AC/DC
| AC/DC | |
|---|---|
AC/DC, from L-R: Brian Johnson, Malcolm Young, Phil Rudd, Angus Young, Cliff Williams, live in Tacoma, Washington, 31 August 2009. |
|
| Background information | |
| Origin | Sydney, Australia |
| Genres | Hard rock, heavy metal, blues rock, rock and roll |
| Years active | 1973–present |
| Labels | Albert, EMI, Columbia, Epic, Atlantic, Atco, Elektra, East West |
| Associated acts | Geordie, The Easybeats, Fraternity, The Valentines, Marcus Hook Roll Band, Rhino Bucket |
| Website | www.acdc.com |
| Members | |
| Malcolm Young Angus Young Phil Rudd Cliff Williams Brian Johnson |
|
| Past members | |
| Dave Evans Larry Van Kriedt Colin Burgess Neil Smith Ron Carpenter Russell Coleman Noel Taylor Peter Clack Rob Bailey Bon Scott Mark Evans Simon Wright Chris Slade |
|
AC/DC are an Australian rock band, formed in 1973 by brothers Malcolm and Angus Young. Commonly classified as hard rock, they are considered pioneers of heavy metal and are sometimes classified as so,[1][2] though they themselves have always classified their music as simply "rock and roll".[3] To date they are one of the highest grossing bands of all time. AC/DC underwent several line-up changes before releasing their first album, High Voltage, on 17 February 1975. Membership remained stable until bassist Mark Evans was replaced by Cliff Williams in 1977 for the album Powerage. Within months of recording the album Highway to Hell, lead singer and co-songwriter Bon Scott died on 19 February 1980, after a night of heavy alcohol consumption. The group briefly considered disbanding, but Scott's parents urged them to continue and hire a new vocalist. Ex-Geordie singer Brian Johnson was auditioned and selected to replace Scott. Later that year, the band released their highest selling album, and ultimately the second highest-selling album by any artist, Back in Black.
The band's next album, For Those About to Rock We Salute You, was their first album to reach number one in the United States. AC/DC declined in popularity soon after drummer Phil Rudd was fired in 1983 and was replaced by future Dio drummer Simon Wright, though the band resurged in the early 1990s with the release of The Razors Edge. Phil Rudd returned in 1994 (after Chris Slade, who was with the band from 1990–1994, was asked to leave in favour of him) and contributed to the band's 1995 album Ballbreaker. Since then, the band's line-up has remained the same. Stiff Upper Lip was released in 2000 and was well received by critics, and the band's latest studio album, Black Ice, was released on 20 October 2008. It was their biggest hit on the charts since For Those About to Rock, reaching No.1 on all the charts eventually.[4]
As of 2010, AC/DC have sold more than 200 million albums worldwide,[5] as of the releases of their latest albums, Black Ice and the Iron Man 2 soundtrack, including 71 million albums in the United States.[6] Back in Black has sold an estimated 49 million units worldwide, making it the highest-selling album by any band and the second-highest-selling album in history, behind Thriller by Michael Jackson.[7][8] The album has sold 22 million in the US alone, where it is the fifth-highest-selling album.[9] AC/DC ranked fourth on VH1's list of the "100 Greatest Artists of Hard Rock"[10][11] and were named the seventh "Greatest Heavy Metal Band of All Time" by MTV.[12] In 2004, AC/DC were ranked number 72 in the Rolling Stone list of the "100 Greatest Artists of All Time".[13] In 2010, AC/DC were ranked number 23 in the VH1 list of the "100 Greatest Artists of All Time".[14]
Contents |
History
Background and name
Brothers Malcolm, Angus, and George Young were born in Glasgow, Scotland, and moved to Sydney with most of their family in 1963. George was the first to learn to play the guitar. He became a member of the Easybeats, one of Australia's most successful bands of the 1960s. In 1966, they became the first local rock act to have an international hit, with the song "Friday on My Mind".[15] Malcolm followed in George's footsteps by playing with a Newcastle, New South Wales, band called the Velvet Underground (not to be confused with the New York–based Velvet Underground).[16] Their Oldest brother Alex Young chose to remain in Britain to pursue musical interests. In 1967, Alexander formed and played bass in the London-based band Grapefruit—initially called "The Grapefruit"—with three former members of Tony Rivers and the Castaways, John Perry, Geoff Swettenham, and Pete Swettenham.
Malcolm and Angus Young developed the idea for the band's name after their older sister, Margaret Young, saw the initials "AC/DC" on a sewing machine.[17] "AC/DC" is an abbreviation meaning "alternating current/direct current" electricity. The brothers felt that this name symbolised the band's raw energy, power-driven performances, and a love for their music.[17][18][19] "AC/DC" is pronounced one letter at a time, though the band are colloquially known as "Acca Dacca" in Australia.[20][21]
Early years (the Dave Evans era, 1973–1974)
In November 1973 Malcolm and Angus Young formed AC/DC and recruited bassist Larry Van Kriedt, vocalist Dave Evans, and Colin Burgess, ex-Masters Apprentices drummer.[22] Pushing hard for the bands success were Australia’s legendary roadie Ray Arnold and his partner Alan Kissack. The two men convinced Chequers entertainment manager Gene Pierson to let the band play at the popular Sydney nightclub on New Year's Eve, 1973.[23] The band was so loud however that management complained. Pierson however took an interest, and booked them into the Bondi Lifesaver and other venues where they further developed their stage show. The early line-up of the band changed often; Colin Burgess was the first member fired, and several bassists and drummers passed through the band during the next year.
By this time, Angus Young had adopted his characteristic school-uniform stage outfit. The idea was his sister Margaret's. Angus had tried other costumes, such as Spider-Man, Zorro, a gorilla, and a parody of Superman, named Super-Ang.[16] In fact in its early days, most members of the band dressed in some form of glam or satin outfit but this approach was abandoned when it was discovered Melbourne band Skyhooks had already adopted this approach to their stage presentation.
The Young brothers decided that Evans was not a suitable frontman for the group, because they felt he was more of a glam rocker like Gary Glitter.[24] On stage, Evans was occasionally replaced by the band's first manager, Dennis Laughlin, who was the original lead singer with Sherbet prior to Daryl Braithwaite joining the band. Evans did not get along with Laughlin, which also contributed to the band's ill feeling toward Evans.[24]
It was Gene Pierson who brokered the arrangement for Bon Scott from Fraternity to join them as lead singer. He was also instrumental in getting personal friend Ted Albert of Albert Productions to listen to AC/DC and arranged with programme manager Rod Muir of Australia’s biggest rock station 2SM to have them on the bill for one of their massive school holiday concerts back at Chequers which helped launch AC/DC's career and led to their being signed to the EMI-distributed Albert Productions label for Australia and New Zealand.
The Bon Scott era (1974–1980)
The journey begins (1974–77)
In September 1974 Ronald Belford "Bon" Scott, an experienced vocalist and friend of George Young, replaced Dave Evans. Like the Young brothers, Scott had been born in Scotland before emigrating to Australia in his childhood. The band had recorded only one single with Evans, "Can I Sit Next to You, Girl" / "Rockin' in the Parlour"; eventually, the song was re-recorded with Bon Scott as "Can I Sit Next to You Girl" (Track 7 on the Australian album T.N.T. (1975), and Track 6 on the international release of High Voltage) (1976).
By October 1974, the Australia-only album High Voltage had been recorded. It took only ten days[25] and was based on instrumental songs written by the Young brothers, with lyrics added by Scott. Within a few months, the band's line-up had stabilised, featuring Scott, the Young brothers, bassist Mark Evans and drummer Phil Rudd. Later that year they released the single "It's a Long Way to the Top (If You Wanna Rock 'n' Roll)", which became their perennial rock anthem.[26] It was included on their second album, T.N.T., (1975) which was also released only in Australia and New Zealand. The album featured another classic song, "High Voltage".
Between 1974 and 1977, aided by regular appearances on Molly Meldrum's Countdown, the ABC’s nationally broadcast pop-music television show, AC/DC became one of the most popular and successful acts in Australia. Their performance on 3 April 1977 was their last live TV appearance for more than 20 years.[25]
International success (1976–80)
In 1976, the band signed an international deal with Atlantic Records and toured extensively throughout Europe including their first UK tour with 'Sounds' Magazine called The 'Lock up your Daughters Summer Tour'. They gained invaluable experience of the stadium circuit, supporting leading rock acts such as Black Sabbath, Aerosmith, Kiss, Styx, UFO, and Blue Öyster Cult, and co-headlined with Cheap Trick.[25]
The first AC/DC album to gain worldwide distribution was a 1976 compilation of tracks taken from the High Voltage and T.N.T. LPs. Also titled High Voltage, and released on the Atlantic Records label, the album, which has to date sold three million copies worldwide,[27] gained the band a following among the then-substantial British punk audience.[28] The track selection was heavily weighted toward the more recent T.N.T., and included only two songs from their first LP. The band's next album, Dirty Deeds Done Dirt Cheap, was released in the same year in both Australian and international versions, like its predecessor. Track listings varied worldwide, and the international version of the album also featured "Rocker" from T.N.T. The original Australian version included "Jailbreak" (now more readily available on the 1984 compilation EP '74 Jailbreak or as a live version on the 1992 Live album). Dirty Deeds was not released in the US until 1981, by which time the band were at the peak of their popularity.
Following the 1977 recording Let There Be Rock, bassist Mark Evans was sacked because of personal differences with Angus Young. He was replaced by Cliff Williams, who also provided backing vocals alongside Malcolm Young. Neither of the Young brothers has elaborated on the departure of Evans, though Richard Griffiths, the CEO of Epic Records and a booking agent for AC/DC in the mid-1970s, later commented, "You knew Mark wasn't going to last, he was just too much of a nice guy."[16] Mark Evan's autobiography, DIRTY DEEDS: My Life Inside/Outside of AC/DC is scheduled to be released fall 2011 by Bazillion Points, and will predominantly deal with his time in AC/DC, including being fired.[29]
AC/DC were a somewhat formative influence on New Wave of British Heavy Metal bands who emerged in the late 1970s, such as Saxon and Iron Maiden, in part as a reaction to the decline of traditional early 1970s hard rock bands. In 2007, critics noted that AC/DC, along with Thin Lizzy, UFO, Scorpions and Judas Priest, were among "the second generation of rising stars ready to step into the breach as the old guard waned."[30]
AC/DC's first American exposure was through the Michigan radio station AM 600 WTAC in 1977. The station's manager, Peter C. Cavanaugh, booked the band to play at Flint's Capitol Theater. The supporting act was MC5, who had just briefly reunited and agreed to play at the event. The band opened with their popular song "Live Wire" and closed with "It's a Long Way to the Top (If You Wanna Rock 'n' Roll)".[31]
AC/DC came to be identified with the punk rock movement by the British press. Their reputation, however, managed to survive the punk upheavals of the late 1970s, and they maintained a cult following in the UK throughout this time.[3] Angus Young gained notoriety for mooning the audience during live performances.
The 1978 release of Powerage marked the debut of bassist Cliff Williams, and with its harder riffs, followed the blueprint set by Let There Be Rock.[32] Only one single was released for Powerage, "Rock 'n' Roll Damnation" and gave AC/DC the highest mark at the time, reaching #24. Eddie Van Halen notes this to be his favourite AC/DC record, along with Highway To Hell.[33] An appearance at the Apollo Theatre, Glasgow during the Powerage tour was recorded and released as If You Want Blood You've Got It, featuring such songs as "Whole Lotta Rosie", "Problem Child", and "Let There Be Rock", as well as lesser-known album tracks like "Riff Raff". The album was the last produced by Harry Vanda and George Young with Bon Scott on vocals and is claimed to be AC/DC's most under-rated album.[34]
The major breakthrough in the band's career came in their collaboration with producer "Mutt" Lange on a sixth album Highway to Hell, released in 1979. It became the first AC/DC LP to break into the US top 100, eventually reaching #17,[25] and it propelled AC/DC into the top ranks of hard rock acts.[3] Highway to Hell had lyrics that shifted away from flippant and comical toward more central rock themes, putting increased emphasis on backing vocals but still featured AC/DC's signature sound: loud, simple, pounding riffs and grooving backbeats.[35] The final track, "Night Prowler", has two breaths in quick succession at the start of the song, intended to create a tone of fear and loathing.[3]
Scott's death (1980)
As 1980 began, the band began work on a new album that would eventually become Back in Black, but Bon Scott would not live to see the project being finished. On 19 February 1980, Scott passed out in the car on the way back to friend Alistair Kinnear's house after a night of heavy drinking at the Music Machine club in London. Upon arrival at his home, Kinnear was unable to move Scott from the car into his home for the night, so he left him in the car overnight to sleep off the effects of the alcohol. Unable to wake Scott late the next morning, Kinnear rushed him to King's College Hospital in Camberwell, where Scott was pronounced dead on arrival. Pulmonary aspiration of vomit was the cause of Scott's death,[36] and the official cause was listed as "acute alcohol poisoning".[37] Scott's family buried him in Fremantle, Western Australia, the area they emigrated to when he was a boy.[38]
Inconsistencies in the official accounts of Scott's death have been cited in conspiracy theories, which suggest that Scott died of a heroin overdose, or was killed by exhaust fumes redirected into the car, or that Kinnear did not exist.[37] Additionally, Scott was asthmatic,[39] and the temperature was below freezing on the morning of his death.
The Brian Johnson era (1980–present)
The rebirth (1980–83)
Following Scott's death, the band briefly considered quitting; they eventually concluded, however, that Scott would have wanted AC/DC to continue, and various candidates were considered for his replacement, including Buzz Shearman, ex-Moxy member, who was not able to join because of voice problems,[40] ex-Back Street Crawler vocalist Terry Slesser and then Slade vocalist, Noddy Holder.[41] The remaining AC/DC members finally decided on ex-Geordie singer Brian Johnson.
Angus Young later recalled, "I remember the first time I had ever heard Brian's (Johnson) name was from Bon. Bon had mentioned that he had been in England once touring with a band and he had mentioned that Brian had been in a band called Geordie and Bon had said 'Brian Johnson, he was a great rock and roll singer in the style of Little Richard.' And that was Bon's big idol, Little Richard. I think when he saw Brian at that time, to Bon it was 'Well he's a guy that knows what rock and roll is all about.' He mentioned that to us in Australia. I suppose when we decided to continue, Brian was the first name that Malcolm and myself came up with, so we said we should see if we can find him.",[42] For the audition, Johnson sang "Whole Lotta Rosie" from Let There Be Rock and Ike & Tina Turner's "Nutbush City Limits".[19] He was hired a few days after the audition.
With Brian Johnson the band completed the songwriting that they had begun with Bon Scott for the album Back in Black. Recording took place at Compass Point Studios in the Bahamas a few months after Scott's death. Back in Black, produced by Mutt Lange and recorded by Tony Platt, became their biggest-selling album and a hard-rock landmark; hits include "Hells Bells", "You Shook Me All Night Long", and the title track. The album was certified platinum three months after its release, and by 2007 it had sold more than 22 million copies in the United States and over 45 million world wide, making it the fourth-highest-selling album ever in the US and the second highest selling in the world (second to Michael Jackson's Thriller).[9] The album reached No.1 in the UK and No.4 in the US, where it spent 131 weeks on the Billboard 200 album chart.[25]
The follow-up album, 1981's For Those About to Rock We Salute You, also sold well and was positively received by critics. The album featured two of the band's most popular singles: "Let's Get It Up"[43] and the title track, "For Those About to Rock", which reached No.13 and No.15 in the UK, respectively. The band split with Lange for their self-produced 1983 album, Flick of the Switch, in an effort to recover the rawness and simplicity of their early albums.[44]
Departure of Rudd and commercial decline (1983–87)
Amid rumours of alcoholism and drug-induced paranoia, drummer Phil Rudd's friendship with Malcolm Young deteriorated and, after a long period of unfriendliness, the men's dislike for each other grew so strong that they fought. Rudd was fired two hours after the fight.[19] Session drummer B.J. Wilson was drafted in to help complete the recordings, but his drum parts were eventually not used.[45] Although Rudd had finished the drum tracks for their next album, he was replaced by Simon Wright in the summer of 1983 after the band held an anonymous audition.
Later in the year, AC/DC released the self-produced album Flick of the Switch, which was less successful than their previous albums, and was considered underdeveloped and unmemorable.[44] One critic stated that the band "had made the same album nine times".[46] AC/DC was voted the eighth-biggest disappointment of the year in the 1984 Kerrang! readers' poll. However, Flick of the Switch eventually reached No.4 on the UK charts,[19] and AC/DC had minor success with the singles "Nervous Shakedown" and "Flick of the Switch". Fly on the Wall, produced by the Young brothers in 1985, was also regarded as uninspired and directionless.[47] A music concept video of the same name featured the band at a bar, playing five of the album's ten songs.
In 1986, the group returned to the charts with the made-for-radio "Who Made Who". The album Who Made Who was the soundtrack to Stephen King's film Maximum Overdrive,[34] It brought together older hits, such as "You Shook Me All Night Long" and "Ride On", with newer songs such as title track "Who Made Who", and two new instrumentals, "D.T." and "Chase the Ace".
In February 1988, AC/DC were inducted into the Australian Recording Industry Association's Hall of Fame.[48]
Back to commercial success (1987–90)
AC/DC's 1988 album, Blow Up Your Video, was recorded at Studio Miraval in Le Val (Occitania), France, and reunited the band with their original producers, Harry Vanda and George Young. The group recorded nineteen songs, choosing ten for the final release; though the album was later criticised for containing excessive "filler",[49] it was a commercial success. Blow Up Your Video sold more copies than the previous two studio releases combined, reaching No.2 on the UK charts—AC/DC's highest position since "Back in Black" in 1980. The album featured the UK top-twenty single "Heatseeker"[43] and popular songs such as "That's the Way I Wanna Rock 'n' Roll". The Blow Up Your Video World Tour began in February 1988, in Perth, Australia. That April, following live appearances across Europe, Malcolm Young announced that he was taking time off from touring, principally to begin recovery from his alcoholism. Another member of the Young family, Stevie Young, temporarily took Malcolm's place.
Following the tour, Wright left the group to work on the upcoming Dio album Lock Up the Wolves, and was replaced by session veteran Chris Slade. Johnson was unavailable for several months while finalising his divorce,[19] so the Young brothers wrote all the songs for the next album, a practice they continued for all subsequent releases through Black Ice in 2008.
Popularity regained (1990–94)
The next album, The Razors Edge, was recorded in Vancouver, Canada, and was mixed and engineered by Mike Fraser and produced by Bruce Fairbairn, who had previously worked with Aerosmith and Bon Jovi. Released in 1990, it was a major comeback for the band, and included the hits "Thunderstruck" and "Are You Ready", which reached No.5 and No.16 respectively on Billboard's Mainstream Rock Tracks Chart, and "Moneytalks", which peaked at No.23 on the Billboard Hot 100.[43] The album went multi-platinum and reached the US top ten. Several shows on the Razors Edge tour were recorded for the 1992 live album, titled Live. Live was produced by Fairbairn, and is considered one of the best live albums of the 1990s.[50] It was during this tour when AC/DC headlined the Monsters of Rock show, which was released on DVD as Live at Donington. A year later, AC/DC recorded "Big Gun" for the soundtrack of the Arnold Schwarzenegger movie Last Action Hero, and was released as a single, reaching No.1 on the US Mainstream Rock chart, the band's first No.1 single on that chart.[25]
Popularity confirmed (1994–2008)
In 1994, Angus and Malcolm invited Rudd to several jam sessions. He was eventually rehired to replace Slade, whose amicable departure arose in part because of the band's strong desire to again work with Rudd. Recorded at the Ocean Way Studios in Los Angeles, California by a 1980–83 line-up back together and produced by Rick Rubin, Ballbreaker was released in 1995. The first single from the album was "Hard as a Rock". Two more singles were released from the album: "Hail Caesar" and "Cover You in Oil".
In 1997, a box set named Bonfire was released. It contained four albums; a remastered version of Back in Black; Volts (a disc with alternate takes, outtakes, and stray live cuts) and two live albums, Live from the Atlantic Studios and Let There Be Rock: The Movie. Live from the Atlantic Studios was recorded on 7 December 1977 at the Atlantic Studios in New York. Let There Be Rock: The Movie was a double album recorded in 1979 at the Pavillon de Paris and was the soundtrack of a motion picture, AC/DC: Let There Be Rock. The US version of the box set included a colour booklet, a two-sided poster, a sticker, a temporary tattoo, a keychain bottle opener, and a guitar pick.[51]
In 2000, the band released Stiff Upper Lip, produced by brother George Young at the Warehouse Studio, again in Vancouver. The album was better received by critics than Ballbreaker but was considered lacking in new ideas.[52][53] The Australian release included a bonus disc with three promotional videos and several live performances recorded in Madrid, Spain in 1996. Stiff Upper Lip reached No.1 in five countries, including Argentina and Germany; No.2 in three countries, Spain, France and Switzerland; No.3 in Australia; No.5 in Canada and Portugal; and No.7 in Norway, the US and Hungary. The first single, "Stiff Upper Lip", remained at No.1 on the US Mainstream Rock charts for four weeks.[25] The other singles released also did very well; "Satellite Blues" and "Safe in New York City" reached No.7 and No.31 on Billboard's Mainstream Rock Tracks, respectively.
In 2002, AC/DC signed a long-term, multi-album deal with Sony Music,[54] who went on to release a series of remastered albums as part of their AC/DC remasters series. Each release contained an expanded booklet featuring rare photographs, memorabilia, and notes.[55] In 2003, the entire back-catalogue (except Ballbreaker and Stiff Upper Lip) was remastered and re-released. Ballbreaker was eventually re-released in October 2005; Stiff Upper Lip was later re-released in April 2007.
On 30 July 2003, the band performed with the Rolling Stones and Rush at Molson Canadian Rocks for Toronto. The concert, held before an audience of half a million, was intended to help the city overcome the negative publicity stemming from the effects of a 2003 SARS epidemic. The concert holds the record for the largest paid music event in North American history.[56] The band came second in a list of Australia's highest-earning entertainers for 2005,[57] and sixth for 2006,[58] despite having neither toured since 2003 nor released an album since 2000. Verizon Wireless has gained the rights to release AC/DC's full albums and the entire Live at Donington concert to download in 2008.[59]
On 16 October 2007, Columbia Records released a double and triple DVD titled Plug Me In. The set consists of five and seven hours of rare footage, and even a recording of AC/DC at a high school performing "School Days", "T.N.T.", "She's Got Balls", and "It's a Long Way to the Top (If You Wanna Rock 'n' Roll)". As with Family Jewels, disc one contains rare shows of the band with Bon Scott, and disc two is about the Brian Johnson era. The collector's edition contains an extra DVD with 21 more rare performances of both Scott and Johnson and more interviews.[60]
AC/DC made their video game debut on Rock Band 2, with "Let There Be Rock" included as a playable track.[61] The setlist from their Live at Donington live album was released as playable songs for the Rock Band series by means of a Wal-Mart-exclusive retail disc titled AC/DC Live: Rock Band Track Pack.[62]
No Bull: The Directors Cut, a newly edited, comprehensive Blu-ray and DVD of the band's July 1996 Plaza De Toros de las Ventas concert in Madrid, Spain, was released on 9 September 2008.[63]
Black Ice (2008–2011)
On 18 August 2008, Columbia Records announced 18 October Australian release, and 20 October worldwide release, of the studio album Black Ice. The 15-track album was the band's first studio release in eight years, was produced by Brendan O'Brien and was mixed and engineered by Mike Fraser. Like Stiff Upper Lip, it was recorded at The Warehouse Studio in Vancouver, British Columbia. Black Ice was sold in the US exclusively at Wal-Mart and Sam's Club and the band's official website.[64]
"Rock 'n' Roll Train", the album's first single, was released to radio on 28 August. On 15 August, AC/DC recorded a video for a song from the new album in London with a special selection of fans getting the chance to be in the video.[65] Black Ice made history debuting at No.1 on album charts in 29 countries and also has the distinction of being Columbia Records' biggest debut album (since Nielsen SoundScan began tracking sales data for Billboard in March 1991). Black Ice has been certified Multi Platinum in eight countries, including the US, Australia, Canada, Switzerland, Sweden, Norway, Germany and the Czech Republic. Additionally Black Ice has achieved Platinum status in twelve countries (Austria, Belgium, Denmark, Finland, France, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, UK, Argentina, Singapore and New Zealand) and Gold status in four countries (The Netherlands, Spain, Poland and Brazil). With over 6.5 million copies of Black Ice shipped worldwide, combined with over 5.5 million in catalogue sold, AC/DC have surpassed The Beatles as the No.1 selling catalogue artist in the US for 2008. The 18-month Black Ice World Tour supporting the new album was announced on 11 September and began on 28 October in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania.[66]
On 15 September 2008, AC/DC Radio debuted on Sirius Channel 19 and XM channel 53. The channel plays AC/DC music along with interviews with the band members.[67]
With the North American release of Black Ice on 20 October 2008, Columbia Records and Walmart created "Rock Again AC/DC Stores" to promote the album. In October 2008, MTV, Walmart, and Columbia created "AC/DC Rock Band Stores" in New York City, at Times Square, and in Los Angeles. "Black Ice" trucks were also dispatched on the streets of these two cities after the release, playing AC/DC music aloud and making various stops each day to sell merchandise.[68]
In late September 2009, the band rescheduled six shows when Brian Johnson underwent an operation for ulcers.[69] On 29 September, the band announced a collection of studio and live rarities, Backtracks, which was released on 10 November 2009 as a 3-CD/2-DVD/1-LP box-set.[70]
On 4 November AC/DC were announced as the Business Review Weekly top Australian earner (entertainment) for 2009 with earnings of $105 million. This displaced The Wiggles from the number one spot for the first time in four years.[71]
On 19 April 2010, AC/DC released Iron Man 2, the soundtrack for the eponymous film.[72] One month later, the band headlined Download Festival at Donington Park,[73] and closed the Black Ice World Tour in Bilbao, Spain on 28 June 2010, after 20 months in which AC/DC went to 108 cities in over 28 countries, with an estimated audience of over five million people.[74] Three concerts in December 2009 at the River Plate Stadium in Argentina were released as the DVD Live at River Plate on 10 May 2011.[75] An exclusive single from the DVD, featuring the songs "Shoot to Thrill" and "War Machine", was issued on Record Store Day.[76] In 2011, the band also issued on DVD and Blu-Ray the concert movie AC/DC: Let There Be Rock, which had its theatrical release in 1980.[77]
Future album and tour (2011–Present)
Angus stated in an interview in early May 2011 that the band was beginning to plan another world tour, saying that "now we're thinking, 'How can we ever better the 'Black Ice' world tour?' But we will".[78] At the band's Live at River Plate DVD premiere on 6 May 2011 at the Hammersmith Apollo in London, England, Angus said that there were plans for the group to release a new studio album "within the next couple of years", which the tour would support.[79] Also, AC/DC's 40th anniversary will be marked for 2013. Most recently, Brian Johnson was a guest on VH1 Classic's "That Metal Show" saying the band would get back in the studio and release an album in mid to late 2012.
Other tributes
section may need tiding
As of 18th August 2011, The Rock and Roll Hall of Fame inductees released AC/DC The Wine. Sourced from wine regions in the Barossa and Coonawarra, the wine was distilled by Australian winery Warburn Estate. Varieties include Back in Black Shiraz, Highway to Hell Cabernet Sauvignon and You Shook Me All Night Long Moscato.It is exclusive toDan Murphy's, BWS and Woolworths Liquor stores.
Recognition
AC/DC were inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame on 10 March 2003.[80] During the ceremony the band performed "Highway to Hell" and "You Shook Me All Night Long", with guest vocals provided by host Steven Tyler of Aerosmith. He described the band's power chords as "the thunder from down under that gives you the second-most-powerful surge that can flow through your body."[81] During the acceptance speech, Brian Johnson quoted their 1977 song "Let There Be Rock".[82]
On 22 March 2000, the municipality of Leganés (near Madrid) named a street in honour of the band as "Calle de AC/DC" ("AC/DC Street"). Malcolm and Angus assisted in the inauguration with many fans. Later that day, the plaque with the name of the group was stolen, perhaps by an enthusiast or collector. The plaque was replaced two hours later, and stolen once again a mere three days after the fact. The plaque had since been stolen numerous times, forcing the municipality of Leganés to begin selling replicas of the official street plaque.
In May 2003, Malcolm Young accepted a Ted Albert Award for Outstanding Service to Australian Music at the 2003 Music Winners Awards, during which he paid special tribute to Bon Scott.[83]
On 1 October 2004, a central Melbourne thoroughfare, Corporation Lane, was renamed ACDC Lane in honour of the band. However, the City of Melbourne forbade the use of the slash character in street names, so the four letters were combined.[84] The lane is near Swanston Street where, on the back of a truck, the band recorded their video for the 1975 hit "It's a Long Way to the Top (If You Wanna Rock 'n' Roll)".[26]
They sold over 1.3 million CDs in the US during 2007 despite not having released a new album since 2000 at that point.[85]
In 2009 the Recording Industry Association of America upgraded the group's US sales figures from 69 million to 71 million, making AC/DC the fifth-best-selling band in US history and the ninth-best-selling artist, selling more albums than Madonna, Mariah Carey and Michael Jackson.[6] The RIAA also certified Back in Black as double Diamond (20 million) in US sales, and by 2007 the album had sold 22 million copies, which moved it into fifth place.[9]
Band members
|
Current members
|
Former members
|
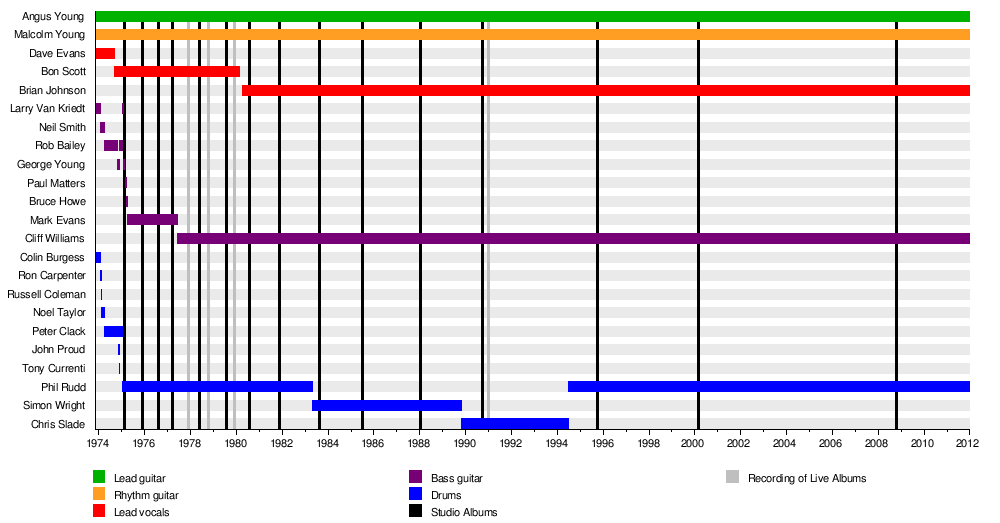
Timeline
Discography
| Date of release | Title | Billboard peak | RIAA cert. | Label |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17 February 1975 | High Voltage (Australia only) | — | — | Albert |
| December 1975 | T.N.T. (Australia only) | — | — | |
| 15 May 1976 | High Voltage (International) | 146 | 3× Platinum | Atlantic |
| 17 December 1976 | Dirty Deeds Done Dirt Cheap | 3 | 6× Platinum | |
| 23 June 1977 | Let There Be Rock | 154 | 2× Platinum | |
| 25 May 1978 | Powerage | 133 | Platinum | |
| 27 July 1979 | Highway to Hell | 17 | 7x Platinum | |
| 25 July 1980 | Back in Black | 4 | 22x Platinum | |
| 23 November 1981 | For Those About to Rock We Salute You | 1 | 4× Platinum | |
| 15 August 1983 | Flick of the Switch | 15 | Platinum | |
| 28 June 1985 | Fly on the Wall | 32 | Platinum | |
| 1 February 1988 | Blow Up Your Video | 12 | Platinum | Epic |
| 24 September 1990 | The Razors Edge | 2 | 5x Platinum | Atlantic |
| 22 September 1995 | Ballbreaker | 4 | 2x Platinum | East West |
| 25 February 2000 | Stiff Upper Lip | 7 | Platinum | |
| 20 October 2008 | Black Ice | 1 | 2x Platinum | Columbia |
Awards and nominations
See also
| Book: AC/DC | |
| Wikipedia books are collections of articles that can be downloaded or ordered in print. | |
Notes
References
- ^ Dale Hoiberg, ed (24 September 2007). "AC/DC". Encyclopædia Britannica Ultimate Reference Suite (2008 ed.). ISBN 1-59339-292-3.
- ^ Dale Hoiberg, ed (24 September 2007). "heavy metal". Encyclopædia Britannica Ultimate Reference Suite (2008 ed.). ISBN 1-59339-292-3.
- ^ a b c d Engleheart, Murray (18 November 1997). AC/DC — Bonfire.
- ^ "AC/DC Completes Recording New Album". Blabbermouth.net. 22 April 2008. http://www.roadrunnerrecords.com/BLABBERMOUTH.NET/news.aspx?mode=Article&newsitemID=95431. Retrieved 22 April 2008.
- ^ Howard Stern Show, 2008, Brian Johnson and Angus Young interview, XM/Sirius Satelite Radio.
- ^ a b "Top Selling Artists". Recording Industry Association of America. http://www.riaa.com/goldandplatinumdata.php?table=tblTopArt. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ Levine, Robert (12 October 2008). "Ageless and Defiant, AC/DC Stays on Top Without Going Digital". The New York Times. http://www.nytimes.com/2008/10/12/arts/music/12levi.html?pagewanted=all. Retrieved 18 July 2009.
- ^ "AC/DC, fuoco alle polveri: <<Lasciate che ci sia il rock!>>". Gazzetta di Parma. http://www.gazzettadiparma.it/primapagina/dettaglio/4/16119/ACDC_fuoco_alle_polveri:_%C2%ABLasciate_che_ci_sia_il_rock%C2%BB.html. Retrieved 20 March 2009.
- ^ a b c "Top 100 Albums". Recording Industry Association of America. http://www.riaa.com/goldandplatinumdata.php?table=tblTop100. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ "100 Greatest artists of hard rock". VH1. http://www.vh1.com/shows/dyn/the_greatest/62188/episode_wildcard.jhtml?wildcard=/shows/dynamic/includes/wildcards/the_greatest/hardrock_list_full.jhtml&event_id=862769&start=81. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ Rock On The Net: VH1: 100 Greatest Hard Rock Artists: 1–50.
- ^ "The Greatest Metal Bands of All Time". MTV. http://www.mtv.com/bands/m/metal/greatest_metal_bands/071406/index8.jhtml. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ "The Greatest Artists of All Time: 72) AC/DC". Rolling Stone. http://www.rollingstone.com/music/lists/100-greatest-artists-of-all-time-19691231/ac-dc-19691231. Retrieved 11 November 2010.
- ^ "The Greatest Artists of All Time". VH1/Stereogum. http://stereogum.com/495331/vh1-100-greatest-artists-of-all-time/list/. Retrieved 19 September 2011.
- ^ Baker, Glenn A.. "History of Albert Music". Albert Music. Archived from the original on 30 December 2007. http://web.archive.org/web/20071230073123/http://www.albertmusic.com/history.htm. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ a b c Walker, Clinton (2001). Highway to Hell: The Life and Times of AC/DC Legend Bon Scott. pp. 128–133. ISBN 1-891241-13-3.
- ^ a b "Band Name Origins". Digital Dream Door. http://www.digitaldreamdoor.com/pages/music0_name.html. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ White, Dave. "AC/DC". About.com – Classic rock. http://classicrock.about.com/od/artistsae1/p/ac_dc.htm. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ a b c d e "AC/DC History". AC/DC — Bedlam in Belgium. http://www.ac-dc.cc. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ "Tracker to Acca Dacca". The Age (theage.com.au) (Melbourne, Australia: Fairfax Digital). 17 May 2004. http://www.theage.com.au/articles/2004/05/16/1084646066908.html. Retrieved 18 October 2008.
- ^ "AC/DC ACDC". Only Melbourne (onlymelbourne.com.au). 1 October 2004. pp. Melbourne, Australia. http://www.onlymelbourne.com.au/melbourne_details.php?id=11169. Retrieved 18 October 2008. "Its now rock 'n' roll history after Melbourne discovered acca-dacca so did the rest of the world, going on to become one of the biggest bands in the world."
- ^ "Rock Snaps". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. http://www.abc.net.au/arts/rocksnaps/photos/s33884.htm. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ "Long Way to the Top". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. http://www.abc.net.au/longway/timeline/. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ a b Stenning, Paul; Rob Johnstone (November 2005). AC/DC — Two Sides to Every Glory. Chrome Dreams. pp. 32–34. ISBN 1-84240-308-7.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Timeline". AC/DC official website. Archived from the original on 12 June 2007. http://web.archive.org/web/20070612165328/http://www.acdcrocks.com/TIMELINE_index.html. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ a b Boulton, Martin (10 September 2004). "Laneway to the top for AC/DC". The Age (Melbourne). http://www.theage.com.au/articles/2004/09/09/1094530766163.html. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ Jeckell, Barry A. (7 June 2005). "Back In Black tips 21M mark". Billboard. http://www.billboard.com/bbcom/news/article_display.jsp?vnu_content_id=1000947787. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ Huey, Steve. "AC/DC — High Voltage". Allmusic. http://www.allmusic.com/album/r78. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ "DIRTY DEEDS: My Life Inside/Outside of AC/DC, by Mark Evans". Bazillionpoints.com. http://www.bazillionpoints.com/dirty-deeds-my-life-insideoutside-of-acdc-by-mark-evans/. Retrieved 2011-10-26.
- ^ Elliott, Paul. "Never Mind the Bollocks". Mojo (February 2007)
- ^ "Peter Cavanaugh". Wild Wednesday. http://wildwednesday.com/index.html. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ Prato, Greg. "AC/DC — Powerage". Allmusic. http://www.allmusic.com/album/r81. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ "Eddie Van Halen Thanks God for Sobriety and Guitar Riffs". Spinner. 11 June 2009. http://www.spinner.com/2009/06/11/eddie-van-halen-thanks-god-for-sobriety-and-guitar-riffs/. Retrieved 1 February 2010.
- ^ a b Christopher, Michael (30 June 2003). "Epic Records AC/DC Re-issues: Second Wave". PopMatters. http://www.popmatters.com/music/reviews/a/acdc-reissues2.shtml. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ Huey, Steve. "AC/DC — Highway to Hell". Allmusic. http://www.allmusic.com/album/r82. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ "Scott [had] choked on his own vomit [in his sleep]." Back in Black 1980,2003 CD booklet.
- ^ a b Jinman, Richard (19 February 2005). "25 years on, AC/DC fans recall how wild rocker met his end". The Guardian (UK). http://arts.guardian.co.uk/news/story/0,11711,1418115,00.html. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ "Bon's Highway leads to the National Trust". Metropolitan Cemeteries Board. 15 February 2006. http://www.mcb.wa.gov.au/MCBNews/mediaRel.html. Retrieved 9 December 2007.
- ^ Stevenson, Jane (22 November 1997). "AC/DC lights a Bonfire in tribute". Canoe JAM! music. http://jam.canoe.ca/Music/Artists/A/Acdc/1997/11/22/742716.html. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ "Moxy Bio". CANOE JAM! MUSIC — Pop Encyclopedia. http://jam.canoe.ca/Music/Pop_Encyclopedia/M/Moxy.html.
- ^ "Noddy Holder interview". Soundchecks.co.uk. http://www.soundchecks.co.uk/articles/noholder.html. Retrieved 9 April 2011.
- ^ bravewords.com. "AC/DC Guitarist Angus Young Remembers Bon Scott – "When I Think Back In Hindsight, He Was A Guy That I Always Knew Was Full Of Life"". Bravewords.com. http://www.bravewords.com/news/132727. Retrieved 9 April 2011.
- ^ a b c "EveryHit". http://www.everyhit.com. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ a b Huey, Steve. "AC/DC — Flick of the Switch". Allmusic. http://www.allmusic.com/album/r86. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ Stenning, Paul (2005). AC/DC: Two Sides to Every Glory. Chrome Dreams. ISBN 1-84240-308-7.
- ^ Fricke, David (27 October 1987). "AC/DC: Flick of the Switch". Rolling Stone. http://www.rollingstone.com/artists/acdc/albums/album/174854/review/5945613/flick_of_the_switch. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ Huey, Steve. "AC/DC — Fly on the Wall". Allmusic. http://www.allmusic.com/album/r88. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ "ARIA Icons: Hall of Fame". Australian Recording Industry Association. http://www.aria.com.au/pages/hall-of-fame.htm. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ Prato, Greg. "AC/DC — Blow Up your Video". Allmusic. http://www.allmusic.com/album/r90. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ Weber, Barry. "AC/DC — AC/DC Live". Allmusic. http://www.allmusic.com/album/r53486. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ "Boxsets". AC/DC discography. http://www.acdc-discography.com/CDBoxSets.html. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ Wild, David (30 March 2000). "AC/DC: Stiff Upper Lip". Rolling Stone. http://www.rollingstone.com/artists/acdc/albums/album/198241/review/5941859/stiff_upper_lip. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ Erlewine, Stephen Thomas. "AC/DC — Stiff Upper Lip". Allmusic. http://www.allmusic.com/album/r465726. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ Richards, Pete (6 December 2002). "AC/DC Sign big contract with Sony". ChartAttack. http://www.chartattack.com/news/32768/acdc-sign-big-contract-with-sony. Retrieved 16 September 2009.
- ^ Rivadavia, Eduardo. "AC/DC — Discography". Allmusic. http://www.allmusic.com/artist/p3496/discography. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ "Stones rock out at Toronto's 'biggest party'". Canadian Broadcasting Corporation. 31 July 2003. http://www.cbc.ca/news/story/2003/07/30/concert_opener030730.html. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ Ziffer, Daniel (13 April 2006). "Wiggles wriggle back into top spot". The Age (Melbourne). http://www.theage.com.au/news/people/wiggles-wriggle-back-into-top-spot/2006/04/12/1144521401699.html. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ Dunn, Emily (18 July 2007). "A wobble, but the Wiggles still rule". The Sydney Morning Herald. http://www.smh.com.au/news/people/a-wobble-but-the-wiggles-still-rule/2007/07/17/1184559786837.html. Retrieved 17 August 2007.
- ^ Bruno, Antony (1 August 2007). "AC/DC goes digital via Verizon wireless". Reuters. http://www.reuters.com/article/technologyNews/idUSN0136768220070802. Retrieved 17 August 2007.
- ^ "Plug Me In press release". PR Newswire. 24 August 2007. http://www.prnewswire.com/cgi-bin/stories.pl?ACCT=ind_focus.story&STORY=/www/story/08-24-2007/0004650891&EDATE=FRI+Aug+24+2007,+08:05+AM. Retrieved 2 September 2007.
- ^ "Rock Band 2 – Unrivaled Song Library". rockband2.com. Archived from the original on 17 July 2008. http://web.archive.org/web/20080717025915/http://www.rockband2.com/song-list. Retrieved 19 November 2008.
- ^ Breckon, Nick; Faylor, Chris (29 September 2008). "First Rock Band Spin-off Revealed: AC/DC Live Coming As $30 Wal-Mart Exclusive". Shacknews. http://www.shacknews.com/onearticle.x/54994. Retrieved 29 September 2008.
- ^ "AC/DC Releases 'No Bull: The Directors Cut". AC/DC.com. 17 September 2008. http://www.acdc.com/news/news.php?uid=22. Retrieved 17 September 2008.
- ^ "AC/DC's 'Black Ice' Set For Release 20 October". AC/DC.com. 18 August 2008. http://www.acdc.com/news/news.php?uid=19. Retrieved 18 August 2008.
- ^ "AC/DC wants YOU for their new video". AC/DC.com. 9 August 2008. http://www.acdc.com/news/news.php?uid=18. Retrieved 9 August 2008.
- ^ "AC/DC Announce 'Black Ice' World Tour". AC/DC.com. 17 September 2008. http://www.acdc.com/news/news.php?uid=24. Retrieved 17 September 2008.
- ^ "AC/DC to hos their own exclusive music channel on Sirius and XM". Sirius. http://www.sirius.com/acdcradio. Retrieved 12 September 2008.
- ^ "AC/DC's Black Ice Rocks Into Walmart Nationwide Oct. 20". PR Newswire. 11 October 2008. http://www.hispanicbusiness.com/news/2008/10/17/acdcs_black_ice_rocks_into_walmart.htm. Retrieved 19 November 2008.
- ^ ACDC.com news.news.
- ^ http://sev.prnewswire.com/music/20090929/NY8281729092009-1.html
- ^ "AC/DC tops BRW entertainment rich list, ahead of Kylie Minogue and the Wiggles". Herald Sun. Australia. 11 April 2009. http://www.heraldsun.com.au/news/acdc-tops-brw-entertainment-rich-list-ahead-of-kylie-minogue-and-the-wiggles/story-e6frf7jo-1225794320822.
- ^ "'AC/DC: Iron Man 2' Album Forthcoming". acdc.com. 26 January 2010. http://acdc.com/news/news.php?uid=129.
- ^ Downloadfestival.co.uk
- ^ "Black Ice World Tour". AC/DC.com. 12 July 2010. http://www.acdc.com/us/acdc-today/black-ice-world-tour. Retrieved 22 February 2011.
- ^ "AC/DC Live At River Plate Available May 10 – NEW YORK, 7 March 2011". New York: Prnewswire.com. http://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/acdc-live-at-river-plate-available-may-10-117535068.html. Retrieved 9 April 2011.
- ^ "Shoot To Thrill: Exclusive Record Store Day 7" Single , The Official AC/DC Site". Acdc.com. 22 February 2011. http://www.acdc.com/us/news/shoot-thrill-exclusive-record-store-day-7-single. Retrieved 9 April 2011.
- ^ "AC/DC Let There Be Rock Blu-ray Announced". Blu-ray.com. http://www.blu-ray.com/news/?id=5871. Retrieved 9 April 2011.
- ^ "AC/DC Planning New World Tour". Blabbermouth.net. 6 May 2011. Archived from the original on 8 May 2011. http://www.webcitation.org/5yX6hdeGC. Retrieved 8 May 2011.
- ^ "AC/DC To Release New Album 'Within The Next Couple Of Years'". Blabbermouth.net. 7 May 2011. Archived from the original on 8 May 2011. http://www.webcitation.org/5yX6ljYGO. Retrieved 8 May 2011.
- ^ "AC/DC". Rockhall.com. http://www.rockhall.com/inductee/ac-dc. Retrieved 1 February 2010.
- ^ "Rock and Roll Hall of Fame open doors". CNN. 3 November 2003. Archived from the original on 3 October 2003. http://web.archive.org/web/20031003075850/http://www.cnn.com/2003/SHOWBIZ/Music/03/11/rock.hall.fame.ap/index.html. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ Johnson, Billy (3 November 2003). "AC/DC, The Clash, The Police And Others Inducted Into Hall Of Fame". Yahoo! Music. http://music.yahoo.com/read/news/12027761. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ "2003 Music Winners Awards Announced". Australasian Performing Right Association. Archived from the original on 23 July 2008. http://web.archive.org/web/20080723033156/http://apra.com.au/awards/music/media_releases/03-music_award_winners_announced.asp. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ "Next stage in AC/DC Lane proposal wins in-principle support". City of Melbourne. 8 July 2004. http://www.melbourne.vic.gov.au/info.cfm?top=228&pg=715&st=191. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ Levine, Robert (10 October 2008). "Ageless and Defiant, AC/DC Stays on Top Without Going Digital". The New York Times. http://www.nytimes.com/2008/10/12/arts/music/12levi.html. Retrieved 19 November 2008.
Further reading
- Bunton, Richard (1983). AC/DC: Hell Ain't No Bad Place to Be. Omnibus Books. ISBN 0-7119-0082-5.
- Dome, Malcolm (1982). AC/DC. Proteus Books. ISBN 0-86276-011-9.
- Engleheart, Murray (2006). AC/DC: Maximum Rock & Roll. Harper Collins. ISBN 978-0-7322-8964-5.
- Holmes, Tim (1986). AC/DC (Monsters of Metal). Ballantine. ISBN 0-345-33239-3.
- Huxley, Martin (1996). AC/DC: The World's Heaviest Rock. Lightning Source Inc.. ISBN 0-312-30220-7.
- Stenning, Paul (2005). AC/DC: Two Sides to Every Glory. Chrome Dreams. ISBN 1-84240-308-7.
External links
- Official website
- AC/DC at the Open Directory Project
- Extended bio- and discography
- AC/DC discography at MusicBrainz
- Official YouTube profile
- ACDC Timeline
- Official AC/DC Backtracks website
- AC/DC footage on Rokpool.com
- Sin City Bon Scott era
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||