Wikipedia
 The logo of Wikipedia, a globe featuring glyphs from many different writing systems |
|
|
Screenshot
 Screenshot of Wikipedia's multilingual portal. |
|
| URL | Wikipedia.org |
|---|---|
| Slogan | The free encyclopedia that anyone can edit. |
| Commercial? | No |
| Type of site | Internet encyclopedia project |
| Registration | Optional (required only for certain tasks such as editing protected pages, creating new article pages or uploading files) |
| Available language(s) | 240 active editions (272 in total) |
| Content license | Creative Commons Attribution/ Share-Alike 3.0 and GFDL dual-license |
| Owner | Wikimedia Foundation (non-profit) |
| Created by | Jimmy Wales, Larry Sanger[1] |
| Launched | January 15, 2001 |
| Alexa rank | |
| Current status | Active |
Wikipedia is a free,[3] web-based, collaborative, multilingual encyclopedia project supported by the non-profit Wikimedia Foundation. Its 16 million articles (over 3.3 million in English) have been written collaboratively by volunteers around the world, and almost all of its articles can be edited by anyone with access to the site.[4] Wikipedia was launched in 2001 by Jimmy Wales and Larry Sanger[5] and is currently the largest and most popular general reference work on the Internet,[2][6][7][8] ranked 7th among all websites on Alexa.[9]
The word Wikipedia (pronounced /ˌwɪkɪˈpiːdi.ə/ or /ˌwɪkiˈpiːdi.ə/ WIK-i-PEE-dee-ə) was coined by Larry Sanger[10] and is a portmanteau from wiki (a technology for creating collaborative websites, from the Hawaiian word wiki, meaning "quick") and encyclopedia.
Although the policies of Wikipedia strongly espouse verifiability and a neutral point of view, critics of Wikipedia accuse it of systemic bias and inconsistencies (including undue weight given to popular culture),[11] and allege that it favors consensus over credentials in its editorial process.[12] Its reliability and accuracy are also targeted.[13] Other criticisms center on its susceptibility to vandalism and the addition of spurious or unverified information,[14] though scholarly work suggests that vandalism is generally short-lived,[15][16] and an investigation in Nature found that the material they compared came close to the level of accuracy of Encyclopædia Britannica and had a similar rate of "serious errors."[17]
Wikipedia's departure from the expert-driven style of the encyclopedia building mode and the large presence of unacademic content have been noted several times. When Time magazine recognized You as its Person of the Year for 2006, acknowledging the accelerating success of online collaboration and interaction by millions of users around the world, it cited Wikipedia as one of several examples of Web 2.0 services, along with YouTube, MySpace, and Facebook.[18] Some noted the importance of Wikipedia not only as an encyclopedic reference but also as a frequently updated news resource because of how quickly articles about recent events appear.[19][20] Students have been assigned to write Wikipedia articles, as an exercise in clearly and succinctly explaining difficult concepts to an uninitiated audience.[21]
Contents |
History
Wikipedia began as a complementary project for Nupedia, a free online English-language encyclopedia project whose articles were written by experts and reviewed under a formal process. Nupedia was founded on March 9, 2000, under the ownership of Bomis, Inc, a web portal company. Its main figures were Jimmy Wales, Bomis CEO, and Larry Sanger, editor-in-chief for Nupedia and later Wikipedia. Nupedia was licensed initially under its own Nupedia Open Content License, switching to the GNU Free Documentation License before Wikipedia's founding at the urging of Richard Stallman.[22]
Larry Sanger and Jimmy Wales founded Wikipedia.[23][24] While Wales is credited with defining the goal of making a publicly editable encyclopedia,[25][26] Sanger is usually credited with the strategy of using a wiki to reach that goal.[27] On January 10, 2001, Larry Sanger proposed on the Nupedia mailing list to create a wiki as a "feeder" project for Nupedia.[28] Wikipedia was formally launched on January 15, 2001, as a single English-language edition at www.wikipedia.com,[29] and announced by Sanger on the Nupedia mailing list.[25] Wikipedia's policy of "neutral point-of-view"[30] was codified in its initial months, and was similar to Nupedia's earlier "nonbiased" policy. Otherwise, there were relatively few rules initially and Wikipedia operated independently of Nupedia.[25]

Wikipedia gained early contributors from Nupedia, Slashdot postings, and web search engine indexing. It grew to approximately 20,000 articles and 18 language editions by the end of 2001. By late 2002, it had reached 26 language editions, 46 by the end of 2003, and 161 by the final days of 2004.[31] Nupedia and Wikipedia coexisted until the former's servers were taken down permanently in 2003, and its text was incorporated into Wikipedia. English Wikipedia passed the 2 million-article mark on September 9, 2007, making it the largest encyclopedia ever assembled, eclipsing even the Yongle Encyclopedia (1407), which had held the record for exactly 600 years.[32]
Citing fears of commercial advertising and lack of control in a perceived English-centric Wikipedia, users of the Spanish Wikipedia forked from Wikipedia to create the Enciclopedia Libre in February 2002.[33] Later that year, Wales announced that Wikipedia would not display advertisements, and its website was moved to wikipedia.org.[34] Various other wiki-encyclopedia projects have been started, largely under a different philosophy from the open and NPOV editorial model of Wikipedia. Wikinfo does not require a neutral point of view and allows original research. New Wikipedia-inspired projects – such as Citizendium, Scholarpedia, Conservapedia, and Google's Knol where the articles are a little more essayistic[35] – have been started to address perceived limitations of Wikipedia, such as its policies on peer review, original research, and commercial advertising.
Though the English Wikipedia reached 3 million articles in August 2009, the growth of the edition, in terms of the numbers of articles and of contributors, appeared to have flattened off around early 2007.[36] In July 2007, about 2,200 articles were added daily to the encyclopedia; as of August 2009[update], that average is 1,300. A team led by Ed H Chi at the Palo Alto Research Center speculated that this is due to the increasing exclusiveness of the project.[37] New or occasional editors have significantly higher rates of their edits reverted (removed) than an elite group of regular editors, colloquially known as the "cabal." This could make it more difficult for the project to recruit and retain new contributors, over the long term resulting in stagnation in article creation. Others simply point out that the low-hanging fruit, the obvious articles like China, already exist, and believe that the growth is flattening naturally.[38][39]
In November 2009, a Ph.D thesis written by Felipe Ortega, a researcher at the Universidad Rey Juan Carlos in Madrid, found that the English Wikipedia had lost 49,000 editors during the first three months of 2009; in comparison, the project lost only 4,900 editors during the same period in 2008.[40][41] The Wall Street Journal reported that "unprecedented numbers of the millions of online volunteers who write, edit and police [Wikipedia] are quitting." The array of rules applied to editing and disputes related to such content are among the reasons for this trend that are cited in the article.[42] These claims were disputed by Jimmy Wales, who denied the decline and questioned the methodology of the study.[43]
Nature of Wikipedia
Editing model
In departure from the style of traditional encyclopedias, Wikipedia employs an open, "wiki" editing model. Except for a few particularly vandalism-prone pages, every article may be edited anonymously or with a user account, while only registered users may create a new article (only in the English edition). No article is owned by its creator or any other editor, or is vetted by any recognized authority; rather, the articles are collectively owned by a community of editors and are agreed on by consensus.[45]
Most importantly, when changes to an article are made, they become available immediately before undergoing any review, no matter if they contain an error, are somehow misguided, or even patent nonsense. The German edition of Wikipedia is an exception to this rule: it has been testing a system of maintaining "stable versions" of articles,[46] to allow a reader to see versions of articles that have passed certain reviews. The English edition of Wikipedia plans to trial a related approach.[47][48] In June 2010, it was announced that the English Wikipedia would remove strict editing restrictions from "controversial" or vandalism-prone articles (such as George W. Bush, David Cameron or homework). In place of an editing prohibition for new or unregistered users, there would be a "new system, called 'pending changes'" which, Jimmy Wales told the British Broadcasting Corporation, would enable the English Wikipedia "to open up articles for general editing that have been protected or semi-protected for years." The "pending changes" system was introduced on June 15, shortly after 11pm GMT. Edits to specified articles are now "subject to review from an established Wikipedia editor before publication." Wales opted against the German Wikipedia model of requiring editor review before edits to any article, describing it as "neither necessary nor desirable." He added that the administrators of the German Wikipedia were "going to be closely watching the English system, and I'm sure they'll at least consider switching if the results are good."[49]

Contributors, registered or not, can take advantage of features available in the software that powers Wikipedia. The "History" page attached to each article records every single past revision of the article, though a revision with libelous content, criminal threats or copyright infringements may be removed afterwards.[50][51] This feature makes it easy to compare old and new versions, undo changes that an editor considers undesirable, or restore lost content. The "Discussion" pages associated with each article are used to coordinate work among multiple editors.[52] Regular contributors often maintain a "watchlist" of articles of interest to them, so that they can easily keep tabs on all recent changes to those articles. Computer programs called Internet bots have been used widely to remove vandalism as soon as it was made,[16] to correct common misspellings and stylistic issues, or to start articles such as geography entries in a standard format from statistical data.
Articles in Wikipedia are organized roughly in three ways according to: development status, subject matter and the access level required for editing. The most developed state of articles is called "featured article" status: articles labeled as such are the ones that will be featured in the main page of Wikipedia.[53][54] Researcher Giacomo Poderi found that articles tend to reach the FA status via intensive works of few editors. In 2007, in preparation for producing a print version, the English-language Wikipedia introduced an assessment scale against which the quality of articles is judged;[55] other editions have also adopted this.
A WikiProject is a place for a group of editors to coordinate work on a specific topic. The discussion pages attached to a project are often used to coordinate changes that take place across articles. Wikipedia also maintains a style guide called the Manual of Style or MoS for short, which stipulates, for example, that, in the first sentence of any given article, the title of the article and any alternate titles should appear in bold.
Rules and laws governing content
For legal reasons, content in Wikipedia is subject to the laws (in particular copyright law) of Florida, where Wikipedia servers are hosted. Beyond that, the Wikipedian editorial principles are embodied in the "five pillars", and numerous policies and guidelines are intended to shape the content appropriately. Even these rules are stored in wiki form, and Wikipedia editors as a community write and revise those policies and guidelines[56] and enforce them by deleting, annotating with tags, or modifying article materials failing to meet them. The rules on the non English editions of the Wikipedia branched off a translation of the rules on the English Wikipedia and have since diverged to some extent. While they still show broad-brush similarities, they differ in many details.
According to the rules on the English Wikipedia, each entry in Wikipedia to be worthy of inclusion must be about a topic that is encyclopedic and is not a dictionary entry or dictionary-like.[57] A topic should also meet Wikipedia's standards of "notability",[58] which usually means that it must have received significant coverage in reliable secondary sources such as mainstream media or major academic journals that are independent of the subject of the topic. Further, Wikipedia must expose knowledge that is already established and recognized.[59] In other words, it must not present, for instance, new information or original works. A claim that is likely to be challenged requires a reference to a reliable source. Among Wikipedia editors, this is often phrased as "verifiability, not truth" to express the idea that the readers, not the encyclopedia, are ultimately responsible for checking the truthfulness of the articles and making their own interpretations.[60] Finally, Wikipedia must not take a side.[61] All opinions and viewpoints, if attributable to external sources, must enjoy appropriate share of coverage within an article.[62] This is known as neutral point of view, or NPOV.
Wikipedia has many methods of settling disputes. A "bold, revert, discuss" cycle sometimes occurs, in which a user makes an edit, another user reverts it, and the matter is discussed on the appropriate talk page. In order to gain a broader community consensus, issues can be raised at the Village Pump, or a Request for Comment can be made soliciting other users' input. "Wikiquette Alerts" is a non-binding noticeboard where users can report impolite, uncivil, or other difficult communications with other editors.
Specialized forums exist for centralizing discussion on specific decisions, such as whether or not an article should be deleted. Mediation is sometimes used, although it has been deemed by some Wikipedians to be unhelpful for resolving particularly contentious disputes. The Wikipedia Arbitration Committee settles disputes when other methods fail. The ArbCom generally does not rule on the factual correctness of article content, although it sometimes enforces the "Neutral Point of View" policy. Statistical analyses suggest that Wikipedia's dispute resolution ignores the content of user disputes and focuses on user conduct instead, functioning not so much to resolve disputes and make peace between conflicting users, but to weed out problematic users while weeding potentially productive users back in to participate. Its remedies include banning users from Wikipedia (used in 15.7% of cases), subject matter remedies (23.4%), article bans (43.3%) and cautions and probations (63.2%). Total bans from Wikipedia are largely limited to instances of impersonation and anti-social behavior. Warnings tend to be issued for editing conduct and conduct that is anti-consensus, rather than anti-social.[63]
Defenses against undesirable edits
The open nature of the editing model has been central to most criticism of Wikipedia. For example, a reader of an article cannot be certain that it has not been compromised by the insertion of false information or the removal of essential information. Former Encyclopædia Britannica editor-in-chief Robert McHenry once described this by saying:[64]
The user who visits Wikipedia to learn about some subject, to confirm some matter of fact, is rather in the position of a visitor to a public restroom. It may be obviously dirty, so that he knows to exercise great care, or it may seem fairly clean, so that he may be lulled into a false sense of security. What he certainly does not know is who has used the facilities before him. Wikipedia [is a] faith-based encyclopedia.[65]

Obvious vandalism is easy to remove from wiki articles, since the previous versions of each article are kept. In practice, the median time to detect and fix vandalisms is very low, usually a few minutes,[15][16] but in one particularly well-publicized incident, false information was introduced into the biography of American political figure John Seigenthaler and remained undetected for four months.[66] John Seigenthaler, the founding editorial director of USA Today and founder of the Freedom Forum First Amendment Center at Vanderbilt University, called Jimmy Wales and asked if Wales had any way of knowing who contributed the misinformation. Wales replied that he did not, but nevertheless the perpetrator was eventually traced.[67][68] This incident led to policy changes on the site, specifically targeted at tightening up the verifiability of all biographical articles of living people.
Wikipedia's open structure inherently makes it an easy target for Internet trolls, spamming, and those with an agenda to push.[50][69] The addition of political spin to articles by organizations including members of the U.S. House of Representatives and special interest groups[14] has been noted,[70] and organizations such as Microsoft have offered financial incentives to work on certain articles.[71] These issues have been parodied, notably by Stephen Colbert in The Colbert Report.[72]
For example, in August 2007, the website WikiScanner began to trace the sources of changes made to Wikipedia by anonymous editors without Wikipedia accounts. The program revealed that many such edits were made by corporations or government agencies changing the content of articles related to them, their personnel or their work.[73]
In practice, Wikipedia is defended from attack by multiple systems and techniques. These include users checking pages and edits, computer programs ('bots') that are carefully designed to try to detect attacks and fix them automatically (or semi-automatically), filters that warn users making undesirable edits,[74] blocks on the creation of links to particular websites, blocks on edits from particular accounts, IP addresses or address ranges.
For heavily attacked pages, particular articles can be semi-protected so that only well established accounts can edit them,[75] or for particularly contentious cases, locked so that only administrators are able to make changes.[76] Such locking is applied sparingly, usually for only short periods of time while attacks appear likely to continue.
Coverage of topics
| 1. Wiki |
| 2. The Beatles |
| 3. Michael Jackson |
| 4. Favicon |
| 5. YouTube |
| 6. Wikipedia |
| 7. Barack Obama |
| 8. Deaths in 2009 |
| 9. United States |
| 10. Facebook |
| 11. Current events portal |
| 12. World War II |
| 13. Twitter |
| 14. Transformers |
| 15. Slumdog Millionaire |
| 16. Lil Wayne |
| 17. Adolf Hitler |
| 18. India |
| 19. Transformers: Revenge of the Fallen |
| 20. Scrubs |
Wikipedia seeks to create a summary of all human knowledge in the form of an online encyclopedia. Since it has virtually unlimited disk space it can have far more topics than can be covered by any conventional print encyclopedias.[79] It also contains materials that some people, including Wikipedia editors,[80] may find objectionable, offensive, or pornographic.[81] It was made clear that this policy is not up for debate, and the policy has sometimes proved controversial. For instance, in 2008, Wikipedia rejected an online petition against the inclusion of Muhammad's depictions in its English edition, citing this policy. The presence of politically sensitive materials in Wikipedia had also led the People's Republic of China to block access to parts of the site.[82] (See also: IWF block of Wikipedia)
As of September 2009[update], Wikipedia articles cover about half a million places on Earth. However, research conducted by the Oxford Internet Institute has shown that the geographic distribution of articles is highly uneven. Most articles are written about North America, Europe, and East Asia, with very little coverage of large parts of the developing world, including most of Africa.[83]
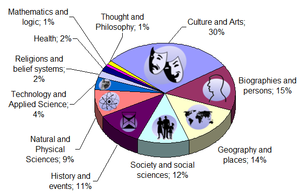
A 2008 study conducted by researchers at Carnegie-Mellon University and Palo Alto Research Center gave a distribution of topics as well as growth (from July 2006 to January 2008) in each field:[77]
- Culture and the arts 30% (210%)
- Biographies and persons: 15% (97%)
- Geography and places: 14% (52%)
- Society and social sciences: 12% (83%)
- History and events: 11% (143%)
- Natural and the physical sciences: 9% (213%)
- Technology and the applied science: 4% (−6%)
- Religions and belief systems: 2% (38%)
- Health: 2% (42%)
- Mathematics and logic: 1% (146%)
- Thought and philosophy: 1% (160%)
However, the exact coverage of Wikipedia is under constant review by the editors, and disagreements are not uncommon (see also deletionism and inclusionism).[84][85]
Quality
Because contributors usually rewrite small portions of an entry rather than making full-length revisions, high- and low-quality content may be intermingled within an entry. Critics sometimes argue that non-expert editing undermines quality. For example, historian Roy Rosenzweig claimed that: "Overall, writing is the Achilles' heel of Wikipedia. Committees rarely write well, and Wikipedia entries often have a choppy quality that results from the stringing together of sentences or paragraphs written by different people."[86]
Reliability
As a consequence of the open structure, Wikipedia "makes no guarantee of validity" of its content, since no one is ultimately responsible for any claims appearing in it.[87] Concerns have been raised regarding the lack of accountability that results from users' anonymity,[88] the insertion of spurious information,[89] vandalism, and similar problems.
Wikipedia has been accused of exhibiting systemic bias and inconsistency;[13] additionally, critics argue that Wikipedia's open nature and a lack of proper sources for much of the information makes it unreliable.[90] Some commentators suggest that Wikipedia is generally reliable, but that the reliability of any given article is not always clear.[12] Editors of traditional reference works such as the Encyclopædia Britannica have questioned the project's utility and status as an encyclopedia.[91] Many university lecturers discourage students from citing any encyclopedia in academic work, preferring primary sources;[92] some specifically prohibit Wikipedia citations.[93] Co-founder Jimmy Wales stresses that encyclopedias of any type are not usually appropriate as primary sources, and should not be relied upon as authoritative.[94]
However, an investigation reported in the journal Nature in 2005 suggested that for scientific articles Wikipedia came close to the level of accuracy of Encyclopædia Britannica and had a similar rate of "serious errors."[17] These claims have been disputed by Encyclopædia Britannica.[95][96]
Economist Tyler Cowen writes, "If I had to guess whether Wikipedia or the median refereed journal article on economics was more likely to be true, after a not so long think I would opt for Wikipedia." He comments that many traditional sources of non-fiction suffer from systemic biases. Novel results are over-reported in journal articles, and relevant information is omitted from news reports. However, he also cautions that errors are frequently found on Internet sites, and that academics and experts must be vigilant in correcting them.[97]
In February 2007, an article in The Harvard Crimson newspaper reported that some of the professors at Harvard University include Wikipedia in their syllabi, but that there is a split in their perception of using Wikipedia.[98] In June 2007, former president of the American Library Association Michael Gorman condemned Wikipedia, along with Google,[99] stating that academics who endorse the use of Wikipedia are "the intellectual equivalent of a dietitian who recommends a steady diet of Big Macs with everything." He also said that "a generation of intellectual sluggards incapable of moving beyond the Internet" was being produced at universities. He complains that the web-based sources are discouraging students from learning from the more rare texts which are either found only on paper or are on subscription-only web sites. In the same article Jenny Fry (a research fellow at the Oxford Internet Institute) commented on academics who cite Wikipedia, saying that: "You cannot say children are intellectually lazy because they are using the Internet when academics are using search engines in their research. The difference is that they have more experience of being critical about what is retrieved and whether it is authoritative. Children need to be told how to use the Internet in a critical and appropriate way."[99]
Community

The Wikipedia community has established "a bureaucracy of sorts," including "a clear power structure that gives volunteer administrators the authority to exercise editorial control."[100][101][102] Wikipedia's community has also been described as "cult-like,"[103] although not always with entirely negative connotations,[104] and criticized for failing to accommodate inexperienced users.[105] Editors in good standing in the community can run for one of many levels of volunteer stewardship; this begins with "administrator,"[106][107] a group of privileged users who have the ability to delete pages, lock articles from being changed in case of vandalism or editorial disputes, and block users from editing. Despite the name, administrators do not enjoy any special privilege in decision-making; instead they are mostly limited to making edits that have project-wide effects and thus are disallowed to ordinary editors, and to block users making disruptive edits (such as vandalism).[108][109]

As Wikipedia grows with an unconventional model of encyclopedia building, "Who writes Wikipedia?" has become one of the questions frequently asked on the project, often with a reference to other Web 2.0 projects such as Digg.[110] Jimmy Wales once argued that only "a community ... a dedicated group of a few hundred volunteers" makes the bulk of contributions to Wikipedia and that the project is therefore "much like any traditional organization." Wales performed a study finding that over 50% of all the edits are done by just 0.7% of the users (at the time: 524 people). This method of evaluating contributions was later disputed by Aaron Swartz, who noted that several articles he sampled had large portions of their content (measured by number of characters) contributed by users with low edit counts.[111] A 2007 study by researchers from Dartmouth College found that "anonymous and infrequent contributors to Wikipedia ... are as reliable a source of knowledge as those contributors who register with the site."[112] Although some contributors are authorities in their field, Wikipedia requires that even their contributions be supported by published and verifiable sources. The project's preference for consensus over credentials has been labeled "anti-elitism."[11]
In a 2003 study of Wikipedia as a community, economics Ph.D. student Andrea Ciffolilli argued that the low transaction costs of participating in wiki software create a catalyst for collaborative development, and that a "creative construction" approach encourages participation.[113] In his 2008 book, The Future of the Internet and How to Stop It, Jonathan Zittrain of the Oxford Internet Institute and Harvard Law School’s Berkman Center for Internet & Society cites Wikipedia's success as a case study in how open collaboration has fostered innovation on the web.[114] A 2008 study found that Wikipedia users were less agreeable and open, though more conscientious, than non-Wikipedia users.[115][116] A 2009 study suggested there was "evidence of growing resistance from the Wikipedia community to new content."[117]
At OOPSLA 2009, Wikimedia CTO and Senior Software Architect Brion Vibber gave a presentation entitled "Community Performance Optimization: Making Your People Run as Smoothly as Your Site"[118] in which he discussed the challenges of handling the contributions from a large community and compared the process to that of software development.
The Wikipedia Signpost is the community newspaper on the English Wikipedia,[119] and was founded by Michael Snow, an administrator and the former chair of the Wikimedia Foundation board of trustees.[120] It covers news and events from the site, as well as major events from sister projects, such as Wikimedia Commons.[121]
Notable users of Wikipedia include film critic Roger Ebert[122][123] and University of Maryland physicist Robert L. Park.[124]
Wikipedians sometimes award one another barnstars for outstanding work. These personalized tokens of appreciation reveal a wide range of valued work extending far beyond simple editing to include social support, administrative actions, and types of articulation work. The barnstar phenomenon has been analyzed by researchers seeking to determine what implications it might have for other communities engaged in large-scale collaborations.[125]
60% of registered users never make another edit after their first 24 hours. Possible explanations are that such users only register for a single purpose, or are scared away by their experiences.[126] Goldman writes that editors who fail to comply with Wikipedia cultural rituals, such as signing talk pages, implicitly signal that they are Wikipedia outsiders, increasing the odds that Wikipedia insiders will target their contributions as a threat. Becoming a Wikipedia insider involves non-trivial costs; the contributor is expected to build a user page, learn Wikipedia-specific technological codes, submit to an arcane dispute resolution process, and learn a "baffling culture rich with in-jokes and insider references." Non-logged-in users are in some sense second-class citizens on Wikipedia,[127] as "participants are accredited by members of the wiki community, who have a vested interest in preserving the quality of the work product, on the basis of their ongoing participation,"[128] but the contribution histories of IP addresses cannot necessarily with any certainty be credited to, or blamed upon, a particular user.
Operation
Wikimedia Foundation and the Wikimedia chapters

Wikipedia is hosted and funded by the Wikimedia Foundation, a non-profit organization which also operates Wikipedia-related projects such as Wiktionary and Wikibooks. The Wikimedia chapters, local associations of users and supporters of the Wikimedia projects, also participate in the promotion, the development, and the funding of the project.
Software and hardware
The operation of Wikipedia depends on MediaWiki, a custom-made, free and open source wiki software platform written in PHP and built upon the MySQL database.[129] The software incorporates programming features such as a macro language, variables, a transclusion system for templates, and URL redirection. MediaWiki is licensed under the GNU General Public License and it is used by all Wikimedia projects, as well as many other wiki projects. Originally, Wikipedia ran on UseModWiki written in Perl by Clifford Adams (Phase I), which initially required CamelCase for article hyperlinks; the present double bracket style was incorporated later. Starting in January 2002 (Phase II), Wikipedia began running on a PHP wiki engine with a MySQL database; this software was custom-made for Wikipedia by Magnus Manske. The Phase II software was repeatedly modified to accommodate the exponentially increasing demand. In July 2002 (Phase III), Wikipedia shifted to the third-generation software, MediaWiki, originally written by Lee Daniel Crocker. Several MediaWiki extensions are installed[130] to extend the functionality of MediaWiki software. In April 2005 a Lucene extension[131][132] was added to MediaWiki's built-in search and Wikipedia switched from MySQL to Lucene for searching. Currently Lucene Search 2.1,[133] which is written in Java and based on Lucene library 2.3,[134] is used.
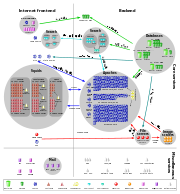
Wikipedia currently runs on dedicated clusters of Linux servers (mainly Ubuntu),[135][136] with a few OpenSolaris machines for ZFS. As of December 2009, there were 300 in Florida and 44 in Amsterdam.[137] Wikipedia employed a single server until 2004, when the server setup was expanded into a distributed multitier architecture. In January 2005, the project ran on 39 dedicated servers in Florida. This configuration included a single master database server running MySQL, multiple slave database servers, 21 web servers running the Apache HTTP Server, and seven Squid cache servers.
Wikipedia receives between 25,000 and 60,000 page requests per second, depending on time of day.[138] Page requests are first passed to a front-end layer of Squid caching servers.[139] Further statistics are available based on a publicly available 3-months Wikipedia access trace.[140] Requests that cannot be served from the Squid cache are sent to load-balancing servers running the Linux Virtual Server software, which in turn pass the request to one of the Apache web servers for page rendering from the database. The web servers deliver pages as requested, performing page rendering for all the language editions of Wikipedia. To increase speed further, rendered pages are cached in a distributed memory cache until invalidated, allowing page rendering to be skipped entirely for most common page accesses. Two larger clusters in the Netherlands and Korea now handle much of Wikipedia's traffic load.
Mobile access
Wikipedia's original medium was for users to read and edit content using any standard web browser through a fixed internet connection. However, Wikipedia content is now also accessible through the mobile web.
Access to Wikipedia from mobile phones was possible as early as 2004, through the Wireless Application Protocol (WAP), via the Wapedia service. In June 2007, Wikipedia launched en.mobile.wikipedia.org, an official website for wireless devices. In 2009 a newer mobile service was officially released,[141] located at en.m.wikipedia.org, which caters to more advanced mobile devices such as the iPhone, Android-based devices, or the Palm Pre. Several other methods of mobile access to Wikipedia have emerged (See Help:Mobile device). Several devices and applications optimise or enhance the display of Wikipedia content for mobile devices, while some also incorporate additional features such as use of Wikipedia metadata (See Wikipedia:Metadata), such as geoinformation.[142]
License and language editions
All text in Wikipedia was covered by GNU Free Documentation License (GFDL), a copyleft license permitting the redistribution, creation of derivative works, and commercial use of content while authors retain copyright of their work,[143] up until June 2009, when the site switched to Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike (CC-by-SA) 3.0.[144] Wikipedia had been working on the switch to Creative Commons licenses because the GFDL, initially designed for software manuals, is not suitable for online reference works and because the two licenses were incompatible.[145] In response to the Wikimedia Foundation's request, in November 2008, the Free Software Foundation (FSF) released a new version of GFDL designed specifically to allow Wikipedia to relicense its content to CC-BY-SA by August 1, 2009. Wikipedia and its sister projects held a community-wide referendum to decide whether or not to make the license switch.[146] The referendum took place from April 9 to 30.[147] The results were 75.8% "Yes," 10.5% "No," and 13.7% "No opinion."[148] In consequence of the referendum, the Wikimedia Board of Trustees voted to change to the Creative Commons license, effective June 15, 2009.[148] The position that Wikipedia is merely a hosting service has been successfully used as a defense in court.[149][150]

The handling of media files (e.g., image files) varies across language editions. Some language editions, such as the English Wikipedia, include non-free image files under fair use doctrine, while the others have opted not to. This is in part because of the difference in copyright laws between countries; for example, the notion of fair use does not exist in Japanese copyright law. Media files covered by free content licenses (e.g., Creative Commons' cc-by-sa) are shared across language editions via Wikimedia Commons repository, a project operated by the Wikimedia Foundation.
There are currently 262 language editions of Wikipedia; of these, 24 have over 100,000 articles and 81 have over 1,000 articles.[151] The largest, the English Wikipedia, has 44,320 articles. According to Alexa, the English subdomain (en.wikipedia.org; English Wikipedia) receives approximately 54% of Wikipedia's cumulative traffic, with the remaining split among the other languages (Japanese: 10%, German: 8%, Spanish: 5%, Russian: 4%, French: 4%, Italian: 3%).[2] As of July 2008, the five largest language editions are (in order of article count) English, German, French, Polish, and Japanese Wikipedias.[152]
Since Wikipedia is web-based and therefore worldwide, contributors of a same language edition may use different dialects or may come from different countries (as is the case for the English edition). These differences may lead to some conflicts over spelling differences, (e.g. color vs. colour)[153] or points of view.[154] Though the various language editions are held to global policies such as "neutral point of view," they diverge on some points of policy and practice, most notably on whether images that are not licensed freely may be used under a claim of fair use.[155][156][157]
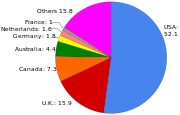
Jimmy Wales has described Wikipedia as "an effort to create and distribute a free encyclopedia of the highest possible quality to every single person on the planet in their own language."[159] Though each language edition functions more or less independently, some efforts are made to supervise them all. They are coordinated in part by Meta-Wiki, the Wikimedia Foundation's wiki devoted to maintaining all of its projects (Wikipedia and others).[160] For instance, Meta-Wiki provides important statistics on all language editions of Wikipedia,[161] and it maintains a list of articles every Wikipedia should have.[162] The list concerns basic content by subject: biography, history, geography, society, culture, science, technology, foodstuffs, and mathematics. As for the rest, it is not rare for articles strongly related to a particular language not to have counterparts in another edition. For example, articles about small towns in the United States might only be available in English.
Translated articles represent only a small portion of articles in most editions, in part because automated translation of articles is disallowed.[163] Articles available in more than one language may offer "InterWiki" links, which link to the counterpart articles in other editions.
Reusing Wikipedia's content
Because Wikipedia content is distributed under an open license, anyone can re-distribute it at no charge. The content of Wikipedia has been published in many forms, both online and offline, outside of the Wikipedia website.
Thousands of "mirror sites" exist that republish content from Wikipedia; two notable ones, that also include content from other reference sources, are Reference.com and Answers.com. Another example is Wapedia, which began to display Wikipedia content in a mobile-device-friendly format before Wikipedia itself did.
Some search engines also display content from Wikipedia on search results: examples include Bing.com (via technology gained from Powerset)[164] and Duck Duck Go.
Some wikis, most notably Enciclopedia Libre and Citizendium, began as forks of Wikipedia content.
The website DBpedia, begun in 2007, is a project that extracts data from the infoboxes and category declarations of the English-language Wikipedia and makes it available in a queriable semantic format, RDF. The possibility has also been raised to have Wikipedia export its data directly in a semantic format, possibly by using the Semantic MediaWiki extension. Such an export of data could also help Wikipedia reuse its own data, both between articles on the same language Wikipedia and between different language Wikipedias.[165]
Collections of Wikipedia articles have also been published on optical disks. An English version, 2006 Wikipedia CD Selection, contained about 2,000 articles.[166][167] The Polish-language version contains nearly 240,000 articles.[168] There are also German-language versions.[169]
"Wikipedia for Schools", the Wikipedia series of CDs/DVDs, produced by Wikipedians and SOS Children, is a free, hand-checked, non-commercial selection from Wikipedia targeted around the UK National Curriculum and intended to be useful for much of the English-speaking world.[170] The project is available online; an equivalent print encyclopedia would require roughly 20 volumes.
There has also been an attempt to put a select subset of Wikipedia's articles into printed book form.[171][172]
Cultural significance


In addition to logistic growth in the number of its articles,[173] Wikipedia has steadily gained status as a general reference website since its inception in 2001.[174] According to Alexa and comScore, Wikipedia is among the ten most visited websites worldwide.[8][175] Of the top ten, Wikipedia is the only non-profit website. The growth of Wikipedia has been fueled by its dominant position in Google search results;[176] about 50% of search engine traffic to Wikipedia comes from Google,[177] a good portion of which is related to academic research.[178] In April 2007 the Pew Internet and American Life project found that one third of US Internet users consulted Wikipedia.[179] In October 2006, the site was estimated to have a hypothetical market value of $580 million if it ran advertisements.[180]
Wikipedia's content has also been used in academic studies, books, conferences, and court cases.[181][182][183] The Parliament of Canada's website refers to Wikipedia's article on same-sex marriage in the "related links" section of its "further reading" list for the Civil Marriage Act.[184] The encyclopedia's assertions are increasingly used as a source by organizations such as the U.S. Federal Courts and the World Intellectual Property Organization[185] – though mainly for supporting information rather than information decisive to a case.[186] Content appearing on Wikipedia has also been cited as a source and referenced in some U.S. intelligence agency reports.[187] In December 2008, the scientific journal RNA Biology launched a new section for descriptions of families of RNA molecules and requires authors who contribute to the section to also submit a draft article on the RNA family for publication in Wikipedia.[188]

Wikipedia has also been used as a source in journalism,[189] often without attribution, and several reporters have been dismissed for plagiarizing from Wikipedia.[190][191][192] In July 2007, Wikipedia was the focus of a 30-minute documentary on BBC Radio 4[193] which argued that, with increased usage and awareness, the number of references to Wikipedia in popular culture is such that the term is one of a select band of 21st-century nouns that are so familiar (Google, Facebook, YouTube) that they no longer need explanation and are on a par with such 20th-century terms as Hoovering or Coca-Cola. Many parody Wikipedia's openness, with characters vandalizing or modifying the online encyclopedia project's articles. Notably, comedian Stephen Colbert has parodied or referenced Wikipedia on numerous episodes of his show The Colbert Report and coined the related term "wikiality."[72]
On September 28, 2007, Italian politician Franco Grillini raised a parliamentary question with the Minister of Cultural Resources and Activities about the necessity of freedom of panorama. He said that the lack of such freedom forced Wikipedia, "the seventh most consulted website" to forbid all images of modern Italian buildings and art, and claimed this was hugely damaging to tourist revenues.[194]

On September 16, 2007, The Washington Post reported that Wikipedia had become a focal point in the 2008 U.S. election campaign, saying, "Type a candidate's name into Google, and among the first results is a Wikipedia page, making those entries arguably as important as any ad in defining a candidate. Already, the presidential entries are being edited, dissected and debated countless times each day."[195] An October 2007 Reuters article, titled "Wikipedia page the latest status symbol," reported the recent phenomenon of how having a Wikipedia article vindicates one's notability.[196]
Wikipedia won two major awards in May 2004.[197] The first was a Golden Nica for Digital Communities of the annual Prix Ars Electronica contest; this came with a €10,000 (£6,588; $12,700) grant and an invitation to present at the PAE Cyberarts Festival in Austria later that year. The second was a Judges' Webby Award for the "community" category.[198] Wikipedia was also nominated for a "Best Practices" Webby. On January 26, 2007, Wikipedia was also awarded the fourth highest brand ranking by the readers of brandchannel.com, receiving 15% of the votes in answer to the question "Which brand had the most impact on our lives in 2006?"[199]
In September 2008, Wikipedia received Quadriga A Mission of Enlightenment award of Werkstatt Deutschland along with Boris Tadić, Eckart Höfling, and Peter Gabriel. The award was presented to Jimmy Wales by David Weinberger.[200]
Some media sources satirize Wikipedia's susceptibility to inserted inaccuracies. An example can be found in a front-page article in The Onion in July 2006, with the title "Wikipedia Celebrates 750 Years of American Independence."[201] Others draw upon Wikipedia's motto, such as in "The Negotiation," an episode of The Office, where character Michael Scott says "Wikipedia is the best thing ever. Anyone in the world can write anything they want about any subject, so you know you are getting the best possible information." "My Number One Doctor", a 2007 episode of the TV show Scrubs, also lampooned Wikipedia's reliance on editors who edit both scholarly and pop culture articles with a scene in which Dr. Perry Cox reacts to a patient who says that a Wikipedia article indicates that the raw food diet reverses the effects of bone cancer by retorting that the same editor who wrote that article also wrote the Battlestar Galactica episode guide.[202]
In July 2009, BBC Radio 4 broadcast a comedy series called Bigipedia, which was set on a website which was a parody of Wikipedia. Some of the sketches were directly inspired by Wikipedia and its articles.[203]
Related projects
A number of interactive multimedia encyclopedias incorporating entries written by the public existed long before Wikipedia was founded. The first of these was the 1986 BBC Domesday Project, which included text (entered on BBC Micro computers) and photographs from over 1 million contributors in the UK, and covering the geography, art, and culture of the UK. This was the first interactive multimedia encyclopedia (and was also the first major multimedia document connected through internal links), with the majority of articles being accessible through an interactive map of the UK. The user-interface and part of the content of the Domesday Project were emulated on a website until 2008.[204] One of the most successful early online encyclopedias incorporating entries by the public was h2g2, which was created by Douglas Adams and is run by the BBC. The h2g2 encyclopedia was relatively light-hearted, focusing on articles which were both witty and informative. Both of these projects had similarities with Wikipedia, but neither gave full editorial freedom to public users. A similar non-wiki project, the GNUPedia project, co-existed with Nupedia early in its history; however, it has been retired and its creator, free software figure Richard Stallman, has lent his support to Wikipedia.[22]
Wikipedia has also spawned several sister projects, which are also run by the Wikimedia Foundation. The first, "In Memoriam: September 11 Wiki,"[205] created in October 2002,[206] detailed the September 11 attacks; this project was closed in October 2006. Wiktionary, a dictionary project, was launched in December 2002;[207] Wikiquote, a collection of quotations, a week after Wikimedia launched, and Wikibooks, a collection of collaboratively written free textbooks and annotated texts. Wikimedia has since started a number of other projects, including Wikiversity, a project for the creation of free learning materials and the provision of online learning activities.[208] None of these sister projects, however, has come to meet the success of Wikipedia.
Several languages of Wikipedia also maintain a reference desk, where volunteers answer questions from the general public. According to a study by Pnina Shachaf in the Journal of Documentation, the quality of the Wikipedia reference desk is comparable to a standard library reference desk, with an accuracy of 55%.[209]
Other websites centered on collaborative knowledge base development have drawn inspiration from or inspired Wikipedia. Some, such as Susning.nu, Enciclopedia Libre, Hudong, Baidu Baike, and WikiZnanie likewise employ no formal review process, whereas others use more traditional peer review, such as Encyclopedia of Life, Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy, Scholarpedia, h2g2, and Everything2. The online wiki-based encyclopedia Citizendium was started by Wikipedia co-founder Larry Sanger in an attempt to create an "expert-friendly" Wikipedia.[210][211][212]
See also
- Academic studies about Wikipedia
- Behind the Mirror: A Search for a Natural History of Human Knowledge, philosophical background
- Criticism of Wikipedia
- Democratization of knowledge
- GNUPedia
- Interpedia, an early proposal for a collaborative Internet encyclopedia
- List of online encyclopedias
- List of wikis
- Logo of Wikipedia
- Network effects
- Nupedia
- Open content
- USA Congressional staff edits to Wikipedia
- User-generated content
- Wikipedia Review
Notes
- ↑ Jonathan Sidener. "Everyone's Encyclopedia". The San Diego Union-Tribune. http://www.signonsandiego.com/uniontrib/20041206/news_mz1b6encyclo.html. Retrieved 2006-10-15.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "Five-year Traffic Statistics for Wikipedia.org". Alexa Internet. http://www.alexa.com/data/details/traffic_details/wikipedia.org?range=5y&size=large&y=t. Retrieved 2010-05-22.
- ↑ Some versions, such as the English language version, contain non-free content.
- ↑ In some parts of the world, the access to Wikipedia had been blocked.
- ↑ Mike Miliard (2008-03-01). "Wikipediots: Who Are These Devoted, Even Obsessive Contributors to Wikipedia?". Salt Lake City Weekly. http://www.cityweekly.net/utah/article-5129-feature-wikipediots-who-are-these-devoted-even-obsessive-contributors-to-wikipedia.html. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- ↑ Bill Tancer (2007-05-01). "Look Who's Using Wikipedia". Time. http://www.time.com/time/business/article/0,8599,1595184,00.html. Retrieved 2007-12-01. "The sheer volume of content [...] is partly responsible for the site's dominance as an online reference. When compared to the top 3,200 educational reference sites in the U.S., Wikipedia is #1, capturing 24.3% of all visits to the category" Cf. Bill Tancer (Global Manager, Hitwise), "Wikipedia, Search and School Homework", Hitwise: An Experian Company (Blog), March 1, 2007. Retrieved December 18, 2008.
- ↑ Alex Woodson (2007-07-08). "Wikipedia remains go-to site for online news". Reuters. http://www.reuters.com/article/internetNews/idUSN0819429120070708. Retrieved 2007-12-16. "Online encyclopedia Wikipedia has added about 20 million unique monthly visitors in the past year, making it the top online news and information destination, according to Nielsen//NetRatings."
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 "Top 500". Alexa. http://www.alexa.com/site/ds/top_sites?ts_mode=global&lang=none. Retrieved 2009-10-13.
- ↑ Wikipedia.org Site Info. Alexa. http://www.alexa.com/siteinfo/wikipedia.org?p=&r=. Retrieved 2010-07-13
- ↑ How I started Wikipedia, presentation by Larry Sanger
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Larry Sanger, Why Wikipedia Must Jettison Its Anti-Elitism, Kuro5hin, December 31, 2004.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Danah Boyd (2005-01-04). "Academia and Wikipedia". Many 2 Many: A Group Weblog on Social Software. Corante. http://many.corante.com/archives/2005/01/04/academia_and_wikipedia.php. Retrieved 2008-12-18. "[The author, Danah Boyd, describes herself as] an expert on social media[,] ... a doctoral student in the School of Information at the University of California, Berkeley [,] and a fellow at the Harvard University Berkman Center for Internet & Society [at Harvard Law School.]"
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Simon Waldman (2004-10-26). "Who knows?". Guardian.co.uk (London). http://www.guardian.co.uk/technology/2004/oct/26/g2.onlinesupplement. Retrieved 2007-02-11.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Ahrens, Frank (2006-07-09). "Death by Wikipedia: The Kenneth Lay Chronicles". The Washington Post. http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2006/07/08/AR2006070800135.html. Retrieved 2006-11-01.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Fernanda B. Viégas, Martin Wattenberg, and Kushal Dave (2004). "Studying Cooperation and Conflict between Authors with History Flow Visualizations" (PDF). Proceedings of the ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI) (Vienna, Austria: ACM SIGCHI): 575–582. doi:10.1145/985921.985953. ISBN 1-58113-702-8. http://alumni.media.mit.edu/~fviegas/papers/history_flow.pdf. Retrieved 2007-01-24.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 Reid Priedhorsky, Jilin Chen, Shyong (Tony) K. Lam, Katherine Panciera, Loren Terveen, and John Riedl (GroupLens Research, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, University of Minnesota) (2007-11-04). "Creating, Destroying, and Restoring Value in Wikipedia" (PDF). Association for Computing Machinery GROUP '07 conference proceedings (Sanibel Island, Florida). http://www-users.cs.umn.edu/~reid/papers/group282-priedhorsky.pdf. Retrieved 2007-10-13.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Jim Giles (December 2005). "Internet encyclopedias go head to head". Nature 438 (7070): 900–901. doi:10.1038/438900a. PMID 16355180. http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v438/n7070/full/438900a.html. The study (that was not in itself peer reviewed) was cited in several news articles, e.g.,
- "Wikipedia survives research test". BBC News (BBC). December 15, 2005. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/technology/4530930.stm.
- ↑ Grossman, Lev (2006-12-13). "Time's Person of the Year: You". TIME (Time, Inc). http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,1569514,00.html. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- ↑ Jonathan Dee (2007-07-01). "All the News That's Fit to Print Out". The New York Times Magazine. http://www.nytimes.com/2007/07/01/magazine/01WIKIPEDIA-t.html. Retrieved 2007-12-01.
- ↑ Andrew Lih (2004-04-16). "Wikipedia as Participatory Journalism: Reliable Sources? Metrics for Evaluating Collaborative Media as a News Resource" (PDF). 5th International Symposium on Online Journalism (University of Texas at Austin). http://jmsc.hku.hk/faculty/alih/publications/utaustin-2004-wikipedia-rc2.pdf. Retrieved 2007-10-13.
- ↑ Witzleb, Normann (2009). Engaging with the World: Students of Comparative Law Write for Wikipedia. 19. Legal Education Review. pp. 83–98
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 Richard M. Stallman (2007-06-20). "The Free Encyclopedia Project". Free Software Foundation. http://www.gnu.org/encyclopedia/encyclopedia.html. Retrieved 2008-01-04.
- ↑ Jonathan Sidener (2004-12-06). "Everyone's Encyclopedia". The San Diego Union-Tribune. http://www.signonsandiego.com/uniontrib/20041206/news_mz1b6encyclo.html. Retrieved 2006-10-15.
- ↑ Meyers, Peter (2001-09-20). "Fact-Driven? Collegial? This Site Wants You". New York Times (The New York Times Company). http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9800E5D6123BF933A1575AC0A9679C8B63&n=Top%2fReference%2fTimes%20Topics%2fSubjects%2fC%2fComputer%20Software. Retrieved 2007-11-22. " 'I can start an article that will consist of one paragraph, and then a real expert will come along and add three paragraphs and clean up my one paragraph,' said Larry Sanger of Las Vegas, who founded Wikipedia with Mr. Wales."
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 25.2 Sanger, Larry (April 18, 2005). "The Early History of Nupedia and Wikipedia: A Memoir". Slashdot. http://features.slashdot.org/features/05/04/18/164213.shtml. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- ↑ Sanger, Larry (January 17, 2001). "Wikipedia Is Up!". Internet Archive. http://web.archive.org/web/20010506042824/www.nupedia.com/pipermail/nupedia-l/2001-January/000684.html. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- ↑ "Wikipedia-l: LinkBacks?". http://lists.wikimedia.org/pipermail/wikipedia-l/2001-October/000671.html. Retrieved 2007-02-20.
- ↑ Sanger, Larry (2001-01-10). "Let's Make a Wiki". Internet Archive. Archived from the original on 2003-04-14. http://web.archive.org/web/20030414014355/http://www.nupedia.com/pipermail/nupedia-l/2001-January/000676.html. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- ↑ "Wikipedia: HomePage". Archived from the original on 2001-03-31. http://web.archive.org/web/20010331173908/http://www.wikipedia.com/. Retrieved 2001-03-31.
- ↑ "Wikipedia:Neutral point of view, Wikipedia (January 21, 2007)
- ↑ "statistics "Multilingual statistics". Wikipedia. March 30, 2005. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Multilingual statistics. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- ↑ "Encyclopedias and Dictionaries". Encyclopædia Britannica, 15th ed.. 18. Encyclopædia Britannica. 2007. pp. 257–286.
- ↑ "[long] Enciclopedia Libre: msg#00008". Osdir. http://osdir.com/ml/science.linguistics.wikipedia.international/2003-03/msg00008.html. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- ↑ Clay Shirky (February 28, 2008). Here Comes Everybody: The Power of Organizing Without Organizations. The Penguin Press via Amazon Online Reader. p. 273. ISBN 1-594201-53-6. http://www.amazon.com/gp/reader/1594201536/ref=sib_dp_srch_pop?v=search-inside&keywords=spanish&go.x=0&go.y=0&go=Go%21. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- ↑ "BBC News". BBC News. 2007-12-15. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/technology/7144970.stm. Retrieved 2010-07-13.
- ↑ Bobbie Johnson (2009-08-12). "Wikipedia approaches its limits". The Guardian (London). http://www.guardian.co.uk/technology/2009/aug/12/wikipedia-deletionist-inclusionist. Retrieved 2010-03-31.
- ↑ "The Singularity is Not Near: Slowing Growth of Wikipedia". the International Symposium on Wikis. Orlando, Florida. 2009. http://www.wikisym.org/ws2009/procfiles/p108-suh.pdf.
- ↑ Evgeny Morozov. "Edit This Page; Is it the end of Wikipedia". Boston review. http://www.bostonreview.net/BR34.6/morozov.php.
- ↑ New York Times
- ↑ Jenny Kleeman (2009-11-26). "Wikipedia falling victim to a war of words". London: Guardian. http://www.guardian.co.uk/technology/2009/nov/26/wikipedia-losing-disgruntled-editors. Retrieved 2010-03-31.
- ↑ (PDF) Wikipedia: A quantitative analysis. http://libresoft.es/Members/jfelipe/thesis-wkp-quantanalysis.
- ↑ Volunteers Log Off as Wikipedia Ages, The Wall Street Journal, November 27, 2009.
- ↑ Barnett, Emma (2009-11-26). "Wikipedia's Jimmy Wales denies site is 'losing' thousands of volunteer editors". London: Telegraph. http://www.telegraph.co.uk/technology/wikipedia/6660646/Wikipedias-Jimmy-Wales-denies-site-is-losing-thousands-of-volunteer-editors.html. Retrieved 2010-03-31.
- ↑ "UX and Usability Study". Usability.wikimedia.org. http://usability.wikimedia.org/wiki/UX_and_Usability_Study. Retrieved 2010-07-13.
- ↑ Wikipedia:Ownership of articles
- ↑ Birken, P. (2008-12-14). "Bericht Gesichtete Versionen" (in German). Wikide-l mailing list. Wikimedia Foundation. http://lists.wikimedia.org/pipermail/wikide-l/2008-December/021594.html. Retrieved 2009-02-15.
- ↑ "Wikimedia blog » Blog Archive » A quick update on Flagged Revisions". http://blog.wikimedia.org/2009/08/26/a-quick-update-on-flagged-revisions/. Retrieved 2009-08-30.
- ↑ "Wikipedia:Flagged protection and patrolled revisions – Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia". http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Flagged_protection_and_patrolled_revisions#cite_ref-7. Retrieved 2009-08-25.
- ↑ "Wikipedia introduces edit mechanism for divisive pages", Jonathan Frewin, British Broadcasting Corporation, June 15, 2010
- ↑ 50.0 50.1 Kleinz, Torsten (February, 2005). "World of Knowledge" (PDF). The Wikipedia Project (Linux Magazine). http://w3.linux-magazine.com/issue/51/Wikipedia_Encyclopedia.pdf. Retrieved 2007-07-13. "The Wikipedia's open structure makes it a target for trolls and vandals who malevolently add incorrect information to articles, get other people tied up in endless discussions, and generally do everything to draw attention to themselves."
- ↑ The Japanese Wikipedia, for example, is known for deleting every mention of real names of victims of certain high-profile crimes, even though they may still be noted in other language editions.
- ↑ Fernanda B. Viégas, Martin Wattenberg, Jesse Kriss, Frank van Ham (2007-01-03) (PDF). Talk Before You Type: Coordination in Wikipedia. Visual Communication Lab, IBM Research. http://www.research.ibm.com/visual/papers/wikipedia_coordination_final.pdf. Retrieved 2008-06-27.
- ↑ "First Monday". First Monday. http://firstmonday.org/htbin/cgiwrap/bin/ojs/index.php/fm/article/view/2365/2182. Retrieved 2010-07-13.
- ↑ Fernanda B. Viégas, Martin Wattenberg, and Matthew M. McKeon (2007-07-22) (PDF). The Hidden Order of Wikipedia. Visual Communication Lab, IBM Research. http://www.research.ibm.com/visual/papers/hidden_order_wikipedia.pdf. Retrieved 2007-10-30.
- ↑ "Wikipedia:Version 1.0 Editorial Team/Assessment". http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Version_1.0_Editorial_Team/Assessment. Retrieved 2007-10-28.
- ↑ "Who's behind Wikipedia?". PC World. 2008-02-06. http://www.pcworld.idg.com.au/index.php/id;1866322157;fp;2;fpid;2. Retrieved 2008-02-07.
- ↑ "Wikipedia:ISNOT". http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:ISNOT. Retrieved 2010-04-01. "Wikipedia is not a dictionary, usage, or jargon guide."
- ↑ "Wikipedia:Notability". http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Notability. Retrieved 2008-02-13. "A topic is presumed to be notable if it has received significant coverage in reliable secondary sources that are independent of the subject."
- ↑ "Wikipedia:No original research". http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:No_original_research. Retrieved 2008-02-13. "Wikipedia does not publish original thought"
- ↑ "Wikipedia:Verifiability". http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Verifiability. Retrieved 2008-02-13. "Material challenged or likely to be challenged, and all quotations, must be attributed to a reliable, published source."
- ↑ "Wikipedia:Neutral_point_of_view". http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Neutral_point_of_view. Retrieved 2008-02-13. "All Wikipedia articles and other encyclopedic content must be written from a neutral point of view, representing significant views fairly, proportionately and without bias."
- ↑ Eric Haas (2007-10-26). "Will Unethical Editing Destroy Wikipedia's Credibility?". AlterNet.org. http://www.alternet.org/story/61365/?page=entire. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- ↑ Hoffman, David A.; Mehra, Salil K. (2009). Wikitruth through Wikiorder. 59. Emory Law Journal. pp. 151–210
- ↑ "Caslon.com". Caslon.com. http://www.caslon.com.au/wikiprofile1.htm. Retrieved 2010-07-13.
- ↑ Robert McHenry (2004-11-15). "The Faith-Based Encyclopedia". TCS Daily. http://www.tcsdaily.com/article.aspx?id=111504A. Retrieved 2009-09-10.
- ↑ 66.0 66.1 Seigenthaler, John (2005-11-29). "A False Wikipedia 'biography'". USA Today. http://www.usatoday.com/news/opinion/editorials/2005-11-29-wikipedia-edit_x.htm. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- ↑ Thomas L. Friedman The World is Flat, p. 124, Farrar, Straus & Giroux, 2007 ISBN 978-0-374-29278-2
- ↑ "Founder shares cautionary tale of libel in cyberspace By Brian J. Buchanan". Firstamendmentcenter.org. 2005-11-30. http://www.firstamendmentcenter.org/news.aspx?id=17798. Retrieved 2010-07-13.
- ↑ "Toward a New Compendium of Knowledge (longer version)". Citizendium.org. http://www.citizendium.org/essay.html. Retrieved 2006-10-10.
- ↑ Kane, Margaret (2006-01-30). "Politicians notice Wikipedia". CNET. http://news.cnet.com/8301-10784_3-6032713-7.html. Retrieved 2007-01-28.
- ↑ Bergstein, Brian (2007-01-23). "Microsoft offers cash for Wikipedia edit". MSNBC. http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/16775981/. Retrieved 2007-02-01.
- ↑ 72.0 72.1 Stephen Colbert (2006-07-30). "Wikiality". Comedycentral.com. http://www.colbertnation.com/the-colbert-report-videos/72347/july-31-2006/the-word---wikiality. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- ↑ Hafner, Katie (2007-08-19). "Seeing Corporate Fingerprints From the Editing of Wikipedia". New York Times. http://www.nytimes.com/2007/08/19/technology/19wikipedia.html. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- ↑ "Wikipedia signpost: Abuse Filter is enabled". En.wikipedia.org. 2009-03-23. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Wikipedia_Signpost/2009-03-23/Abuse_Filter. Retrieved 2010-07-13.
- ↑ English Wikipedia's semi-protection policy
- ↑ English Wikipedia's full protection policy
- ↑ 77.0 77.1 Kittur, A., Chi, E. H., and Suh, B. 2009. What’s in Wikipedia? Mapping Topics and Conflict Using Socially Annotated Category Structure In Proceedings of the 27th international Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (Boston, MA, USA, April 04 – 09, 2009). CHI '09. ACM, New York, NY, 1509–1512.
- ↑ "The 50 most-viewed Wikipedia articles in 2009 and 2008". London: The Daily Telegraph. 2009-08-17. http://www.telegraph.co.uk/technology/wikipedia/6043534/The-50-most-viewed-Wikipedia-articles-in-2009-and-2008.html. Retrieved 2010-03-31.
- ↑ Wikipedia:PAPER
- ↑ Schliebs, Mark (2008-09-09). "Wikipedia users divided over sexual material". news.com.au. http://www.news.com.au/technology/story/0,25642,24318423-5014239,00.html. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- ↑ "Wikipedia is not censored". Wikipedia. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Wikipedia_is_not#Wikipedia_is_not_censored. Retrieved 2008-04-30.
- ↑ Sophie Taylor (2008-04-05). "China allows access to English Wikipedia". Reuters. http://in.reuters.com/article/technologyNews/idINIndia-32865420080405. Retrieved 2008-07-29.
- ↑ "Mapping the Geographies of Wikipedia Content". Mark Graham Oxford Internet Institute. ZeroGeography. http://zerogeography.blogspot.com/2009/11/mapping-geographies-of-wikipedia.html. Retrieved 2009-11-16.
- ↑ "The battle for Wikipedia's soul". The Economist. 2008-03-06. http://www.economist.com/printedition/displaystory.cfm?story_id=10789354. Retrieved 2008-03-07.
- ↑ Douglas, Ian (2007-11-10). down deletionist/creationsistcted/main.jhtml?xml=/connected/2007/10/11/dlwiki11.xml "Wikipedia: an online encyclopedia torn apart". London: Daily Telegraph. http://www.telegraph.co.uk/connemoved down deletionist/creationsistcted/main.jhtml?xml=/connected/2007/10/11/dlwiki11.xml. Retrieved 2008-03-11.
- ↑ Roy Rosenzweig. "Can History be Open Source? Wikipedia and the Future of the Past". The Journal of American History Volume 93, Number 1 (June, 2006): 117–46. http://chnm.gmu.edu/resources/essays/d/42. Retrieved 2007-10-29.
- ↑ "Wikipedia:General disclaimer". English Wikipedia. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:General_disclaimer. Retrieved 2008-04-22.
- ↑ "Public Information Research". Wikipedia Watch.
- ↑ Raphel, JR. "The 15 Biggest Wikipedia Blunders". PC World. http://www.pcworld.com/article/170874/the_15_biggest_wikipedia_blunders.html. Retrieved 2009-09-02.
- ↑ Stacy Schiff (2006-07-31). "Know It All". The New Yorker.
- ↑ Robert McHenry, "The Faith-Based Encyclopedia," Tech Central Station, November 15, 2004.
- ↑ "Wide World of Wikipedia". The Emory Wheel. April 21, 2006. http://www.emorywheel.com/detail.php?n=17902. Retrieved 2007-10-17.
- ↑ Jaschik, Scott (2007-01-26). "A Stand Against Wikipedia". Inside Higher Ed. http://www.insidehighered.com/news/2007/01/26/wiki. Retrieved 2007-01-27.
- ↑ Helm, Burt (2005-12-14). "Wikipedia: "A Work in Progress"". BusinessWeek. http://www.businessweek.com/technology/content/dec2005/tc20051214_441708.htm. Retrieved 2007-01-29.
- ↑ Fatally Flawed: Refuting the recent study on encyclopedic accuracy by the journal Nature Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc., March 2006
- ↑ "Encyclopaedia Britannica and Nature: a response". http://www.nature.com/press_releases/Britannica_response.pdf?item. Retrieved 2010-07-13.
- ↑ Tyler Cowen (2008-03-14). "Cooked Books". The New Republic. Archived from the original on 2008-03-18. http://web.archive.org/web/20080318103017/http://www.tnr.com/story.html?id=82eb5d70-13bd-4086-9ec0-cb0e9e8411b3. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- ↑ Child, Maxwell L.,"Professors Split on Wiki Debate", The Harvard Crimson, Monday, February 26, 2007.
- ↑ 99.0 99.1 Chloe Stothart, Web threatens learning ethos, The Times Higher Education Supplement, 2007, 1799 (June 22), page 2
- ↑ Hafner, Kate (June 17, 2006). "Growing Wikipedia Refines Its 'Anyone Can Edit' Policy". New York Times. http://www.nytimes.com/2006/06/17/technology/17wiki.html?scp=8&sq=wikipedia&st=cse. Retrieved 2009-07-12.
- ↑ Corner, Stuart (June 18, 2006). "What's all the fuss about Wikipedia?". iT Wire. http://www.itwire.com/content/view/4666/127/. Retrieved 2007-03-25.
- ↑ Wilson, Chris (2008-02-22). "The Wisdom of the Chaperones". Slate. http://www.slate.com/id/2184487. Retrieved 2008-03-04.
- ↑ Arthur, Charles (2005-12-15). "Log on and join in, but beware the web cults". London: Guardian. http://www.guardian.co.uk/technology/2005/dec/15/wikipedia.web20. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- ↑ Lu Stout, Kristie (2003-08-04). "Wikipedia: The know-it-all Web site". CNN. http://www.cnn.com/2003/TECH/internet/08/03/wikipedia/index.html. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- ↑ "Wikinfo (2005-03-30). "Critical views of Wikipedia". http://wikinfo.org/index.php/Critical_views_of_Wikipedia. Retrieved 2007-01-29.
- ↑ Wikipedia:Administrators
- ↑ Mehegan, David (February 13, 2006). "Many contributors, common cause". The Boston Globe. http://www.boston.com/business/technology/articles/2006/02/13/many_contributors_common_cause/. Retrieved 2007-03-25.
- ↑ "Wikipedia:Administrators". http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Administrators#Administrator_conduct. Retrieved 2009-07-12.
- ↑ "Wikipedia:RfA_Review/Reflect". http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:RfA_Review/Reflect. Retrieved 2009-09-24.
- ↑ Kittur, Aniket. "Power of the Few vs. Wisdom of the Crowd: Wikipedia and the Rise of the Bourgeoisie" (PDF). http://www.viktoria.se/altchi/submissions/submission_edchi_1.pdf. Retrieved 2008-02-23.
- ↑ Swartz, Aaron (2006-09-04). "Raw Thought: Who Writes Wikipedia?". http://www.aaronsw.com/weblog/whowriteswikipedia. Retrieved 2008-02-23.
- ↑ "Wikipedia "Good Samaritans Are on the Money". Scientific American. 2007-10-19. http://www.sciam.com/article.cfm?id=good-samaritans-are-on-the-money. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- ↑ Andrea Ciffolilli, "Phantom authority, self-selective recruitment and retention of members in virtual communities: The case of Wikipedia," First Monday December 2003.
- ↑ Zittrain, Jonathan (2008). The Future of the Internet and How to Stop It — Chapter 6: The Lessons of Wikipedia. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0300124873. http://yupnet.org/zittrain/archives/16. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- ↑ Yair Amichai–Hamburger, Naama Lamdan, Rinat Madiel, Tsahi Hayat Personality Characteristics of Wikipedia Members CyberPsychology & Behavior December 1, 2008, 11(6): 679–681. doi:10.1089/cpb.2007.0225
- ↑ "Wikipedians are 'closed' and 'disagreeable'". Newscientist.com. http://www.newscientist.com/article/mg20126883.900-wikipedians-are-closed-and-disagreeable.html. Retrieved 2010-07-13.
- ↑ Jim Giles After the boom, is Wikipedia heading for bust? New Scientist 04 August 2009
- ↑ "Infoq.com". Infoq.com. http://www.infoq.com/presentations/vibber-community-perf-opt. Retrieved 2010-07-13.
- ↑ "The Wikipedia Signpost". Wikipedia. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Wikipedia_Signpost. Retrieved 2009-03-24.
- ↑ Cohen, Noam (2007-03-05). "A Contributor to Wikipedia Has His Fictional Side". The New York Times. http://www.nytimes.com/2007/03/05/technology/05wikipedia.html?pagewanted=2&_r=1. Retrieved 2008-10-18.
- ↑ Rubel, Steve (2005-12-19). "Ten More Wikipedia Hacks". WebProNews. http://www.webpronews.com/blogtalk/2005/12/19/ten-more-wikipedia-hacks. Retrieved 2008-10-18.
- ↑ Ebert, Roger. ''Roger Ebert's Movie Yearbook 2009'' Page 529. Books.google.com. http://books.google.com/books?id=-U3y_SgnQ6kC&pg=PA529&lpg=PA529&dq=Roger+Ebert,+%22according+to+Wikipedia%22&source=bl&ots=Ir48y1qiBa&sig=RpFKMr24CxqXhXX4lfTdQv2wzQE&hl=en&ei=5GiZSs-SKZmf8Qax-9GjBQ&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=6#v=onepage&q=&f=false. Retrieved 2010-07-13.
- ↑ Ebert, Roger. Review of Good Hair; rogerebert.suntimes.com October 7, 2009
- ↑ "Bob Park. "What's New" bobpark.org; August 28, 2009". Bobpark.physics.umd.edu. 2009-08-28. http://bobpark.physics.umd.edu/WN09/wn082809.html. Retrieved 2010-07-13.
- ↑ T Kriplean, I Beschastnikh, et al (2008). Articulations of wikiwork: uncovering valued work in wikipedia through barnstars. Proceedings of the ACM. http://portal.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1460563.1460573
- ↑ Panciera, Katherine et al. (2009). Wikipedians Are Born, Not Made. Association for Computing Machinery, Proceedings of the ACM Conference on Supporting Group Work. pp. 51, 59
- ↑ Goldman, Eric. Wikipedia's Labor Squeeze and its Consequences. 8. Journal on Telecommunications and High Technology Law
- ↑ Noveck, Beth Simone. Wikipedia and the Future of Legal Education. 57. Journal of Legal Education
- ↑ Mark Bergman. "Wikimedia Architecture" (PDF). Wikimedia Foundation Inc.. http://www.nedworks.org/~mark/presentations/san/Wikimedia%20architecture.pdf. Retrieved 2008-06-27.
- ↑ "Version: Installed extensions". http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Special:Version#Installed_extensions.
- ↑ Michael Snow. "Lucene search: Internal search function returns to service". Wikimedia Foundation Inc.. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Wikipedia_Signpost/2005-04-18/Lucene_search. Retrieved 2009-02-26.
- ↑ Brion Vibber. "[Wikitech-l] Lucene search". http://lists.wikimedia.org/pipermail/wikitech-l/2005-April/016297.html. Retrieved 2009-02-26.
- ↑ "Extension:Lucene-search". Wikimedia Foundation Inc.. http://www.mediawiki.org/wiki/Extension:Lucene-search. Retrieved 2009-08-31.
- ↑ "mediawiki — Revision 55688: /branches/lucene-search-2.1/lib". Wikimedia Foundation Inc.. http://svn.wikimedia.org/svnroot/mediawiki/branches/lucene-search-2.1/lib/. Retrieved 2009-08-31.
- ↑ Todd R. Weiss (October 9, 2008 (Computerworld)). "Wikipedia simplifies IT infrastructure by moving to one Linux vendor". Computerworld.com. http://www.computerworld.com/action/article.do?command=viewArticleBasic&taxonomyName=Servers+and+Data+Center&articleId=9116787&taxonomyId=154&pageNumber=1. Retrieved 2008-11-01.
- ↑ "Wikipedia adopts Ubuntu for its server infrastructure". Arstechnica.com. http://arstechnica.com/news.ars/post/20081009-wikipedia-adopts-ubuntu-for-its-server-infrastructure.html. Retrieved 2008-11-01.
- ↑ "Server roles at wikitech.wikimedia.org". http://wikitech.wikimedia.org/view/Server_roles. Retrieved 2009-12-08.
- ↑ "Monthly request statistics," Wikimedia. Retrieved on 2008-10-31.
- ↑ Domas Mituzas. "Wikipedia: Site internals, configuration, code examples and management issues" (PDF). MySQL Users Conference 2007. http://dammit.lt/uc/workbook2007.pdf. Retrieved 2008-06-27.
- ↑ Guido Urdaneta, Guillaume Pierre and Maarten van Steen. "Wikipedia Workload Analysis for Decentralized Hosting". Elsevier Computer Networks 53(11), pp. 1830–1845, June 2009. http://www.globule.org/publi/WWADH_comnet2009.html.
- ↑ "Wikimedia Mobile is Officially Launched". Wikimedia Technical Blog. 2009-06-30. http://techblog.wikimedia.org/2009/06/wikimedia-mobile-launch/. Retrieved 2009-07-22.
- ↑ "iPhone Gems: Wikipedia Apps". 30 November 2008. http://www.ilounge.com/index.php/articles/comments/15802/. Retrieved 22 July 2008.
- ↑ "Wikipedia:Copyrights". English Wikipedia. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Copyrights. Retrieved 2008-04-22.
- ↑ "Wikimedia community approves license migration". Wikimedia Foundation. Wikimedia Foundation. http://blog.wikimedia.org/2009/05/21/wikimedia-community-approves-license-migration/. Retrieved 2009-05-21.
- ↑ Walter Vermeir (2007). "Resolution:License update". Wikizine. http://wikimediafoundation.org/wiki/Resolution:License_update. Retrieved 2007-12-04.
- ↑ "Licensing update/Questions and Answers". Wikimedia Meta. Wikimedia Foundation. http://meta.wikimedia.org/wiki/Licensing_update/Questions_and_Answers. Retrieved 2009-02-15.
- ↑ "Licensing_update/Timeline". Wikimedia Meta. Wikimedia Foundation. http://meta.wikimedia.org/wiki/Licensing_update/Timeline. Retrieved 2009-04-05.
- ↑ 148.0 148.1 Wikimedia.org
- ↑ "Wikipedia cleared in French defamation case". Reuters. 2007-11-02. http://www.reuters.com/article/internetNews/idUSL0280486220071102?feedType=RSS&feedName=internetNews. Retrieved 2007-11-02.
- ↑ Anderson, Nate (2008-05-02). "Dumb idea: suing Wikipedia for calling you "dumb"". Ars Technica. http://arstechnica.com/news.ars/post/20080502-dumb-idea-suing-wikipedia-for-calling-you-dumb.html. Retrieved 2008-05-04.
- ↑ "Statistics". English Wikipedia. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Special:Statistics. Retrieved 2008-06-21.
- ↑ "Wikipedia:Multilingual statistics". English Wikipedia. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Multilingual_statistics. Retrieved 2007-12-23.
- ↑ "spelling". Manual of Style. Wikipedia. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Spelling. Retrieved 2007-05-19.
- ↑ "Countering systemic bias". http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:WikiProject_Countering_systemic_bias. Retrieved 2007-05-19.
- ↑ "Fair use". Meta wiki. http://meta.wikimedia.org/wiki/Fair_use. Retrieved 2007-07-14.
- ↑ "Images on Wikipedia". http://meta.wikimedia.org/wiki/Images_on_Wikipedia. Retrieved 2007-07-14.
- ↑ Fernanda B. Viégas (2007-01-03) (PDF). The Visual Side of Wikipedia. Visual Communication Lab, IBM Research. http://www.research.ibm.com/visual/papers/viegas_hicss_visual_wikipedia.pdf. Retrieved 2007-10-30.
- ↑ "Edits by project and country of origin". 2006-09-04. http://meta.wikimedia.org/wiki/Edits_by_project_and_country_of_origin. Retrieved 2007-10-25.
- ↑ Jimmy Wales, "Wikipedia is an encyclopedia," March 8, 2005, <Wikipedia-l@wikimedia.org>
- ↑ "Meta-Wiki". Wikimedia Foundation. http://meta.wikimedia.org/. Retrieved 2009-03-24.
- ↑ "Meta-Wiki Statistics". Wikimedia Foundation. http://meta.wikimedia.org/wiki/Statistics. Retrieved 2008-03-24.
- ↑ "List of articles every Wikipedia should have". Wikimedia Foundation. http://meta.wikimedia.org/wiki/List_of_articles_every_Wikipedia_should_have. Retrieved 2008-03-24.
- ↑ "Wikipedia: Translation". English Wikipedia. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Translations. Retrieved 2007-02-03.
- ↑ Researching With Bing Reference, Bing Community blog, July 27, 2009
- ↑ Wikipedia to Add Meaning to Its Pages, Tom Simonite, Technology Review, July 7, 2010
- ↑ "Wikipedia on DVD." Linterweb. Accessed June 1, 2007. "Linterweb is authorized to make a commercial use of the Wikipedia trademark restricted to the selling of the Encyclopedia CDs and DVDs."
- ↑ "Wikipedia 0.5 Available on a CD-ROM." Wikipedia on DVD. Linterweb. Accessed June 1, 2007. "The DVD or CD-ROM version 0.5 was commercially available for purchase."
- ↑ "Polish Wikipedia on DVD". http://meta.wikimedia.org/wiki/Polska_Wikipedia_na_DVD_%28z_Helionem%29/en. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- ↑ "Wikipedia:DVD". http://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Wikipedia-Distribution. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- ↑ Wikipedia CD Selection. Retrieved 2009 September 8.
- ↑ "Wikipedia turned into book". Telegraph.co.uk (London: Telegraph Media Group). 2009-06-16. Archived from the original on 2009-09-08. http://www.webcitation.org/5jeCgQjpj. Retrieved 2009-09-08.
- ↑ Wikipedia Selection for Schools. Retrieved 2009 September 8.
- ↑ "Wikipedia:Modelling Wikipedia's growth". http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Modelling_Wikipedia%27s_growth. Retrieved 2007-12-22.
- ↑ "694 Million People Currently Use the Internet Worldwide According To comScore Networks". comScore. 2006-05-04. http://www.comscore.com/press/release.asp?press=849. Retrieved 2007-12-16. "Wikipedia has emerged as a site that continues to increase in popularity, both globally and in the U.S."
- ↑ "comScore Data Center". October 2007. http://www.comscore.com/press/data.asp. Retrieved 2008-01-19.
- ↑ Petrilli, Michael J. "Wikipedia or Wickedpedia?". Hoover Institution 8 (2). Archived from the original on 2008-03-27. http://web.archive.org/web/20080327230211/http://www.hoover.org/publications/ednext/16111162.html. Retrieved 2008-03-21.
- ↑ "Google Traffic To Wikipedia up 166% Year over Year". Hitwise. 2007-02-16. http://weblogs.hitwise.com/leeann-prescott/2007/02/wikipedia_traffic_sources.html. Retrieved 2007-12-22.
- ↑ "Wikipedia and Academic Research". Hitwise. 2006-10-17. http://weblogs.hitwise.com/leeann-prescott/2006/10/wikipedia_and_academic_researc.html. Retrieved 2008-02-06.
- ↑ Rainie, Lee; Bill Tancer (2007-12-15). "Wikipedia users" (PDF). Pew Internet & American Life Project. Pew Research Center. Archived from the original on 2008-03-06. http://web.archive.org/web/20080306031354/http://www.pewinternet.org/pdfs/PIP_Wikipedia07.pdf. Retrieved 2007-12-15. "36% of online American adults consult Wikipedia. It is particularly popular with the well-educated and current college-age students."
- ↑ Karbasfrooshan, Ashkan (2006-10-26). "What is Wikipedia.org's Valuation?". http://www.watchmojo.com/web/blog/?p=626. Retrieved 2007-12-01.
- ↑ in the media "Wikipedia:Wikipedia in the media". Wikipedia. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Wikipedia in the media. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- ↑ "Bourgeois et al. v. Peters et al." (PDF). http://www.ca11.uscourts.gov/opinions/ops/200216886.pdf. Retrieved 2007-02-06.
- ↑ "Wikipedian Justice" (PDF). http://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/Delivery.cfm/SSRN_ID1346311_code835394.pdf?abstractid=1346311. Retrieved 2009-06-09.
- ↑ C-38 Government of Canada Site | Site du gouvernement du Canada, LEGISINFO (March 28, 2005)
- ↑ Arias, Martha L. (2007-01-29). "Wikipedia: The Free Online Encyclopedia and its Use as Court Source". Internet Business Law Services. http://www.ibls.com/internet_law_news_portal_view.aspx?s=latestnews&id=1668. Retrieved 2008-12-26. (the name "World Intellectual Property Office" should however read "World Intellectual Property Organization" in this source)
- ↑ Cohen, Noam (2007-01-29). "Courts Turn to Wikipedia, but Selectively". New York Times. http://www.nytimes.com/2007/01/29/technology/29wikipedia.html. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- ↑ Aftergood, Steven (2007-03-21). "The Wikipedia Factor in U.S. Intelligence". Federation of American Scientists Project on Government Secrecy. http://www.fas.org/blog/secrecy/2007/03/the_wikipedia_factor_in_us_int.html. Retrieved 2007-04-14.
- ↑ Butler, Declan (December 16, 2008). "Publish in Wikipedia or perish". Nature News. doi:10.1038/news.2008.1312.
- ↑ Shaw, Donna (February/March 2008). "Wikipedia in the Newsroom". American Journalism Review. http://www.ajr.org/Article.asp?id=4461. Retrieved 2008-02-11.
- ↑ Shizuoka newspaper plagiarized Wikipedia article, Japan News Review, July 5, 2007
- ↑ "Express-News staffer resigns after plagiarism in column is discovered," San Antonio Express-News, January 9, 2007.
- ↑ "Inquiry prompts reporter's dismissal," Honolulu Star-Bulletin, January 13, 2007.
- ↑ "Radio 4 Documentary". http://www.bbc.co.uk/radio4/factual/pip/efv21/. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- ↑ "Comunicato stampa. On. Franco Grillini. Wikipedia. Interrogazione a Rutelli. Con "diritto di panorama" promuovere arte e architettura contemporanea italiana. Rivedere con urgenza legge copyright". October 12, 2007. http://www.grillini.it/show.php?4885. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- ↑ Jose Antonio Vargas (2007-09-17). "On Wikipedia, Debating 2008 Hopefuls' Every Facet". The Washington Post. http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2007/09/16/AR2007091601699_pf.html. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- ↑ Jennifer Ablan (2007-10-22). "Wikipedia page the latest status symbol". Reuters. http://www.reuters.com/article/domesticNews/idUSN2232893820071022?sp=true. Retrieved 2007-10-24.
- ↑ "Trophy Box," Meta-Wiki (March 28, 2005).
- ↑ "Webby Awards 2004". The International Academy of Digital Arts and Sciences. 2004. http://www.webbyawards.com/webbys/winners-2004.php. Retrieved 2007-06-19.
- ↑ Zumpano, Anthony (2007-01-29). "Similar Search Results: Google Wins". Interbrand. http://www.brandchannel.com/features_effect.asp?pf_id=352. Retrieved 2007-01-28.
- ↑ "Die Quadriga — Award 2008". http://loomarea.com/die_quadriga/e/index.php?title=Award_2008. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- ↑ "Wikipedia Celebrates 750 Years Of American Independence". The Onion. 2006. http://www.theonion.com/content/node/50902. Retrieved October 15, 2006.
- ↑ Bakken, Janae. "My Number One Doctor"; Scrubs; ABC; December 6, 2007
- ↑ "Interview With Nick Doody and Matt Kirshen". British Comedy Guide. http://www.comedy.org.uk/guide/radio/bigipedia/interview/. Retrieved 31 July 2009.
- ↑ Website discussing the emulator of the Domesday Project User Interface for the data from the Community Disc (contributions from the general public); the site is currently out of action following the death of its creator
- ↑ "In Memoriam: September 11, 2001". http://www.sep11memories.org/wiki/In_Memoriam. Retrieved 2007-02-06.
- ↑ First edit to the wiki In Memoriam: September 11 wiki (October 28, 2002),
- ↑ "Announcement of Wiktionary's creation," December 12, 2002. Retrieved on 2007-02-02.
- ↑ "Our projects," Wikimedia Foundation. Retrieved on 2007-01-24
- ↑ "Wikipedia Reference Desk," fetched 17 February 2010
- ↑ Frith, Holden (March 26, 2007,). "Wikipedia founder launches rival online encyclopedia". London: The Times. http://technology.timesonline.co.uk/tol/news/tech_and_web/the_web/article1571519.ece. Retrieved 2007-06-27. "Wikipedia's de facto leader, Jimmy Wales, stood by the site's format. – Holden Frith."
- ↑ Orlowski, Andrew (September 18, 2006). "Wikipedia founder forks Wikipedia, More experts, less fiddling?". The Register. http://www.theregister.co.uk/2006/09/18/sanger_forks_wikipedia/. Retrieved 2007-06-27. "Larry Sanger describes the Citizendium project as a "progressive or gradual fork," with the major difference that experts have the final say over edits." – Andrew Orlowski.
- ↑ Lyman, Jay (September 20, 2006). "Wikipedia Co-Founder Planning New Expert-Authored Site". LinuxInsider. http://www.crmbuyer.com/story/53137.html. Retrieved 2007-06-27.
Further reading
- Academic studies
- Nielsen, Finn (August 2007). "Scientific Citations in Wikipedia". First Monday 12 (8). http://www.firstmonday.org/issues/issue12_8/nielsen/index.html. Retrieved 2008-02-22.
- Pfeil, Ulrike; Panayiotis Zaphiris and Chee Siang Ang (2006). "Cultural Differences in Collaborative Authoring of Wikipedia". Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication 12 (1): 88. doi:10.1111/j.1083-6101.2006.00316.x. http://jcmc.indiana.edu./vol12/issue1/pfeil.html. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- Priedhorsky, Reid, Jilin Chen, Shyong (Tony) K. Lam, Katherine Panciera, Loren Terveen, and John Riedl. "Creating, Destroying, and Restoring Value in Wikipedia". Proc. GROUP 2007, doi: 1316624.131663.
- Reagle, Joseph (2007). "Do as I Do: Authorial Leadership in Wikipedia". WikiSym '07: Proceedings of the 2007 International Symposium on Wikis. Montreal, Canada: ACM. http://reagle.org/joseph/2007/10/Wikipedia-Authorial-Leadership.pdf. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- Wilkinson, Dennis M.; Bernardo A. Huberman (April 2007). "Assessing the Value of Cooperation in Wikipedia". First Monday 12 (4). http://www.firstmonday.org/issues/issue12_4/wilkinson/index.html. Retrieved 2008-02-22.
- Goldman, Eric (2010). "Wikipedia’s Labor Squeeze and its Consequences". Journal of Telecommunications and High Technology Law 8. http://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=1458162##. (a blog post by the autor)
- Books
- Phoebe Ayers, Charles Matthews, and Ben Yates (September 2008). How Wikipedia Works: And How You Can Be a Part of It. San Francisco: No Starch Press. ISBN 978-1-59327-176-3.
- Broughton, John (2008). Wikipedia - The Missing Manual. O'Reilly Media. ISBN 0-596-51516-2. (See book rev. by Baker, as listed below.)
- Broughton, John (2008). Wikipedia Reader's Guide. Sebastopol: Pogue Press. ISBN 059652174X.
- Lih, Andrew (2009). The Wikipedia Revolution. New York: Hyperion. ISBN 1401303714.
- Dalby, Andrew (2009). The World and Wikipedia: How We are Editing Reality. Siduri. ISBN 978-0956205209.
- Book reviews and other articles
- Crovitz, L. Gordon. "Wikipedia's Old-Fashioned Revolution: The online encyclopedia is fast becoming the best." (Originally published in Wall Street Journal online – April 6, 2009, 8:34 A.M. ET)
- Baker, Nicholson. "The Charms of Wikipedia". The New York Review of Books, March 20, 2008. Accessed December 17, 2008. (Book rev. of The Missing Manual, by John Broughton, as listed above.)
- Rosenzweig, Roy. Can History be Open Source? Wikipedia and the Future of the Past. (Originally published in Journal of American History 93.1 (June 2006): 117–46.)
- Learning resources
- Wikiversity list of learning resources. (Includes related courses, Web-based seminars, slides, lecture notes, text books, quizzes, glossaries, etc.)
- Other media coverage
- Dee, Jonathan (2007-07-01). "All the News That's Fit to Print Out". The New York Times Magazine (The New York Times Company). http://www.nytimes.com/2007/07/01/magazine/01WIKIPEDIA-t.html?_r=1&ref=magazine&oref=slogin. Retrieved 2008-02-22.
- "For Music Fans: Wikipedia; MySpace". Houston Chronicle (Blog). March 2008. http://blogs.chron.com/brokenrecord/2008/03/for_music_fans_wikipedia_myspa.html. Retrieved 2008-12-17.
- Freeman, Sarah (2007-08-16). "Can We Really Trust Wikipedia?". Yorkshire Post (yorkshirepost.co.uk). http://www.yorkshirepost.co.uk/highlights?articleid=3115718. Retrieved 2008-09-20.
- Giles, Jim (2007-09-20). "Wikipedia 2.0 – Now with Added Trust". New Scientist. http://www.newscientist.com/article/mg19526226.200. Retrieved 2008-01-14.
- Miliard, Mike (2007-12-02). "Wikipedia Rules". The Phoenix. http://thephoenix.com/Boston/Life/52864-Wikipedia-rules/. Retrieved 2008-02-22.
- Poe, Marshall (September 2006). "The Hive". The Atlantic Monthly. http://www.theatlantic.com/doc/200609/wikipedia. Retrieved 2008-03-22.
- Taylor, Chris (2005-05-29). "It's a Wiki, Wiki World". Time (Time, Inc). http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,1066904-1,00.html. Retrieved 2008-02-22.
- "Technological Quarterly: Brain Scan: The Free-knowledge Fundamentalist". The Economist Web and Print. 2008-06-05. http://www.economist.com/science/tq/displaystory.cfm?story_id=11484062. Retrieved 2008-06-05. "Jimmy Wales changed the world with Wikipedia, the hugely popular online encyclopedia that anyone can edit. What will he do next? [leader]."
- "Hoaxers force Wiki to weigh pre-checks Wikipedia". Metro Boston edition. 2009-01-28. http://www.metrobostonnews.com/us/article/2009/01/28/03/4644-72/index.xml.
- Is Wikipedia Cracking Up?, The Independent, February 3, 2009
- The Wiki-snobs Are Taking Over, The Sunday Times, timesonline.co.uk, February 8, 2009
- Runciman, David (2009-05-28). "Like Boiling a Frog". London Review of Books. http://www.lrb.co.uk/v31/n10/runc01_.html. Retrieved 2009-06-03.
- Rosenwald, Michael S. (2009-10-23). "Gatekeeper of D.C.'s entry: Road to city's Wikipedia page goes through a DuPont Circle bedroom". The Washington Post. http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2009/10/22/AR2009102204715.html?hpid=topnews. Retrieved 2009-10-22.
External links
- Wikipedia – multilingual portal (contains links to all language editions of the project)
- Press coverage of Wikipedia at the English Wikipedia
- Wikipedia on Twitter
- Wikipedia at the Open Directory Project
- Wikipedia topic page at The New York Times
- Video of TED Talk by Jimmy Wales on the birth of Wikipedia
- Audio of interview with Jimmy Wales about Wikipedia in general on the EconTalk podcast
- Wikipedia and why it matters – Larry Sanger's 2002 talk at Stanford University about Wikipedia. video archive and transcript of the talk
- "Intelligence in Wikipedia" Google TechTalk at YouTube, describing an intelligence project utilizing Wikipedia, and how Wikipedia articles could be auto-generated from web content
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||