium (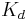 ), rate (
), rate (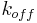 ,
, 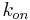 ) constants and thermodynamic (ΔH, ΔS) parameters of aptamer-target interaction. Kinetic capillary electrophoresis is the technology used for the selection of smart aptamers. It obtains aptamers in a few rounds of selection.
) constants and thermodynamic (ΔH, ΔS) parameters of aptamer-target interaction. Kinetic capillary electrophoresis is the technology used for the selection of smart aptamers. It obtains aptamers in a few rounds of selection.
Recent developments in aptamer-based therapeutics have been rewarded in the form of the first aptamer-based drug approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in treatment for age-related macular degeneration (AMD), called Macugen offered by OSI Pharmaceuticals. In addition, Cambridge, MA - based Archemix (http://www.archemix.com) is leading the development of aptamers as a new class of directed therapeutics for the prevention and treatment of chronic and acute diseases. ARC1779, its lead proprietary candidate, is a potent, selective, first-in-class antagonist of von Willebrand Factor (vWF). ARC1779 is being evaluated in patients diagnosed with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) who are undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). Phase I testing for ARC1779 was initiated in December 2006, and a Phase 2 study in ACS is planned to begin by the end of 2007.
Non-modified aptamers are cleared rapidly from the bloodstream, with a half-life of minutes to hours, mainly due to nuclease degradation and clearance from the body by the kidneys, a result of the aptamer's inherently low molecular weight. Unmodified aptamer applications currently focus on treating transient conditions such as blood clotting, or treating organs such as the eye where local delivery is possible. This rapid clearance can be an advantage in applications such as in vivo diagnostic imaging. An example is a tenascin-binding aptamer under development by Schering AG for cancer imaging. Several modifications, such as 2'-fluorine-substituted pyrimidines, polyethylene glycol (PEG) linkage, etc. (both of which are used in Macugen, an FDA-approved aptamer) are available to scientists with which to increase the serum half-life of aptamers easily to the day or even week time scale.
Another approach to increase the nuclease resistance of aptamers is to use a Spiegelmer.
In addition to the development of aptamer-based therapeutics, many researchers such as the Ellington lab and independently another company SomaLogic (Boulder, CO) have been developing diagnostic techniques for aptamer based plasma protein profiling called aptamer plasma proteomics. This technology will enable future multi-biomarker protein measurements that can aid diagnostic distinction of disease versus healthy states. Somalogic aptamers to HER2 and EGFR membrane proteins have also been demonstrated to work in the context of rapid frozen tissue intraoperative diagnostic pathology applications.[1]
As a resource for all in vitro selection and SELEX experiments, the Ellington lab has developed the Aptamer Database cataloging all published experiments. This is found at http://aptamer.icmb.utexas.edu/.
Peptide aptamers
Peptide aptamers are proteins that are designed to interfere with other protein interactions inside cells. They consist of a variable peptide loop attached at both ends to a protein scaffold. This double structural constraint greatly increases the binding affinity of the peptide aptamer to levels comparable to an antibody's (nanomolar range).
The variable loop length is typically composed of ten to twenty amino acids, and the scaffold may be any protein which has good solubility and compacity properties. Currently, the bacterial protein Thioredoxin-A is the most used scaffold protein, the variable loop being inserted within the reducing active site, which is a -Cys-Gly-Pro-Cys- loop in the wild protein, the two Cysteines lateral chains being able to form a disulfide bridge.
Peptide aptamer selection can be made using different systems, but the most used is currently the yeast two-hybrid system.
Selection of Ligand Regulated Peptide Aptamers (LiRPAs) has been demonstrated. By displaying 7 amino acid peptides from a novel scaffold protein based on the trimeric FKBP-rapamycin-FRB structure, interaction between the randomized peptide and target molecule can be controlled by the small molecule Rapamycin or non-immunosuppressive analogs.
Peptide aptamer can also be selected from combinatorial peptide libraries constructed by phage dsiplay and other surface display technologies such as mRNA display, ribosome display, bacterial display and yeast display. These experimental procedures are also known as biopannings. Among peptides obtained from biopannings, mimotopes can be considered as a kind of peptide aptamers. All the peptides panned from combinatorial peptide libraries have been stored in a special database with the name MimoDB,[2] which is freely available at http://immunet.cn/mimodb.
AptaBiD
AptaBiD or Aptamer-Facilitated Biomarker Discovery is a technology for biomarker discovery.[3] AptaBiD is based on multi-round generation of an aptamer or a pool of aptamers for differential molecular targets on the cells which facilitates exponential detection of biomarkers. It involves three major stages: (i) differential multi-round selection of aptamers for biomarker of target cells; (ii) aptamer-based isolation of biomarkers from target cells; and (iii) mass spectrometry identification of biomarkers. The important feature of the AptaBiD technology is that it produces synthetic affinity probes (aptamers) simultaneously with biomarker discovery. In AptaBiD, aptamers are developed for cell surface biomarkers in their native state and conformation. In addition to facilitating biomarker identification, such aptamers can be directly used for cell isolation, cell visualization, and tracking cells in vivo. They can also be used to modulate activities of cell receptors and deliver different agents (e.g., siRNA and drugs) into the cells.
References
- Ellington AD, Szostak JW (Aug 1990). "In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands". Nature 346 (6287): 818–22. doi:10.1038/346818a0. PMID 1697402.
- Bock LC, Griffin LC, Latham JA, Vermaas EH, Toole JJ (Feb 1992). "Selection of single-stranded DNA molecules that bind and inhibit human thrombin". Nature 355 (6360): 564–6. doi:10.1038/355564a0. PMID 1741036.
- Hoppe-Seyler F, Butz K (2000). "Peptide aptamers: powerful new tools for molecular medicine". J Mol Med. 78 (8): 426–30. doi:10.1007/s001090000140. PMID 11097111. http://link.springer.de/link/service/journals/00109/bibs/0078008/00780426.htm.
- Carothers JM, Oestreich SC, Davis JH, Szostak JW (Apr 2004). "Informational complexity and functional activity of RNA structures". J Am Chem Soc. 126 (16): 5130–7. doi:10.1021/ja031504a. PMID 15099096.
- Cohen BA, Colas P, Brent R (Nov 1998). "An artificial cell-cycle inhibitor isolated from a combinatorial library". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95 (24): 14272–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.24.14272. PMC 24363. PMID 9826690. http://www.pnas.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=9826690.
- Binkowski BF, Miller RA, Belshaw PJ (Jul 2005). "Ligand-regulated peptides: a general approach for modulating protein-peptide interactions with small molecules". Chem Biol. 12 (7): 847–55. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2005.05.021. PMID 16039531.
- Sullenger BA, Gilboa E (Jul 2002). "Emerging clinical applications of RNA". Nature 418 (6894): 252–8. doi:10.1038/418252a. PMID 12110902.
- Ng EW, Shima DT, Calias P, Cunningham ET, Guyer DR, Adamis AP (Feb 2006). "Pegaptanib, a targeted anti-VEGF aptamer for ocular vascular disease". Nat Rev Drug Discov 5 (2): 123–32. doi:10.1038/nrd1955. PMID 16518379.
- Drabovich AP, Berezovski M, Okhonin V, Krylov SN (May 2006). "Selection of smart aptamers by methods of kinetic capillary electrophoresis". Anal Chem. 78 (9): 3171–8. doi:10.1021/ac060144h. PMID 16643010.
- Cho EJ, Lee JW, Ellington, AD (2009). "Applications of Aptamers as Sensors". Annual Review of Analytical Chemistry 2 (1): 241–64. doi:10.1146/annurev.anchem.1.031207.112851. PMID 20636061. http://arjournals.annualreviews.org/doi/abs/10.1146/annurev.anchem.1.031207.112851.
- ^ Gupta S, Thirstrup D, Jarvis TC, Schneider DJ, Wilcox SK, Carter J, Zhang C, Gelinas A, Weiss A, Janjic N, Baird GS. (Jan 2011). "Rapid Histochemistry Using Slow Off-rate Modified Aptamers With Anionic Competition.". Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology 19 (1): Epub ahead of print. doi:10.1097/PAI.0b013e3182008c29. PMID 21217521.
- ^ Huang, J; Ru, B, Zhu, P, Nie, F, Yang, J, Wang, X, Dai, P, Lin, H, Guo, FB, Rao, N (2011-11-03). "MimoDB 2.0: a mimotope database and beyond.". Nucleic Acids Research 40 (1): D271–7. doi:10.1093/nar/gkr922. PMID 22053087.
- ^ Berezovski MV, Lechmann M, Musheev MU, Mak TW, Krylov SN (Jul 2008). "Aptamer-facilitated biomarker discovery (AptaBiD)". J Am Chem Soc. 130 (28): 9137–43. doi:10.1021/ja801951p. PMID 18558676.