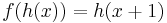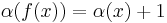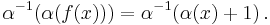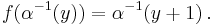Abel equation
The Abel equation, named after Niels Henrik Abel, is special case of functional equations which can be written in the form
or
and shows non-trivial properties at the iteration.
Contents |
Equivalence
These equations are equivalent. Assuming that α is an invertible function, the second equation can be written as
Taking 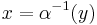 , the equation can be written as
, the equation can be written as
For a function f(x) assumed to be known, the task is to solve the functional equation for the function α−1, possibly satisfying additional requirements, such as α−1(0)=1.
The change of variables sα(x) = Ψ(x), for a real parameter s, brings Abel's equation into the celebrated Schröder's equation, Ψ (f(x)) = s Ψ (x) .
History
Initially, the equation in the more general form [1] [2] was reported. Then it happens that even in the case of single variable, the equation is not trivial, and requires special analysis [3][4]
In the case of linear transfer function, the solution can be expressed in compact form [5]
Special cases
Equation of tetration is special case of Abel's equation, with 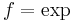 . In the case of integer argument, the equation is just a recurrent procedure.
. In the case of integer argument, the equation is just a recurrent procedure.
See also
References
- ^ Abel, N.H. (1826). "Untersuchung der Functionen zweier unabhängig veränderlichen Größen x und y, wie f(x, y), welche die Eigenschaft haben, ...". Journal für die reine und angewandte Mathematik 1: 11–15. http://gdz.sub.uni-goettingen.de/ru/dms/load/img/?PPN=PPN243919689_0001&DMDID=dmdlog6.
- ^ A. R. Schweitzer (1903). "Theorems on functional equations". Bulletin des Sciences Mathématiques 27 (2): 31. http://projecteuclid.org/DPubS/Repository/1.0/Disseminate?handle=euclid.bams/1183421988&view=body&content-type=pdf_1.
- ^ G. Belitskii; Yu. Lubish (1999). "The real-analytic solutions of the Abel functional equations". Studia Mathematica 134 (2): 135–141. http://matwbn.icm.edu.pl/ksiazki/sm/sm134/sm13424.pdf.
- ^ Jitka Laitochová (2007). "Group iteration for Abel’s functional equation". Nonlinear Analysis: Hybrid Systems 1 (1): 95–102. doi:10.1016/j.nahs.2006.04.002.
- ^ G. Belitskii; Yu. Lubish (1998). "The Abel equation and total solvability of linear functional equtions". Studia Mathematica 127: 81–89. http://matwbn.icm.edu.pl/ksiazki/sm/sm127/sm12716.pdf.