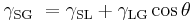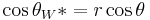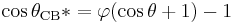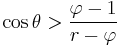Hydrophobe
In chemistry, hydrophobicity (from the combining form of water in Attic Greek hydro- and for fear phobos) is the physical property of a molecule (known as a hydrophobe) that is repelled from a mass of water.[1]
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be non-polar and thus prefer other neutral molecules and non-polar solvents. Hydrophobic molecules in water often cluster together, forming micelles. Water on hydrophobic surfaces will exhibit a high contact angle.
Examples of hydrophobic molecules include the alkanes, oils, fats, and greasy substances in general. Hydrophobic materials are used for oil removal from water, the management of oil spills, and chemical separation processes to remove non-polar from polar compounds.
Hydrophobic is often used interchangeably with lipophilic, "fat loving." However, the two terms are not synonymous. While hydrophobic substances are usually lipophilic, there are exceptions—such as the silicones and fluorocarbons.
Contents |
Chemical background
According to thermodynamics, matter seeks to be in a low-energy state, and bonding reduces chemical energy. Water is electrically polarized, and is able to form hydrogen bonds internally, which gives it many of its unique physical properties. But, since hydrophobes are not electrically polarized, and because they are unable to form hydrogen bonds, water repels hydrophobes, in favour of bonding with itself. It is this effect that causes the hydrophobic interaction—which in itself is misleadingly named as the energetic force comes from the hydrophilic molecules.[2] Thus the two immiscible phases (hydrophilic vs. hydrophobic) will change so that their corresponding interfacial area will be minimal. This effect can be visualized in the phenomenon called phase separation.
Superhydrophobicity
Superhydrophobic surfaces, such as the leaves of the lotus plant, are those that are extremely difficult to wet. The contact angles of a water droplet exceeds 150° and the roll-off angle is less than 10°.[3] This is referred to as the Lotus effect.
Theory
In 1805, Thomas Young defined the contact angle θ by analyzing the forces acting on a fluid droplet resting on a solid surface surrounded by a gas.[4]
where
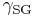 = Interfacial tension between the solid and gas
= Interfacial tension between the solid and gas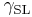 = Interfacial tension between the solid and liquid
= Interfacial tension between the solid and liquid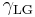 = Interfacial tension between the liquid and gas
= Interfacial tension between the liquid and gas
θ can be measured using a contact angle goniometer.
Wenzel determined that when the liquid is in intimate contact with a microstructured surface, θ will change to θW*
where r is the ratio of the actual area to the projected area.[5] Wenzel's equation shows that microstructuring a surface amplifies the natural tendency of the surface. A hydrophobic surface (one that has an original contact angle greater than 90°) becomes more hydrophobic when microstructured – its new contact angle becomes greater than the original. However, a hydrophilic surface (one that has an original contact angle less than 90°) becomes more hydrophilic when microstructured – its new contact angle becomes less than the original.[6] Cassie and Baxter found that if the liquid is suspended on the tops of microstructures, θ will change to θCB*:
where φ is the area fraction of the solid that touches the liquid.[7] Liquid in the Cassie–Baxter state is more mobile than in the Wenzel state.
We can predict whether the Wenzel or Cassie–Baxter state should exist by calculating the new contact angle with both equations. By a minimization of free energy argument, the relation that predicted the smaller new contact angle is the state most likely to exist. Stated mathematically, for the Cassie–Baxter state to exist, the following inequality must be true.[8]
A recent alternative criterion for the Cassie–Baxter state asserts that the Cassie–Baxter state exists when the following 2 criteria are met: 1) Contact line forces overcome body forces of unsupported droplet weight and 2) The microstructures are tall enough to prevent the liquid that bridges microstructures from touching the base of the microstructures.[9]
A new criterion for the switch between Wenzel and Cassie-Baxter states has been developed recently based on surface roughness and surface energy. [10] The criterion focuses on the air-trapping capability under liquid droplets on rough surfaces, which could tell whether Wenzel's model or Cassie-Baster's model should be used for certain combination of surface roughness and energy.
Contact angle is a measure of static hydrophobicity, and contact angle hysteresis and slide angle are dynamic measures. Contact angle hysteresis is a phenomenon that characterizes surface heterogeneity.[11] When a pipette injects a liquid onto a solid, the liquid will form some contact angle. As the pipette injects more liquid, the droplet will increase in volume, the contact angle will increase, but its three phase boundary will remain stationary until it suddenly advances outward. The contact angle the droplet had immediately before advancing outward is termed the advancing contact angle. The receding contact angle is now measured by pumping the liquid back out of the droplet. The droplet will decrease in volume, the contact angle will decrease, but its three phase boundary will remain stationary until it suddenly recedes inward. The contact angle the droplet had immediately before receding inward is termed the receding contact angle. The difference between advancing and receding contact angles is termed contact angle hysteresis and can be used to characterize surface heterogeneity, roughness, and mobility. Surfaces that are not homogeneous will have domains which impede motion of the contact line. The slide angle is another dynamic measure of hydrophobicity and is measured by depositing a droplet on a surface and tilting the surface until the droplet begins to slide. Liquids in the Cassie–Baxter state generally exhibit lower slide angles and contact angle hysteresis than those in the Wenzel state.
Research and development
The self-cleaning property of superhydrophobic micro-nanostructured surfaces was reported in 1977,[12] and perfluoroalkyl and perfluoropolyether superhydrophobic materials were developed in 1986 for handling chemical and biological fluids. Other biotechnical applications have emerged since the 1990s.[13][14][15][16][17]
In recent research, superhydrophobicity has been reported by allowing alkylketene dimer (AKD) to solidify into a nanostructured fractal surface.[18] Many papers have since presented fabrication methods for producing superhydrophobic surfaces including particle deposition,[19] sol-gel techniques,[20] plasma treatments,[21] vapor deposition,[22] and casting techniques.[23] Current opportunity for research impact lies mainly in fundamental research and practical manufacturing.[24] Debates have recently emerged concerning the applicability of the Wenzel and Cassie–Baxter models. In an experiment designed to challenge the surface energy perspective of the Wenzel and Cassie–Baxter model and promote a contact line perspective, water drops were placed on a smooth hydrophobic spot in a rough hydrophobic field, a rough hydrophobic spot in a smooth hydrophobic field, and a hydrophilic spot in a hydrophobic field.[25] Experiments showed that the surface chemistry and geometry at the contact line affected the contact angle and contact angle hysteresis, but the surface area inside the contact line had no effect. An argument that increased jaggedness in the contact line enhances droplet mobility has also been proposed.[26]
Many very hydrophobic materials found in nature rely on Cassie's law and are biphasic on the submicrometer level with one component air. The Lotus effect is based on this principle. Inspired by it, a lot of functional superhydrophobic surfaces were prepared.[27]
An example of a biomimetic superhydrophobic material in nanotechnology is nanopin film. In one study a vanadium pentoxide surface is presented that can switch reversibly between superhydrophobicity and superhydrophilicity under the influence of UV radiation.[28] According to the study any surface can be modified to this effect by application of a suspension of rose-like V2O5 particles for instance with an inkjet printer. Once again hydrophobicity is induced by interlaminar air pockets (separated by 2.1 nm distances). The UV effect is also explained. UV light creates electron-hole pairs, with the holes reacting with lattice oxygen creating surface oxygen vacancies while the electrons reduce V5+ to V3+. The oxygen vacancies are met by water and this water absorbency by the vanadium surface makes it hydrophilic. By extended storage in the dark, water is replaced by oxygen and hydrophilicity is once again lost.
Potential applications
Active recent research on superhydrophobic materials might eventually lead to industrial applications. For example, a simple routine of coating cotton fabric with silica[29] or titania[30] particles by sol-gel technique has been reported, which protects the fabric from UV light and makes it superhydrophobic. Also, an efficient routine has been reported for making polyethylene superhydrophobic and thus self-cleaning[31]—99% of dirt adsorbed on such surface is easily washed away. Patterned superhydrophobic surfaces also have the promises for the lab-on-a-chip, microfluidic devices and can drastically improve the surface based bioanalysis.[32]
See also
References
- ^ Aryeh Ben-Na'im Hydrophobic Interaction Plenum Press, New York, ISBN 0-306-40222-X
- ^ Goss, Kai-Uwe; Schwarzenbach, René P. (2003). "Rules of Thumb for Assessing Equilibrium Partitioning of Organic Compounds: Successes and Pitfalls". Journal of Chemical Education 80 (4): 450. Bibcode 2003JChEd..80..450G. doi:10.1021/ed080p450.
- ^ Wang, Shutao; Jiang, L. (2007). "Definition of superhydrophobic states". Advanced Materials 19 (21): 3423–3424. doi:10.1002/adma.200700934.
- ^ Young, T. (1805). "An Essay on the Cohesion of Fluids". Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 95: 65–87. doi:10.1098/rstl.1805.0005.
- ^ Wenzel, RN (1936). "Resistance of Solid Surfaces to Wetting by Water". Ind. Eng. Chem. 28 (8): 988–994. doi:10.1021/ie50320a024.
- ^ de Gennes, Pierre-Gilles (2004). Capillarity and Wetting Phenomena. ISBN 0387005927.
- ^ Cassie, ABD; Baxter, S. (1944). "Wettability of Porous Surfaces". Trans. Faraday Soc. 40: 546–551. doi:10.1039/tf9444000546.
- ^ Quere, D (2005). "Non-sticking Drops". Reports on Progress in Physics 68 (11): 2495–2532. Bibcode 2005RPPh...68.2495Q. doi:10.1088/0034-4885/68/11/R01.
- ^ Extrand, C (2005). "Modeling of ultralyophobicity: Suspension of liquid drops by a single asperity". Langmuir 21 (23): 10370–10374. doi:10.1021/la0513050.
- ^ Zhang, YL; Sundararajan, Sriram (2008). "Superhydrophobic engineering surfaces with tunable air-trapping ability". Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering 18 (3): 035024. Bibcode 2008JMiMi..18c5024Z. doi:10.1088/0960-1317/18/3/035024.
- ^ Johnson, RE; Dettre, Robert H. (1964). "Contact Angle Hysteresis". J. Phys. Chem. 68 (7): 1744–1750. doi:10.1021/j100789a012.
- ^ Barthlott, Wilhelm; Ehler, N. (1977). "Raster-Elektronenmikroskopie der Epidermis-Oberflächen von Spermatophyten". Tropische und subtropische Pflanzenwelt (Akad. Wiss. Lit. Mainz) 19: 110.
- ^ Barthlott, Wilhelm; C. Neinhuis (1997). "The purity of sacred lotus or escape from contamination in biological surfaces". Planta 202: 1–8. doi:10.1007/s004250050096.
- ^ Cheng, Y. T., Rodak, D. E. (2005). "Is the lotus leaf superhydrophobic?". Appl. Phys. Lett. 86 (14): 144101. Bibcode 2005ApPhL..86n4101C. doi:10.1063/1.1895487.
- ^ Narhe, R. D., Beysens, D. A. (2006). "Water condensation on a super-hydrophobic spike surface". Europhys. Lett. 75 (1): 98–104. Bibcode 2006EL.....75...98N. doi:10.1209/epl/i2006-10069-9.
- ^ Lai, S.C.S.. "Mimicking nature: Physical basis and artificial synthesis of the Lotus effect". http://members.ziggo.nl/scslai/lotus.pdf.
- ^ Koch, K.; Bhushan, B. & Barthlott, W. (2008). "Diversity of structure, Morphology and Wetting of Plant Surfaces. Soft matter". Soft Matter 4 (10): 1943. doi:10.1039/b804854a.
- ^ Onda, T.; Shibuichi, S.; Satoh, N.; Tsujii, K. (1996). "Super-Water-Repellent Fractal Surfaces". Langmuir 12 (9): 2125–2127. doi:10.1021/la950418o.
- ^ Miwa, M; Nakajima, Akira; Fujishima, Akira; Hashimoto, Kazuhito; Watanabe, Toshiya (2000). "Effects of the Surface Roughness on Sliding Angles of Water Droplets on Superhydrophobic Surfaces". Langmuir 16 (13): 5754–60. doi:10.1021/la991660o.
- ^ Shirtcliffe, NJ; McHale, G.; Newton, M. I.; Perry, C. C. (2003). "Intrinsically superhydrophobic organosilica sol-gel foams". Langmuir 19 (14): 5626–5631. doi:10.1021/la034204f.
- ^ Teare, DOH; Spanos, C. G.; Ridley, P.; Kinmond, E. J.; Roucoules, V.; Badyal, J. P. S.; Brewer, S. A.; Coulson, S. et al. (2002). "Pulsed plasma deposition of super-hydrophobic nanospheres". Chemistry of Materials 14 (11): 4566–4571. doi:10.1021/cm011600f.
- ^ Miwa, M; Nakajima, Akira; Fujishima, Akira; Hashimoto, Kazuhito; Watanabe, Toshiya (2000). "Effects of the surface roughness on sliding angles of water droplets on superhydrophobic surfaces". Langmuir 16 (13): 5754–5760. doi:10.1021/la991660o.
- ^ Bico, J; Marzolin, C; Quéré, D (1999). "Pearl drops". Europhysics Letters 47 (6): 743–744. Bibcode 1999EL.....47..743B. doi:10.1209/epl/i1999-00453-y.
- ^ Extrand, C (2008). "Self-Cleaning Surfaces: An Industrial Perspective". MRS Bulletin: 733.
- ^ Gao, LC; McCarthy, TJ (2007). "How Wenzel and Cassie Were Wrong". Langmuir 23 (7): 3762–3765. doi:10.1021/la062634a. PMID 17315893.
- ^ Chen, W; Fadeev, Alexander Y.; Hsieh, Meng Che; Öner, Didem; Youngblood, Jeffrey; McCarthy, Thomas J. (1999). "Ultrahydrophobic and ultralyophobic surfaces: Some comments and examples". Langmuir 15 (10): 3395–3399. doi:10.1021/la990074s.
- ^ Wang, S.T.; Liu, Huan; Jiang, Lei (2006). "Recent process on bio-inspired surface with special wettability". Annual Review of Nano Research 1: 573–628. doi:10.1142/9789812772374_0013.
- ^ UV-Driven Reversible Switching of a Roselike Vanadium Oxide Film between Superhydrophobicity and SuperhydrophilicityHo Sun Lim, Donghoon Kwak, Dong Yun Lee, Seung Goo Lee, and Kilwon Cho J. Am. Chem. Soc.; 2007; 129(14) pp. 4128–4129; (Communication) doi:10.1021/ja0692579
- ^ C-H Xue et al. "Preparation of superhydrophobic surfaces on cotton textiles" Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 9 (2008) 035008 free download
- ^ C-H Xue et al. "Superhydrophobic cotton fabrics prepared by sol–gel coating of TiO2 and surface hydrophobization" Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 9 (2008) 035001 free download
- ^ Z. Yuan et al. "Preparation and characterization of self-cleaning stable superhydrophobic linear low-density polyethylene" Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 9 (2008) 045007 free download
- ^ Ressine, A.; Marko-Varga, G., Laurell, T. (2007). "Porous silicon protein microarray technology and ultra-/superhydrophobic states for improved bioanalytical readout". Biotechnology Annual Review 13: 149–200. doi:10.1016/S1387-2656(07)13007-6. PMID 17875477.
External links
|
||||||||||||||