United States Army
| United States Army | |
|---|---|
 United States Army Seal |
|
| Active | 14 June 1775 – present |
| Country | United States |
| Type | Army |
| Size | 549,015 Active personnel 563,688 Reserve and National Guard personnel |
| Part of | Department of Defense Department of the Army |
| Motto | "This We'll Defend" |
| Engagements | Revolutionary War Indian Wars War of 1812 Mexican-American War Utah War American Civil War Spanish-American War Philippine-American War Banana Wars Boxer Rebellion World War I World War II Korean War Vietnam War Gulf War Somali Civil War Kosovo War War In Afghanistan Iraq War |
| Commanders | |
| Chief of Staff | GEN George W. Casey, Jr. |
| Vice Chief of Staff | GEN Peter W. Chiarelli |
| Sergeant Major | SMA Kenneth O. Preston |
| Insignia | |
| Recruiting Logo "Army Strong" |  |
The United States Army is the branch of the United States armed forces responsible for land-based military operations. It is the largest and oldest established branch of the U.S. military, and is one of seven uniformed services. The modern Army has its roots in the Continental Army which was formed on 14 June 1775,[1] before the establishment of the United States, to meet the demands of the American Revolutionary War. Congress officially created the United States Army on 3 June 1784[2][3] after the end of the war to replace the disbanded Continental Army. The Army considers itself to be descended from the Continental Army and thus dates its inception from the origins of that force.[1]
The primary mission of the Army is to "provide necessary forces and capabilities ... in support of the National Security and Defense Strategies."[4] Control and operation is administered by the Department of the Army, one of the three military departments of the Department of Defense. The civilian head is the Secretary of the Army and the highest ranking military officer in the department is the Chief of Staff, unless the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff or Vice Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff are Army officers. In fiscal year 2009, the Regular Army reported a strength of 549,015 soldiers; the Army National Guard (ARNG) reported 358,391 and the United States Army Reserve (USAR) reported 205,297 putting the combined component strength total at 1,112,703 soldiers.[5]
Contents |
Mission
The United States Army serves as the land-based branch of the U.S. Military. §3062 of Title 10 US Code defines the purpose of the Army as:[6]
- preserving the peace and security, and providing for the defense, of the United States, the Commonwealths and possessions, and any areas occupied by the United States
- supporting the national policies
- implementing the national objectives
- overcoming any nations responsible for aggressive acts that imperil the peace and security of the United States

Values
In the mid to late 1990s, the Army officially adopted what have come to be known as "The 7 Army Core Values." The Army began to teach these values as basic warrior traits. The seven Army Core Values are as follows:
- Loyalty – Bear true faith and allegiance to the U.S. Constitution, the Army, your unit, and fellow Soldiers.
- Duty – Fulfill your obligations.
- Respect – Treat others as they should be treated.
- Selfless Service – Put the welfare of the nation, the Army, and your subordinates before your own.
- Honor – Live the Army Values.
- Integrity – Do what's right, both legally and morally.
- Personal Courage – Face fear, danger, or adversity, both physical and moral.
The values were arranged to form the acronym LDRSHIP (leadership).[7]
History
Origins

The Continental Army was created on 14 June 1775 by the Continental Congress as a unified army for the states to fight Great Britain, with George Washington appointed as its commander.[1] The Army was initially led by men who had served in the British Army or colonial militias and who brought much of British military heritage with them. As the Revolutionary war progressed, French aid, resources, and military thinking influenced the new army, while Prussian assistance and instructors, such as Friedrich Wilhelm von Steuben, had a strong influence.
George Washington used the Fabian strategy and used hit-and-run tactics, hitting where the enemy was weakest, to wear down the British forces and their Hessian mercenary allies. Washington led victories against the British at Trenton and Princeton, and then turned south. With a decisive victory at Yorktown, and the help of the French, the Spanish and the Dutch, the Continental Army prevailed against the British, and with the Treaty of Paris, the independence of the United States was acknowledged.
After the war, though, the Continental Army was quickly disbanded as part of the American distrust of standing armies, and irregular state militias became the new nation's sole ground army, with the exception of a regiment to guard the Western Frontier and one battery of artillery guarding West Point's arsenal. However, because of continuing conflict with Native Americans, it was soon realized that it was necessary to field a trained standing army. The first of these, the Legion of the United States, was established in 1791.
19th century
The War of 1812, the second and last American war against the British, was less successful than the Revolution had been. An invasion of Canada failed, and U.S. troops were unable to stop the British from burning the new capital of Washington, D.C.. However, the Regular Army, under Generals Winfield Scott and Jacob Brown, proved they were professional and capable of defeating a British army in the Niagara campaign of 1814. Two weeks after a treaty was signed, though, Andrew Jackson defeated the British invasion of New Orleans. However this had little effect; as per the treaty both sides returned to the status quo.
Between 1815 and 1860, a spirit of Manifest Destiny was common in the U.S., and as settlers moved west the U.S. Army engaged in a long series of skirmishes and battles with Native Americans that the settlers uprooted. The U.S. Army also fought and won the Mexican–American War (1846–1848), which was a defining event for both countries.[8] The U.S. victory resulted in acquisition of territory that eventually became all or parts of the states of California, Nevada, Utah, Colorado, Arizona, Wyoming and New Mexico.

The Civil War was the most costly war for the U.S. in terms of casualties. After most states in the South seceded to form the Confederate States of America, CSA troops opened fire on the Union-held Fort Sumter in Charleston, South Carolina, starting the war. For the first two years Confederate forces solidly defeated the U.S. Army, but after the decisive battles of Gettysburg in the east and Vicksburg in the west, combined with superior industrial might and numbers, Union troops fought a brutal campaign through Confederate territory and the war ended with a Confederate surrender at Appomatox Courthouse in April 1865. Based on 1860 census figures, 8% of all white males aged 13 to 43 died in the war, including 6% in the North and 18% in the South.[9]
Following the Civil War, the U.S. Army fought a long battle with Native Americans, who resisted U.S. expansion into the center of the continent. By the 1890s the U.S. saw itself as a potential international player. U.S. victories in the Spanish-American War and the controversial and less well known Philippine-American War, as well as U.S. intervention in Latin America and the Boxer Rebellion, gained America more land.
20th century

Starting in 1910, the Army began acquiring Fixed-wing aircraft.[10] The United States joined World War I in 1917 on the side of Britain, France, Russia, and other allies. U.S. troops were sent to the front and were involved in the push that finally broke through the German lines. With the armistice in November 1918, the Army once again decreased its forces.
The U.S. joined World War II after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor. On the European front, U.S. Army troops formed a significant portion of the forces that captured North Africa and Sicily. On D-Day and in the subsequent liberation of Europe and defeat of Nazi Germany, millions of U.S. Army troops played a central role. In the Pacific, Army soldiers participated alongside U.S. Marines in capturing the Pacific Islands from Japanese control. Following the Axis surrenders in May (Germany) and August (Japan) of 1945, Army troops were deployed to Japan and Germany to occupy the two defeated nations. Two years after World War II, the Army Air Forces separated from the Army to become the United States Air Force in September 1947 after decades of attempting to separate. Also, in 1948 the Army was desegregated.
However, the end of World War II set the stage for the East-West confrontation known as the Cold War. With the outbreak of the Korean War, concerns over the defense of Western Europe rose. Two corps, V and VII, were reactivated under Seventh United States Army in 1950 and American strength in Europe rose from one division to four. Hundreds of thousands of U.S. troops remained stationed in West Germany, with others in Belgium, the Netherlands and the United Kingdom, until the 1990s in anticipation of a possible Soviet attack.

During the Cold War, American troops and their allies fought Communist forces in Korea and Vietnam. The Korean War began in 1950, when the Soviets walked out of a U.N. Security meeting, removing their possible veto. Under a United Nations umbrella, hundreds of thousands of U.S. troops fought to prevent the takeover of South Korea by North Korea, and later, to invade the northern nation. After repeated advances and retreats by both sides, and the Peoples' Republic of China 's entry into the war, a cease-fire returned the peninsula to the status quo in 1953.
The Vietnam War is often regarded as a low point in the Army's record due to the use of drafted personnel, the unpopularity of the war with the American public, and frustrating restrictions placed on the Army by US political leaders. While American forces had been stationed in the Republic of Vietnam since 1959, in intelligence & advising/training roles, they did not deploy in large numbers until 1965, after the Gulf of Tonkin Incident. American forces effectively established and maintained control of the "traditional" battlefield, however they struggled to counter the guerrilla hit and run tactics of the communist Viet Cong and the North Vietnamese Army. On a tactical level, American soldiers (and the US military as a whole) did not lose a sizable battle.[11]
The Total Force Policy was adopted by Chief of Staff of the Army General Creighton Abrams in the aftermath of the Vietnam War and involves treating the three components of the Army – the Regular Army, the Army National Guard and the Army Reserve as a single force.[12] Believing that no U.S. president should be able to take the United States (and more specifically the US Army) to war without the support of the American people, General Abrams intertwined the structure of the three components of the Army in such a way as to make extended operations impossible, without the involvement of both the Army National Guard and the Army Reserve.[13]
The 1980s was mostly a decade of reorganization. The Army converted to an all-volunteer force with greater emphasis on training and technology. The Goldwater-Nichols Act of 1986 created Unified Combatant Commands bringing the Army together with the other four military under unified, geographically organized command structures. The Army also played a role in the invasions of Grenada in 1983 (Operation Urgent Fury) and Panama in 1989 (Operation Just Cause).
By 1989 Germany was nearing reunification and the Cold War was coming to a close. The Army leadership reacted by starting to plan for a reduction in strength. By November 1989 Pentagon briefers were laying out plans to reduce Army endstrength by 23%, from 750,000 to 580,000.[14] A number of incentives such as early retirement were used. In 1990 Iraq invaded its smaller neighbor, Kuwait, and U.S. land forces, led by an Airborne Division, quickly deployed to assure the protection of Saudi Arabia. In January 1991 Operation Desert Storm commenced, a U.S.-led coalition which deployed over 500,000 troops, the bulk of them from U.S. Army formations, to drive out Iraqi forces. The campaign ended in total victory for the Army, as Western coalition forces routed the Iraqi Army, organized along Soviet lines, in just one hundred hours.
After Desert Storm, the Army did not see major combat operations for the remainder of the 1990s but did participate in a number of peacekeeping activities. In 1990 the Department of Defense issued guidance for "rebalancing" after a review of the Total Force Policy,[15] but in 2004, Air War College scholars concluded the guidance would reverse the Total Force Policy which is an "essential ingredient to the successful application of military force."[16]
21st century

After the September 11 attacks, and as part of the Global War on Terror, U.S. and NATO combined arms (i.e. Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine, Special Operations) forces invaded Afghanistan in 2001, displacing the Taliban government.
The Army led the combined U.S. and allied Invasion of Afghanistan in 2001, and Iraq in 2003. In the following years the mission changed from conflict between regular militaries to counterinsurgency, with large numbers of suicide attacks resulting in the deaths of more than 4,000 U.S. service members (as of March 2008) and injuries to thousands more.[17] The lack of stability in the theater of operations has led to longer deployments for Regular Army as well as Reserve and Guard troops.
The Army's chief modernization plan was the FCS program. Many systems were canceled and the remaining were swept into the BCT modernization program.
Organization
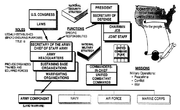
Army components
back row (left to right): Stearley, Vandenberg, Smith, Weyland, Nugent;
front row: Simpson, Patton, Spaatz, Eisenhower, Bradley, Hodges, Gerow.
The task of organizing the U.S. Army commenced in 1775.[19] During World War I, the "National Army" was organized to fight the conflict.[20] It was demobilized at the end of World War I, and was replaced by the Regular Army, the Organized Reserve Corps, and the State Militias. In the 1920s and 1930s, the "career" soldiers were known as the "Regular Army" with the "Enlisted Reserve Corps" and "Officer Reserve Corps" augmented to fill vacancies when needed.[21]
In 1941, the "Army of the United States" was founded to fight World War II. The Regular Army, Army of the United States, the National Guard, and Officer/Enlisted Reserve Corps (ORC and ERC) existed simultaneously. After World War II, the ORC and ERC were combined into the United States Army Reserve. The Army of the United States was re-established for the Korean War and Vietnam War and was demobilized upon the suspension of the Draft.[21]
Currently, the Army is divided into the Regular Army, the Army Reserve, and the Army National Guard.[20] The Army is also divided into major branches such as Air Defense Artillery, Infantry, Aviation, Signal Corps, Corps of Engineers, and Armor. Prior to 1903 members of the National Guard were considered state soldiers unless federalized by the President. Since the Militia Act of 1903 all National Guard soldiers have held dual status: as National Guardsmen under the authority of the governor of their state and as a reserve of the U.S. Army under the authority of the President.
Since the adoption of the total force policy, in the aftermath of the Vietnam War, reserve component soldiers have taken a more active role in U.S. military operations. Reserve and Guard units took part in the Gulf War, peacekeeping in Kosovo, and the 2003 invasion of Iraq.
Various State Defense Forces also exist, sometimes known as State Militias, which are sponsored by individual state governments and serve as an auxiliary to the National Guard. Except in times of extreme national emergency, such as a mainland invasion of the United States, State Militias are operated independently from the U.S. Army and are seen as state government agencies rather than a component of the military.
Although the present-day Army exists as an all volunteer force, augmented by Reserve and National Guard forces, measures exist for emergency expansion in the event of a catastrophic occurrence, such as a large scale attack against the U.S. or the outbreak of a major global war.
The final stage of Army mobilization, known as "activation of the unorganized militia" would effectively place all able bodied males in the service of the U.S. Army. The last time an approximation of this occurred was during the American Civil War when the Confederate States of America activated the "Home Guard" in 1865, drafting all males, regardless of age or health, into the Confederate Army.
Army commands and army service component commands
| Army commands | Current commander | Location of headquarters |
|---|---|---|
| United States Army Forces Command (FORSCOM) | GEN James D. Thurman | Fort Bragg, North Carolina |
| United States Army Training and Doctrine Command (TRADOC) | GEN Martin Dempsey | Fort Monroe, Virginia |
| United States Army Materiel Command (AMC) | GEN Ann E. Dunwoody | Fort Belvoir, Virginia |
| Army service component commands | Current commander | Location of headquarters |
| United States Army Africa (USARAF) | MG William B. Garrett III | Vicenza, Italy |
| United States Army Central (USARCENT) | LTG William G. Webster[22] | Fort McPherson, Georgia |
| United States Army North (USANORTH) | LTG Thomas R. Turner II | Fort Sam Houston, Texas |
| United States Army South (USARSO) | MG Keith M. Huber | Fort Sam Houston, Texas |
| United States Army Europe (USAREUR) | GEN Carter F. Ham[23] | Campbell Barracks, Heidelberg, Germany |
| United States Army Pacific (USARPAC) | LTG Benjamin R. Mixon[24] | Fort Shafter, Hawaii |
| United States Army Special Operations Command (USASOC) | LTG John F. Mulholland Jr | Fort Bragg. North Carolina |
| Surface Deployment and Distribution Command (SDDC) | BG James L. Hodge[25] | Scott AFB, Illinois |
| United States Army Space and Missile Defense Command/United States Army Strategic (USASMDC/ARSTRAT) | LTG Kevin T. Campbell | Redstone Arsenal, Alabama |
| Field army headquarters | Current commander | Location of headquarters |
| Eighth United States Army (EUSA) | LTG Joseph F. Fil, Jr. | Yongsan Garrison, Seoul |
| Direct reporting units | Current commander | Location of headquarters |
| Network Enterprise Technology Command/9th Signal Command (Army) (NETCOM/9thSC(A)) | MG Susan Lawrence | Fort Huachuca, Arizona |
| United States Army Medical Command (MEDCOM) | LTG Eric Schoomaker | Fort Sam Houston, Texas |
| United States Army Intelligence and Security Command (INSCOM) | MG David B. Lacquement | Fort Belvoir, Virginia |
| United States Army Criminal Investigation Command (USACIDC) | BG Colleen L. McGuire | Fort Belvoir, Virginia |
| United States Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) | LTG Robert Van Antwerp Jr. | Washington, D.C. |
| United States Army Military District of Washington (MDW) | MG Karl Horst | Fort McNair, Washington, D.C. |
| U.S. Army Test & Evaluation Command (ATEC) | MG Roger A. Nadeau | Alexandria, Virginia |
| United States Military Academy (USMA) | LTG David H. Huntoon | West Point, New York |
| United States Army Reserve Command (USARC) | LTG Jack C. Stultz | Fort McPherson, Georgia |
| United States Army Installation Management Command (IMCOM) | LTG Rick Lynch | Arlington, Virginia |
| IMCOM Subordinate: United States Army Family and Morale, Welfare and Recreation Command (FMWRC)[26] | MG Reuben D. Jones | Alexandria, Virginia |
Source: U.S. Army organization[27]
Structure
The United States Army is made up of three components: the active component, the Regular Army; and two reserve components, the Army National Guard and the Army Reserve. Both reserve components are primarily composed of part-time soldiers who train once a month, known as Battle Assembly or Unit Training Assemblies (UTAs), and conduct two to three weeks of annual training each year. Both the Regular Army and the Army Reserve are organized under Title 10 of the United States Code, while the National Guard is organized under Title 32. While the Army National Guard is organized, trained and equipped as a component of the U.S. Army, when it is not in federal service it is under the command of individual state and territorial governors, and the Mayor of the District of Columbia. However the National Guard can be federalized by presidential order and against the governor's wishes.[28]

The Army is led by a civilian Secretary of the Army, who has the statutory authority to conduct all the affairs of the Army; under the authority, direction and control of the Secretary of Defense.[29] The Chief of Staff of the Army who is the highest ranked military officer in the Army has dual roles; one as the principal military adviser and executive agent for the Secretary of the Army, i.e. its service chief; and secondly as a member of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, a body composed of the service chiefs from each of the four military services belonging to the Department of Defense who advise the President of the United States, the Secretary of Defense, and the National Security Council on operational military matters, under the guidance of the Chairman and Vice Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff.[30][31] In 1986, the Goldwater-Nichols Act mandated that operational control of the services follows a chain of command from the President to the Secretary of Defense directly to the Unified Combatant Commanders, who have control of all armed forces units in their geographic or function area of responsibility. Thus, the Secretaries of the military departments (and their respective service chiefs underneath them) only have the responsibility to organize, train and equip their service components. The Army provides trained forces to the Combatant Commanders for use as directed by the Secretary of Defense.[32]
Through 2013, the Army is shifting to six geographical commands that will line up with the six geographical Unified Combatant Commands (COCOM):
- United States Army Central headquartered at Fort McPherson, Georgia
- United States Army North headquartered at Fort Sam Houston, Texas
- United States Army South headquartered at Fort Sam Houston, Texas
- United States Army Europe headquartered at Heidelberg, Germany
- United States Army Pacific headquartered at Fort Shafter, Hawaii (eventually to be merged with the Eighth Army).
- United States Army Africa headquartered at Vicenza, Italy
Each command will receive a numbered army as operational command, except U.S. Army Pacific, which will have a numbered army for U.S. Army forces in the Republic of Korea.
The Army is also changing its base unit from divisions to brigades. When finished, the active army will have increased its combat brigades from 33 to 48, with similar increases in the National Guard and Reserve forces. Division lineage will be retained, but the divisional HQs will be able to command any brigades, not just brigades that carry their divisional lineage. The central part of this plan is that each brigade will be modular, i.e. all brigades of the same type will be exactly the same, and thus any brigade can be commanded by any division. There will be three major types of ground combat brigades:
- Heavy brigades will have around 3,700 troops and be equivalent to a mechanized infantry or tank brigade.
- Stryker brigades will have around 3,900 troops and be based on the Stryker family of vehicles.
- Infantry brigades will have around 3,300 troops and be equivalent to a light infantry or airborne brigade.
In addition, there will be combat support and service support modular brigades. Combat support brigades include Aviation brigades, which will come in heavy and light varieties, Fires (artillery) brigades, and Battlefield Surveillance Brigades. Combat service support brigades include Sustainment brigades and come in several varieties and serve the standard support role in an army.
Regular combat maneuver organizations

.jpg)
The U.S. Army currently consists of 10 active divisions as well as several independent units. The force is in the process of growth, with four additional brigades scheduled to activate by 2013, with a total increase of 74,200 soldiers from January 2007. Each division will have four ground maneuver brigades, and will also include at least one aviation brigade as well as a fires brigade and a service support brigade. Additional brigades can be assigned or attached to a division headquarters based on its mission.
Within the Army National Guard and the Army Reserve there are a further eight divisions, over fifteen maneuver brigades, additional combat support and combat service support brigades, and independent cavalry, infantry, artillery, aviation, engineer, and support battalions. The Army Reserve in particular provide virtually all psychological operations and civil affairs units.
| Name | Headquarters | Subunits |
|---|---|---|
| Wiesbaden Army Airfield, Germany | 2nd, 4th Heavy Brigade Combat Teams, 1st Stryker Brigade Combat Team and 3rd Infantry Brigade Combat Team at Fort Bliss.The 1st Armored Division Combat Aviation Brigade will arrive at Biggs Army Airfield on Fort Bliss sometime in 2011. The Division HQ will finish moving to Fort Bliss sometime in 2011. | |
| Fort Hood, Texas | 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th Heavy Brigade Combat Teams and Combat Aviation Brigade at Fort Hood. | |
| Fort Riley, Kansas | 1st, 2nd Heavy Brigade Combat Teams, 4th Infantry Brigade Combat Team and Combat Aviation Brigade at Fort Riley, 3rd Infantry Brigade Combat Team at Fort Knox, Kentucky. | |
| Camp Red Cloud, South Korea | 1st Heavy Brigade Combat Team and Combat Aviation Brigade at Camp Humphreys and Camp Casey, South Korea, and 2nd 3rd and 4th and Stryker Brigade Combat Teams (SBCTs) at Fort Lewis, Washington. | |
| Fort Stewart, Georgia | 1st, 2nd Heavy Brigade Combat Teams and 4th Infantry Brigade Combat Team at Fort Stewart, Georgia, 3rd Heavy Brigade Combat Team at Fort Benning, Georgia, and Combat Aviation Brigade at Hunter Army Airfield, Georgia. | |
| Fort Carson, Colorado | 1st, 2nd, 3rd Heavy brigade combat teams and 4th Infantry Brigade Combat Team at Fort Carson, Colorado. Combat Aviation Brigade at Fort Hood, Texas until 2011. | |
| Fort Drum, New York | 1st, 2nd, 3rd Infantry Brigade Combat Teams and Combat Aviation Brigade at Fort Drum and 4th Infantry Brigade Combat Team at Fort Polk, Louisiana. | |
| Schofield Barracks, Hawaii | 3rd Infantry Brigade Combat Team and 2nd Stryker Brigade Combat Team at Schofield Barracks, Combat Aviation Brigade at Wheeler Army Airfield, 1st Stryker Brigade Combat Team at Fort Wainwright, Alaska, and 4th Airborne Infantry Brigade Combat Team at Fort Richardson, Alaska. | |
| Fort Bragg, North Carolina | 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th Airborne Infantry Brigade Combat Teams and Combat Aviation Brigade at Fort Bragg. | |
| Fort Campbell, Kentucky | 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th Infantry Brigade Combat Teams (air assault), 101st and 159th Combat Aviation Brigades at Fort Campbell. | |
| Baumholder, Germany | Two mechanized infantry battalions, one M1A1 Abrams battalion, one self-propelled 155mm field artillery battalion, one combat engineer battalion. | |
| Grafenwöhr, Germany | Two mechanized infantry battalions, one M1A1 Abrams battalion, one self-propelled 155mm field artillery battalion, one combat engineer battalion. | |
| Vicenza, Italy | Two airborne infantry battalions, one cavalry squadron, one airborne field artillery battalion, one special troops battalion, and one support battalion. | |
| Vilseck, Germany | 6 subordinate Squadrons: 1st (Stryker Infantry), 2nd (Stryker Infantry), 3rd (Stryker Infantry), 4th (Recon, Surveillance, Target Acquisition), Fires (6x3 155mm Towed Arty), & RSS (Logistical Support); 5 Separate Troops/Companies: Regimental Headquarters Troop, Military Intelligence Troop, Signal Troop, 84th Engineer Company, and Anti-Tank Troop. | |
| Fort Hood, Texas | Three armored cavalry squadrons, one aviation squadron, and one support squadron. Converting to a Stryker Brigade Combat Team. | |
| Fort Irwin, California | Serves as the Opposing Force (OPFOR) at the National Training Center (NTC). Multi-compo Generating Force HBCT. |
Special Operations Forces
![]() US Army Special Operations Command (Airborne):
US Army Special Operations Command (Airborne):
| Name | Headquarters | Structure and purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Fort Bragg, North Carolina | Seven groups capable of unconventional warfare, foreign internal defense, special reconnaissance, direct action, and counter-terrorism. | |
| Fort Benning, Georgia | Three battalions of elite airborne infantry. | |
| Fort Campbell, Kentucky | Four battalions, providing helicopter aviation support for general purpose forces and Special Operations Forces. | |
| Fort Bragg, North Carolina | Psychological operations unit, six battalions. | |
| Fort Bragg, North Carolina | Civil affairs brigade. | |
| Fort Bragg, North Carolina | ||
| Fort Bragg, North Carolina | Elite special operations and counter-terrorism unit. Its operators are chosen primarily from the Special Forces Groups and the Ranger Regiment, however some come from non-USASOC units. |
Personnel
These are the U.S. Army ranks in use today and their equivalent NATO designations.
| “ | There are several paths to becoming a commissioned officer including Army ROTC, the United States Military Academy at West Point or the United States Merchant Marine Academy at Kings Point, and Officer Candidate School. Certain professionals, physicians, nurses, lawyers, and chaplains are commissioned directly into the Army. But no matter what road an officer takes, the insignia are the same.
Address all personnel with the rank of general as "General (last name)" regardless of the number of stars. Likewise, address both colonels and lieutenant colonels as "Colonel (last name)" and first and second lieutenants as "Lieutenant (last name)." |
” |
| US DoD Pay Grade | O-1 | O-2 | O-3 | O-4 | O-5 | O-6 | O-7 | O-8 | O-9 | O-10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insignia | 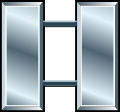 |
 |
 |
||||||||
| Title | Second Lieutenant | First Lieutenant | Captain | Major | Lieutenant Colonel | Colonel | Brigadier General | Major General | Lieutenant General | General | |
| Abbreviation | 2LT | 1LT | CPT | MAJ | LTC | COL | BG | MG | LTG | GEN | |
| NATO Code | OF-1 | OF-2 | OF-3 | OF-4 | OF-5 | OF-6 | OF-7 | OF-8 | OF-9 | ||
Warrant Officers:[33]
| “ | Warrant Officers are single track, specialty officers with subject matter expertise in a particular area. They are initially appointed as warrant officers (in the rank of WO1) by the Secretary of the Army, but receive their commission upon promotion to Chief Warrant Officer Two (CW2).
Technically, warrant officers are to be addressed as "Mr. (last name)" or "Ms. (last name)." However, many personnel do not use those terms, but instead say "Sir", "Ma'am", or most commonly, "Chief". |
” |
| US DoD pay grade | W-1 | W-2 | W-3 | W-4 | W-5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insignia | |||||
| Title | Warrant Officer 1 | Chief Warrant Officer 2 | Chief Warrant Officer 3 | Chief Warrant Officer 4 | Chief Warrant Officer 5 |
| Abbreviation | WO1 | CW2 | CW3 | CW4 | CW5 |
| NATO Code | WO-1 | WO-2 | WO-3 | WO-4 | WO-5 |
| “ | Sergeants are referred to as NCOs, short for non-commissioned officers. Corporals are also non-commisioned officers, and serve as the base of the non-commissioned Officer (NCO) ranks. Corporals are also called "hard stripes", in recognition of their leadership position. This distinguishes them from specialists who might have the same pay grade, but not the leadership responsibilities.
Address privates (E1 and E2) and privates first class (E3) as "Private (last name)." Address specialists as "Specialist (last name)." Address sergeants, staff sergeants, and sergeants first class as "Sergeant (last name)." Address higher ranking sergeants by their full ranks in conjunction with their names. |
” |
| US DoD Pay grade | E-1 | E-2 | E-3 | E-4 | E-5 | E-6 | E-7 | E-8 | E-9 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insignia | No Insignia |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
| Title | Private | Private | Private First Class |
Specialist | Corporal | Sergeant | Staff Sergeant |
Sergeant First Class |
Master Sergeant |
First Sergeant |
Sergeant Major |
Command Sergeant Major |
Sergeant Major of the Army |
| Abbreviation | PVT ¹ | PV2 ¹ | PFC | SPC ² | CPL | SGT | SSG | SFC | MSG | 1SG | SGM | CSM | SMA |
| NATO Code | OR-1 | OR-2 | OR-3 | OR-4 | OR-4 | OR-5 | OR-6 | OR-7 | OR-8 | OR-8 | OR-9 | OR-9 | OR-9 |
| ¹ PVT is also used as an abbreviation for both Private ranks when pay grade need not be distinguished ² SP4 is sometimes encountered in lieu of SPC for Specialist. This is a holdover from when there were additional specialist ranks at higher pay grades. |
|||||||||||||
Training
Training in the United States Army is generally divided into two categories – individual and collective.
Basic training consists of 10 weeks for most recruits followed by AIT (Advanced Individualized Training) where they receive training for their MOS (military occupational specialties) with the length of AIT school varying by the MOS, some individuals MOS's range anywhere from 14–20 weeks of One Station Unit Training,(OSUT) which counts as basic and AIT. Support and other MOS hopefuls attend nine to eleven weeks of Basic Combat Training followed by Advanced Individual Training in their primary (MOS) at any of the numerous MOS training facilities around the country. The length of time spent in AIT depends on the MOS of the soldier. (ex. 25B- IT Specialist MOS is 24 Weeks, 11B- Infantry 15–17 weeks) Depending on the needs of the Army BCT is conducted at a number of locations, but two of the longest running are the Armor School at Fort Knox, Kentucky and the Infantry School at Fort Benning, Georgia. For officers this training includes pre-commissioning training either at USMA, ROTC, or OCS. After commissioning, officers undergo branch specific training at the Basic Officer Leaders Course, (formerly called Officer Basic Course) which varies in time and location based on their future jobs.
Collective training takes place both at the unit's assigned station, but the most intensive collective training takes place at the three Combat Training Centers (CTC); the National Training Center (NTC) at Fort Irwin, California, the Joint Readiness Training Center (JRTC) at Fort Polk, Louisiana, and the Joint Multinational Training Center (JMRC) at the Hohenfels Training Area in Hohenfels, Germany.
Six Sigma Training
The largest business transformation attempted to date was by the United States Army and its 1.3 million employees. Six Sigma first found its way into the Army in 2002 in the Army Material Command division, which is responsible for purchasing virtually everything in the army, from cornmeal to aircraft. Efficiencies from Six Sigma achieved in this department, a few others, as well as an increasingly disproportional amount of demands compared to funds post 9/11, led to an army wide implementation of the program in late 2005.[35]
After careful consideration, the army decided to implement the program the way the army does everything: centrally plan and de-centrally execute. Army generals and members of the government went behind closed doors for two days, learning their responsibilities of the implementation and the benefits they will achieve. Army employees with leadership roles were asked to define areas their departments were experiencing problems in as well as identify key personnel they felt were capable of learning Six Sigma. Eventually, the lowest ranking employees were asked to define the largest problems they faced on a day to day basis, and the answers were sent to the Army generals who, with the help of Six Sigma, strategically developed and proposed proper solutions.[35]
Army employees were trained in Six Sigma through the use of experts. Since training began in June 2006, they have trained 1,240 Green Belts, 446 Black Belts, and 15 Master Black Belts; completed 1,069 projects; and managed to save nearly two billion dollars to date. The army realized such huge savings by implementing new, more efficient methods, eliminating waste as well as the elimination of non-value adding activities.[35]
Improvements in the Army’s business processes should be credited to the vast improvements in efficiency. In particular, the dramatic effect Six Sigma has had on eliminating redundancies in efforts and resources has resulted in savings nearly a quarter of their cost. Productivity has increased and costs have decreased because of such eliminations, resulting in a more financially secure Army. New software uncovered that the Army was paying to provide foreign language instruction to a substantial number of non army personnel; this discovery, followed by the restructuring of the program, saved the Army $400 million the following year. Other Six Sigma improvements, saving the Army millions, include streamlining the recruiting process, preventing food waste at West Point, and improving foreign military sales. Such successes enjoyed by the Army have recently lead to the full implementation of Six Sigma by both the Air Force and Navy, as well as initiating talks with the Secretary of Defense to incorporate lean Six Sigma throughout the entire department.[35]
Equipment
Weapons

The Army employs various individual weapons to provide light firepower at short ranges. The most common weapons used by the army are the M16 series assault rifle[36] and its compact variant, the M4 carbine,[37] which is slowly replacing selected M16 series rifles in some units and is primarily used by infantry, Ranger, and Special Operations forces.[38] Soldiers whose duties require a more compact weapon, such as combat vehicle crew members, staff officers, and military police, are also issued the M4. The most common sidearm in the U.S. Army is the 9 mm M9 pistol[39] which is issued to the majority of combat and support units.
Many combat units' arsenals are supplemented with a variety of specialized weapons, including the M249 SAW (squad automatic weapon), to provide suppressive fire at the fire-team level,[40] the M1014 Joint Service Combat Shotgun or the Mossberg 590 Shotgun for door breaching and close-quarters combat, the M14EBR for long-range marksmen, and the M107 Long Range Sniper Rifle, the M24 Sniper Weapon System, or the M110 Semi-Automatic Sniper Rifle for snipers. Hand grenades, such as the M67 fragmentation grenade and M18 smoke grenade, are also used by combat troops.
The Army employs various crew-served weapons to provide heavy firepower at ranges exceeding that of individual weapons.
The M249 is the Army's standard light machine gun. The M240 is the Army's standard medium machine gun.[41] The .50 Cal. BMG. M2 heavy machine gun is used as an anti-materiel and anti-personnel machine gun. The M2 is also the primary weapon on most Stryker variants and the secondary weapon system on the M1 Abrams. The 40 mm MK 19 grenade machine gun is mainly used by motorized units.[42] It is commonly employed in a complementary role to the M2.
The Army uses three types of mortar for indirect fire support when heavier artillery may not be appropriate or available. The smallest of these is the 60 mm M224, normally assigned at the infantry company level.[43] At the next higher echelon, infantry battalions are typically supported by a section of 81 mm M252 mortars.[44] The largest mortar in the Army's inventory is the 120 mm M120/M121, usually employed by mechanized battalions, Stryker units, and cavalry troops because its size and weight require it to be transported in a tracked carrier or towed behind a truck.[45]
Fire support for light infantry units is provided by towed howitzers, including the 105 mm M119A1[46] and the 155 mm M777 (which will replace the M198).[47]
The Army utilizes a variety of direct-fire rockets and missiles to provide infantry with an offensive and defensive anti-armor capability. The SMAW and AT4 are unguided rockets that can destroy armor and fixed defenses (e.g., bunkers) at ranges up to 500 meters. The FGM-148 Javelin and BGM-71 TOW are anti-tank guided missiles. The Javelin can utilize top-attack profiles to avoid heavy frontal armor. The Javelin and TOW are heavier missiles effective past 2,000 meters that give infantry an offensive capability against armor.
Vehicles
The U.S. Army spends a sizable portion of its military budget to maintain a diverse inventory of vehicles.
The Army's most common vehicle is the High Mobility Multipurpose Wheeled Vehicle (HMMWV), which is capable of serving as a cargo/troop carrier, weapons platform, and ambulance, among many other roles.[48] While they operate a wide variety of combat support vehicles, one of the most common types centers on the family of HEMTT vehicles. The M1A2 Abrams is the Army's primary main battle tank,[49] while the M2A3 Bradley is the standard infantry fighting vehicle.[50] Other vehicles include the M3A3 cavalry fighting vehicle, the Stryker,[51] and the M113 armored personnel carrier,[52] and multiple types of Mine Resistant Ambush Protected (MRAP) vehicles.
The U.S. Army's principal artillery weapons are the M109A6 Paladin self-propelled howitzer[53] and the M270 Multiple Launch Rocket System (MLRS),[54] both mounted on tracked platforms and assigned to heavy mechanized units.
While the U.S. Army operates a few fixed-wing aircraft, it mainly operates several types of rotary-wing aircraft. These include the AH-64 Apache attack helicopter,[55] the OH-58D Kiowa Warrior armed reconnaissance/light attack helicopter,[56] the UH-60 Black Hawk utility tactical transport helicopter,[57] and the CH-47 Chinook heavy-lift transport helicopter.[58]
Uniforms

The Army Combat Uniform (ACU) features a digital camouflage pattern and is designed for use in woodland, desert, and urban environments. Soldiers operating in Afghanistan will soon be issued an fire-resistant ACU with the more appropriate "MultiCam" pattern.[59]
The standard garrison service uniform is known as Army Greens or Class-As and has been worn by all officers and enlisted personnel since its introduction in 1956 when it replaced earlier olive drab (OD) and khaki (and tan worsted or TW) uniforms worn between the 1950s and 1985. The Army Blue uniform, dating back to the mid-19th century, is currently the Army's formal dress uniform, but in 2014, it will replace the Army Green and the Army White uniforms (a uniform similar to the Army Green uniform, but worn in tropical postings) and will become the new Army Service Uniform, which will function as both a garrison uniform (when worn with a white shirt and necktie) and a dress uniform (when worn with a white shirt and either a necktie for parades or a bow tie for after six or black tie events). The beret will continue to be worn with the new ACU for garrison duty and with the Army Service Uniform for non-ceremonial functions. The Army Blue Service Cap, formerly allowed for wear by all enlisted personnel, are now only allowed for wear by any soldier ranked CPL or above at the discretion of the commander.
Personal armor in most units is the Improved Outer Tactical Vest and the MICH TC-2000 Combat Helmet.
Tents

The Army has relied heavily on tents to provide the various facilities they need while on deployment. The US Department of Defense has strict rules on tent quality and tent specifications. The most common tent uses for the military are temporary barracks (sleeping quarters), DFAC buildings (dining facilities), Forward Operating Bases (FOBs), After Action Review (AAR), Tactical Operations Center (TOC), Morale, Welfare, and Recreation (MWR) facilities, and security checkpoints. Furthermore, most of these tents are set up and operated through the support of Natick Soldier Systems Center. One of the most popular military designs currently fielded by the US DoD is the TEMPER Tent. TEMPER is an acronym for Tent Expandable Modular PERsonnel.
The U.S. military is beginning to use a more modern tent called the deployable rapid assembly shelter or DRASH. In 2008, DRASH became part of the Army's Standard Integrated Command Post System.[60]
Branch Establishment
The U.S. Army was officially founded on 14 June 1775, when the Continental Congress authorized enlistment of riflemen to serve the United Colonies for one year.
Basic branches
- Infantry, 14 June 1775
Ten companies of riflemen were authorized by a resolution of the Continental Congress on 14 June 1775. However, the oldest Regular Army infantry regiment, the 3rd Infantry Regiment, was constituted on 3 June 1784, as the First American Regiment.
- Adjutant General's Corps, 16 June 1775
The post of Adjutant General was established 16 June 1775, and has been continuously in operation since that time. The Adjutant General's Department, by that name, was established by the act of 3 March 1812, and was redesignated the Adjutant General's Corps in 1950.
- Corps of Engineers, 16 June 1775
Continental Congress authority for a "Chief Engineer for the Army" dates from 16 June 1775. A corps of Engineers for the United States was authorized by the Congress on 11 March 1789. The Corps of Engineers as it is known today came into being on 16 March 1802, when the President was authorized to "organize and establish a Corps of Engineers … that the said Corps … shall be stationed at West Point in the State of New York and shall constitute a Military Academy." A Corps of Topographical Engineers, authorized on 4 July 1838, was merged with the Corps of Engineers on March 1863.
- Finance Corps, 16 June 1775.
The Finance Corps is the successor to the old Pay Department, which was created in June 1775. The Finance Department was created by law on 1 July 1920. It became the Finance Corps in 1950.
- Quartermaster Corps, 16 June 1775
The Quartermaster Corps, originally designated the Quartermaster Department, was established on 16 June 1775. While numerous additions, deletions, and changes of function have occurred, its basic supply and service support functions have continued in existence.
- Field Artillery, 17 November 1775
The Continental Congress unanimously elected Henry Knox "Colonel of the Regiment of Artillery" on 17 November 1775. The regiment formally entered service on 1 January 1776.
- Armor, 12 June 1776
The Armor branch traces its origin to the Cavalry. A regiment of cavalry was authorized to be raised by the Continental Congress Resolve of 12 December 1776. Although mounted units were raised at various times after the Revolution, the first in continuous service was the United States Regiment of Dragoons, organized in 1833. The Tank Service was formed on 5 March 1918. The Armored Force was formed on 10 July 1940. Armor became a permanent branch of the Army in 1950.
- Ordnance Corps, 14 May 1812
The Ordnance Department was established by act of Congress on 14 May 1812. During the Revolutionary War, ordnance material was under supervision of the Board of War and Ordnance. Numerous shifts in duties and responsibilities have occurred in the Ordnance Corps since colonial times. It acquired its present designation in 1950. Ordnance soldiers and officers provide maintenance and ammunition support.
- Signal Corps, 21 June 1860
The Signal Corps was authorized as a separate branch of the Army by act of Congress on 3 March 1863. However, the Signal Corps dates its existence from 21 June 1860, when Congress authorized the appointment of one signal officer in the Army, and a War Department order carried the following assignment: "Signal Department--Assistant Surgeon Albert J. Myer to be Signal Officer, with the rank of Major, 27 June 1860], to fill an original vacancy."
- Chemical Corps, 28 June 1918
The Chemical Warfare Service was established on 28 June 1918, combining activities that until then had been dispersed among five separate agencies of Government. It was made a permanent branch of the Regular Army by the National Defense Act of 1920. In 1945, it was redesignated the Chemical Corps.
- Military Police Corps, 26 September 1941
A Provost Marshal General's Office and Corps of Military Police were established in 1941. Prior to that time, except during the Civil War and World War I, there was no regularly appointed Provost Marshal General or regularly constituted Military Police Corps, although a "Provost Marshal" can be found as early as January 1776, and a "Provost Corps" as early as 1778.
- Transportation Corps, 31 July 1942
The historical background of the Transportation Corps starts with World War I. Prior to that time, transportation operations were chiefly the responsibility of the Quartermaster General. The Transportation Corps, essentially in its present form, was organized on 31 July 1942. The Transportation Corps is headquartered at Fort Eustis, VA under the mantra "Spearhead of Logistics" and command of Brigadier General Brian R. Layer.
- Military Intelligence Corps, 1 July 1962
Intelligence has been an essential element of Army operations during war as well as during periods of peace. In the past, requirements were met by personnel from the Army Intelligence and Army Security Reserve branches, two-year obligated tour officers, one-tour levies on the various branches, and Regular Army officers in the specialization programs. To meet the Army's increased requirement for national and tactical intelligence, an Intelligence and Security Branch was established in the Army effective 1 July 1962, by General Orders No. 38, 3 July 1962. On 1 July 1967, the branch was redesignated as Military Intelligence.
- Air Defense Artillery, 20 June 1968.
Separated from the Field Artillery and established as a basic branch on 20 June 1968, per General Order 25, 14 June 1968.
- Aviation, 12 April 1983
Following the establishment of the U.S. Air Force as a separate service in 1947, the Army began to develop further its own aviation assets (light planes and rotary wing aircraft) in support of ground operations. The Korean War gave this drive impetus, and the war in Vietnam saw its fruition, as Army aviation units performed a variety of missions, including reconnaissance, transport, and fire support. After the war in Vietnam, the role of armed helicopters as tank destroyers received new emphasis. In recognition of the growing importance of aviation in Army doctrine and operations, Aviation became a separate branch on 12 April 1983, and a full member of the Army's combined arms team.
- Special Forces, 9 April 1987
The first Special Forces unit in the Army was formed on 11 June 1952, when the 10th Special Forces Group was activated at Fort Bragg, North Carolina. A major expansion of Special Forces occurred during the 1960s, with a total of eighteen groups organized in the Regular Army, Army Reserve, and Army National Guard. As a result of renewed emphasis on special operations in the 1980s, the Special Forces Branch was established as a basic branch of the Army effective 9 April 1987, by General Orders No. 35, 19 June 1987.
- Civil Affairs Corps, 17 August 1955 (special branch); 16 October 2006 (basic branch)
The Civil Affairs/Military Government Branch in the Army Reserve Branch was established on 17 August 1955. Subsequently redesignated the Civil Affairs Branch on 2 October 1955, it has continued its mission to provide guidance to commanders in a broad spectrum of activities ranging from host-guest relationships to the assumption of executive, legislative, and judicial processes in occupied or liberated areas. Became a basic branch per General Order 29, 12 January 2007.
- Psychological Operations, 16 October 2006
Established as a basic branch per General Order 30, 12 January 2007. Name will change to Military Information Support Operations at a date TBD.
- Logistics, 1 January 2008
Established by General Order 6, 27 November 2007. Consists of multi-functional logistics officers in the rank of captain and above, drawn from the Ordnance, Quartermaster and Transportation Corps.
Special branches
- Army Medical Department, 27 July 1775
Medical Department and the Medical Corps trace their origins to 27 July 1775, when the Continental Congress established the Army hospital headed by a "Director General and Chief Physician." Congress provided a medical organization of the Army only in time of war or emergency until 1818, which marked the inception of a permanent and continuous Medical Department. The Army Organization Act of 1950 renamed the Medical Department as the Army Medical Service. In June 1968, the Army Medical Service was redesignated the Army Medical Department. The Medical Department has the following branches:
-
- Medical Corps, 27 July 1775
- Army Nurse Corps, 2 February 1901
- Dental Corps, 3 March 1911
- Veterinary Corps, 3 June 1916
- Medical Service Corps, 30 June 1917
- Army Medical Specialist Corps, 16 April 1947
- Chaplain Corps, 29 July 1775
The legal origin of the Chaplain Corps is found in a resolution of the Continental Congress, adopted 29 July 1775, which made provision for the pay of chaplains. The Office of the Chief of Chaplains was created by the National Defense Act of 1920.
- Judge Advocate General's Corps, 29 July 1775
The Office of Judge Advocate of the Army may be deemed to have been created on 29 July 1775, and has generally paralleled the origin and development of the American system of military justice. The Judge Advocate General's Department, by that name, was established in 1884. Its present designation as a corps was enacted in 1948.
See also
- America's Army (Video games for recruitment)
- Comparative Military Ranks
- JROTC
- List of United States military history events
- Military Organizations
- ROTC
- Special Operations Forces
- Transformation of the United States Army
- U.S. Army air defense
- U.S. Army Basic Training
- U.S. Army branch insignia
- U.S. Army Judge Advocate General's Corps
- U.S. Army Chaplain Corps
- United States Army Center of Military History
- U.S. Army Medical Department
- U.S. Army Soldier's Creed
- U.S. special operations forces
- Vehicle markings of the United States military
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "14 June: The Birthday of the U.S. Army". United States Army Center of Military History. http://www.history.army.mil/html/faq/birth.html. an excerpt from Robert Wright, The Continental Army
- ↑ Library of Congress, Journals of the Continental Congress, Volume 27
- ↑ Army Birthdays. history.army.mil
- ↑ 2005 Posture Statement. U.S. Army, 6 February 2005
- ↑ Army FY2009 Demographics brochure. US Army
- ↑ DA Pamphlet 10-1 Organization of the United States Army; Figure 1.2 Military Operations.
- ↑ "The 7 Army Values". The Corps of Discovery, The United States Army. United States Army Center of Military History. http://www.history.army.mil/LC/The%20Mission/the_seven_army_values.htm. Retrieved 5 January 2007.
- ↑ "The US-Mexican War (1846-1848)" PBS.org
- ↑ The Deadliest War
- ↑ Cragg, p.272.
- ↑ Woodruff, Mark. Unheralded Victory: The Defeat of the Viet Cong and the North Vietnamese Army 1961-1973 (Arlington, VA: Vandamere Press, 1999).
- ↑ Army National Guard Constitution
- ↑ Carafano, James, Total Force Policy and the Abrams Doctrine: Unfulfilled Promise, Uncertain Future, Foreign Policy Research Institute, 3 February 2005.
- ↑ An Army at War: Change in the Midst of Conflict, p.515, via Google Books
- ↑ Section 1101, National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Years 1990 and 1991, Department of Defense Interim Report to Congress, September 1990. (See "rebalancing" as used in finance.)
- ↑ Downey, Chris, The Total Force Policy and Effective Force, Air War College, 19 March 2004.
- ↑ U.S. Casualties in Iraq
- ↑ DA Pam 10-1 Organization of the United States Army; Figure 1-1. Army Organizations Execute Specific Functions and Assigned Missions
- ↑ Organization of the United States Army: America's Army 1775 - 1995, DA PAM 10–1. Headquarters, Department of the Army, Washington, 14 June 1994
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 History.army.mil
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 Army Reserve Marks First 100 Years : Land Forces : Defense News Air Force
- ↑ "United States Army Central, CG's Bio". United States Army Central. 11 February 2008. http://www.arcent.army.mil/welcome/cg_site/cg.asp. Retrieved 4 July 2008.
- ↑ "United States Army, Seventh Army, Leaders". United States Army, Seventh Army. 25 June 2008. http://www.hqusareur.army.mil/institution/Leaders/default.htm. Retrieved 4 July 2008.
- ↑ "Commanding General". United States Army, Pacific. 23 April 2008. http://www.usarpac.army.mil/bios/comgen.asp. Retrieved 4 July 2008.
- ↑ "Commanding General". United States Army, Surface Deployment and Distribution Command. 30 June 2008. http://www.sddc.army.mil/Public/Home/About%20SDDC/Commanding%20General. Retrieved 4 July 2008.
- ↑ Organization, Installation Management Command
- ↑ Organization, United States Army
- ↑ Perpich v. Department of Defense, 496 U.S. 334 (1990)
- ↑ 10 U.S.C. 3013
- ↑ 10 U.S.C. 3033
- ↑ 10 U.S.C. 151
- ↑ 10 U.S.C. 162
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 33.2 From the Future Soldiers Web Site.
- ↑ From the Enlisted Soldiers Descriptions Web Site.
- ↑ 35.0 35.1 35.2 35.3 Military.isixsigma.com
- ↑ M16 Rifle. U.S. Army Fact Files.
- ↑ M4. U.S. Army Fact Files
- ↑ Army position: M4 Carbine is Soldier's battlefield weapon of choice, www.army.mil
- ↑ M9 pistol, U.S. Army Fact Files
- ↑ M249, U.S. Army Fact Files
- ↑ M240, U.S. Army Fact Files
- ↑ MK 19, U.S. Army Fact Files
- ↑ M224, U.S. Army Fact Files
- ↑ M252, U.S. Army Fact Files
- ↑ M120, U.S. Army Fact Files
- ↑ M119, U.S. Army Fact Files
- ↑ M777 Lightweight 155 mm howitzer (LW155)
- ↑ HMMWV, U.S. Army Fact Files
- ↑ Abrams, U.S. Army Fact Files
- ↑ Bradley, U.S. Army Fact Files
- ↑ Stryker, U.S. Army Fact Files
- ↑ M113, U.S. Army Fact Files
- ↑ Paladin, Army.mil
- ↑ MLRS, U.S. Army Fact Files
- ↑ Apache, U.S. Army Fact Files
- ↑ Kiowa, U.S. Army Fact Files
- ↑ Blackhawk, U.S. Army Fact Files
- ↑ Chinook, U.S. Army Fact Files
- ↑ Lopez, C. (20 February 2010). "Soldiers to get new cammo pattern for wear in Afghanistan". US Army. US Army. http://www.army.mil/-news/2010/02/20/34738-soldiers-to-get-new-cammo-pattern-for-wear-in-afghanistan/?ref=news-home-title0. Retrieved 22 February 2010.
- ↑ NG, DHS Technologies to support SICPS/TMSS United Press International
- Cragg, Dan, ed., Sgt. Maj. USA (Ret.). The guide to military installations, Stackpole Books, Harrisburg, 1983
- A Century of Lawmaking for a New Nation: U.S. Congressional Documents and Debates, 1774–1875.
External links
- Army.mil - Official site of the United States Army
- GoArmy.com - Official recruiting site
- America's Army Official Army Game Project site
- Army Collection -- Missouri History Museum
- Finding Aids for researching the US Army compiled by the United States Army Center of Military History
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from the United States Army Center of Military History document "Army Birthdays".
This article incorporates public domain material from the United States Army Center of Military History document "Army Birthdays".
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

