Answer/seizure ratio
The answer/seizure ratio (ASR) is a measurement of network quality and call success rate in telecommunications. It is the percentage of answered telephone calls with respect to the total call volume.
Definition
The answer/seizure ratio is defined as 100 times the ratio of successfully answered calls divided by the total number of call attempts (seizures):
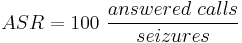
Busy signals and other rejections by the called number count as call failures. This makes the ASR highly dependent on end-user action or behavior and is out of control by the telecommunications carrier. Low ASR values may be caused by far-end switch congestion, not answering by called parties and busy destination lines.
The ASR is a measure of network quality defined by the ITU.[1]
See also
References
- ^ ITU SG2 Recommendation E.411: International network management - Operational guidance.