United Nations list of Non-Self-Governing Territories
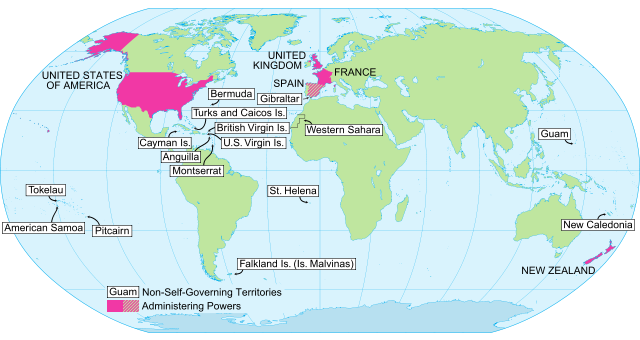
The United Nations list of Non-Self-Governing Territories is a list of countries that, according to the United Nations, are non-decolonized. The list was initially prepared in 1946 pursuant to Chapter XI of the United Nations Charter, and has been updated by the General Assembly on recommendation of the Special Committee on Decolonization and its predecessors. Only permanently inhabited territories are considered for inclusion in this list, excluding many remote atolls (e.g., Clipperton Island and Kingman Reef) and Southern Ocean territories (e.g., French Southern and Antarctic Lands and Heard Island and McDonald Islands). The list currently contains 16 entries.
Contents |
History
The list draws its origins from the period of colonialism and the Charter's concept of non-self-governing territories. Thus, Western Sahara was initially included in 1963 by Moroccan demand when it was a Spanish colony. The same can be said about the situation of Namibia (removed upon its independence in 1990), which was seen, due to its former status as a mandate territory, as a vestige of German colonial legacy in Africa. A set of criteria for determining whether a territory is to be considered "non-self-governing" was established in General Assembly Resolution 1541 (XV) of 1960.
Also in 1960, the General Assembly adopted Resolution 1514 (XV), promulgating the "Declaration on the Granting of Independence to Colonial Countries and Peoples", which declared that all remaining non-self-governing territories and trust territories were entitled to self-determination and independence. The following year, the General Assembly established the Special Committee on the Situation with Regard to the Implementation of the Declaration on the Granting of Independence to Colonial Countries and Peoples (sometimes referred to as the Special Committee on Decolonization, or the "Committee of 24" because for much of its history the committee was composed of 24 members), which reviews the situation in non-self-governing territories each year and reports to the General Assembly.
Criticism
The list remains controversial for various reasons.
Choosing to remain a territory
One reason for the remaining controversy is the fact that the list includes many dependencies that, some contend, have democratically chosen to maintain their territorial status, and rejected independence (or in some cases the territory periodically organizes referenda, as in the United States Virgin Islands, but there is insufficient voter participation). Other non-self-determining areas are excluded.
Another example is Tokelau. In response to attempts at decolonizing Tokelau, New Zealand journalist Michael Field wrote in 2004: "The UN [...] is anxious to rid the world of the last remaining vestiges of colonialism by the end of the decade. It has a list of 16 territories around the world, virtually none of which wants to be independent to any degree".[1] Tokelau is seen by some as a case in point. Field further notes that Patuki Isaako, who was head of Tokelau's government at the time of a UN seminar on decolonization in 2004, informed the United Nations that his country had no wish to be decolonized, and that Tokelauans had opposed the idea of decolonization ever since the first visit by UN officials in 1976. In 2006, a UN-supervised referendum on decolonization was held in Tokelau, where voters rejected the offer of self-government. When the first referendum failed, a second was held in 2007, and Tokelauans rejected it again. This led New Zealand politician and former diplomat John Hayes, on behalf of the National Party, to state that "Tokelau did the right thing to resist pressure from [the New Zealand government and] the United Nations to pursue self-government".[2] The United Nations most likely supported there being a referendum because clear majorities of Tokelauans support self-government in association with New Zealand. This was reinforced by the results of the referendum, which show that over 60% (60.07% in the first referendum, and 64.40% in the second) voted for self-government. However, the terms of the referendum required a two-thirds majority to vote in favor of self-government. On the second occasion, the proposition failed by just 16 votes. In May 2008, the United Nations' Secretary General Ban Ki-moon urged colonial powers "to complete the decolonization process in every one of the remaining 16 Non-Self-Governing Territories".[3] This led the New Zealand Herald to comment that the United Nations was "apparently frustrated by two failed attempts to get Tokelau to vote for independence from New Zealand".[4]
Gibraltar is another prime example of resident desires to remain with the status quo. Gibraltar, a largely self-governing British territory on the tip of the Iberian Peninsula whose territory is claimed by Spain has twice held referenda to resolve their status. In the first referendum, held in 1967, the choices in the ballot were either to retain their current status or to become part of Spain. the status quo was favoured by 12,138 votes to 44. In th second referendum, held in 2002, a proposal for a joint Anglo-Spanish administration of the territory was proposed, and was voted down by 17,900 votes to 187 - the "no" vote accounting for more than 85% of Gibraltar's entire voting population.[5]
Population (or lack thereof) is also an issue regarding at least one territory included on the list: the British colony Pitcairn Islands, with a total population of 48 (many of whom are related), has simply too small a population base (and habitable landmass for expansion), to be realistically viable as an independent state.
Completely autonomous dependencies

Another criticism is that a number of the listed territories, such as Bermuda, consider themselves completely autonomous and self-governing, with the "administering power" retaining limited oversight over matters such as defence and diplomacy.
Removed under other circumstances
Territories that have achieved a status described by the administering countries ("the colonizing power") as internally self-governing — such as Puerto Rico, the Netherlands Antilles, and the Cook Islands — have been removed from the list by vote of the General Assembly, often under pressure of the colonizing power or similar circumstances. In 1972, for example, Hong Kong (then administered by the United Kingdom) and Macau (then administered by Portugal) were removed from the list at the request of the People's Republic of China, which had just been recognized as holding China's seat at the United Nations. Many critics charge the Committee that drafts this list with the intent of using it as a political instrument.
Some territories that have been annexed and incorporated into the legal framework of the controlling state (such as the overseas departments of France) are considered by the UN to have been decolonized, since they then no longer constitute "non-self-governing" entities; their populations are assumed to have agreed to merge with the former parent state. However, in 1961, the General Assembly voted to end this treatment for the then-"overseas provinces" of Portugal such as Angola and Mozambique, which were active foci of United Nations attention until they attained independence in the mid-1970s.
Status revocation
On December 2, 1986, New Caledonia, then an overseas territory, was reinstated on the list of non-self-governing territories, an action that France protested. New Caledonia is the only French-administered territory now on the list; it has enjoyed the status of a collectivité sui generis, or a one-of-a-kind community, since 1999. Under the 1998 Nouméa Accord, its Territorial Congress has the right to call for a referendum on independence after 2014.
List not complete
Another point of controversy the criteria set down in 1960 by Resolution 1541 (XV), which only focused on colonies of the Western World, namely Australia, Belgium, Denmark, France, Italy, Netherlands, New Zealand, Portugal, South Africa, Spain, United Kingdom, and United States. Of the 111 members who joined the UN between 1960 and 2008, 41 were never included on the list. Of those 41 in 1960, eight (mostly Arab) were ruled by the "Western" countries but 12 were ruled by the Soviet Union (now Russia), two by Czechoslovakia (now dissolved), one by Ethiopia, one each by Pakistan and India, and 11 by themselves, namely Andorra, Bhutan, Germany, Liechtenstein, Monaco, Mongolia (still claimed by the Republic of China), Oman, Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Republic of Korea, San Marino, and Switzerland. Hindsight consideration of the list as incomplete often results in criticism from independence activists for Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization members like the Tibetan independence movement, which sees China as another colonial power. In 1993, the London Conference of International Lawyers recommended "Calls in the United Nations General Assembly to expand the mandate of the Special Committee on Decolonization to include Tibet in its mandate."[6][7]
Current entries
| Continent/Ocean | Country name[8] | Administering country | Status | Other claimants | Population | Area / km2 | Area / mi2 | See also |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Africa | Western Sahara | See notea | 393,831 | 266,000 | 102,700 | Legal status of Western Sahara | ||
| Atlantic Ocean | Overseas territory | None | 7,601 | 413 | 159.5 | Politics of Saint Helena | ||
| Atlantic Ocean | Overseas territory | None | 67,837 (listed as 6,997) | 53.3 | 20.6 | Politics of Bermuda | ||
| Atlantic Ocean | Overseas territory | 3,140 | 12,200 | 4,700 | Sovereignty of the Falkland Islands | |||
| Caribbean | Overseas territory | None | 14,108 | 102 | 39.4 | Politics of Anguilla | ||
| Caribbean | Overseas territory | None | 24,041 | 153 | 59.1 | Politics of the British Virgin Islands | ||
| Caribbean | Overseas territory | None | 47,862 | 262 | 101.2 | Foreign relations of the Cayman Islands | ||
| Caribbean | Overseas territory | None | 5,079 | 102 | 39.4 | Government of Montserrat | ||
| Caribbean | Overseas territory | None | 22,352 | 430 | 166.0 | Politics of the Turks and Caicos Islands | ||
| Caribbean | Unincorporated organized territory | None | 109,840 | 346.36 | 133.730 | Politics of the United States Virgin Islands | ||
| Europe | Overseas territory | 28,002 | 6.5 | 2.5 | Disputed status of Gibraltar | |||
| Pacific Ocean | Unincorporated unorganized territory | None | 64,827 | 199 | 76.8 | Politics of American Samoa | ||
| Pacific Ocean | Unincorporated organized territory | None | 175,877 | 541.3 | 209.0 | Politics of Guam | ||
| Pacific Ocean | Sui Generis Collectivity | None | 224,824 | 19,060 | 7,359 | Politics of New Caledonia | ||
| Pacific Ocean | Overseas territory | None | 48 | 47 | 18.1 | Politics of the Pitcairn Islands | ||
| Pacific Ocean | Territory | None | 1,433 | 10. | 3.9 | Politics of Tokelau |
^a A Spanish colony up to 1976, 85% of the territory of Western Sahara is now occupied and administered by Morocco. The rest of the territory is under the control of the Polisario Front and administerd by the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic. The UN however still considers Spain as administrating country.[9] The rest is administered by the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic, awaiting the outcome of the ongoing Manhasset negotiations and resulting election to be overseen by the United Nations Mission for the Referendum in Western Sahara.
Former entries
The following territories have all been on the List of Non-Self-Governing Territories in the past. The date, former administering colonial power, and the reason for removal from the list are given for each.
Territories that have been removed from the list under any status other than independence
| Continent | Non-Self-Governing Territory[10] | Reason for removal | Current status | Administering country before removal | Population | Area / km2 | Area / mi2 | Year of removal | See also |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Africa | Northern Cameroons integrated into Nigeria; Southern Cameroons integrated into Cameroon | Adamawa and Taraba states of Nigeria, Northwest and Southwest provinces of Cameroon | 1961 | Politics of Nigeria Politics of Cameroon |
|||||
| Africa | Integrated into Morocco | Tiznit Province, Souss-Massa-Draâ region, Morocco | 51,517 | 1,502 | 580 | 1969 | Politics of Morocco | ||
| Africa | Integrated into Benin | Ouidah commune, Atlantique department, Benin | 2 | 1961 | Politics of Benin | ||||
| Africa | Mandate terminated | Independent nation of Namibia | 2,088,669 | 825,418 | 318,696 | 1966 | Foreign relations of Namibia | ||
| Africa | Joined British Gold Coast to form Ghana | Volta, Northern and Upper East Region of Ghana | 1957 | Foreign relations of Ghana | |||||
| Arctic Ocean | Gained home rule | Community within the Kingdom of Denmark[11][12] | 57,564 | 2,166,086 | 836,330.5 | 1954 | Politics of Greenland | ||
| Asia | Integrated into Union of India | Puducherry union territory of India | 973,829 | 492 | 190.0 | 1947 | Pondicherry Legislative Assembly | ||
| Asia | Integrated into India | Goa state and Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu union territories of India | 1961 | ||||||
| Asia | Removed from the list on request of the PRC | Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China | 7,018,636 | 1,092 | 421.6 | 1972 | Politics of Hong Kong | ||
| Asia | Removed from the list on request of the PRC | Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China | 545,674 | 28.2 | 10.89 | 1972 | Politics of Macau | ||
| Atlantic Ocean | Integrated into French Republic | Overseas collectivity of France | 7,044 | 242 | 93.4 | 1947 | Politics of Saint Pierre and Miquelon | ||
| Caribbean | Integrated into French Republic | French Overseas department of Guadeloupe and overseas collectivities of Saint-Barthelemy and Saint-Martin | 408,000 | 1,628 | 628.6 | 1947 | Politics of Guadeloupe | ||
| Caribbean | Integrated into French Republic | Overseas department of France | 401,000 | 1,128 | 435.5 | 1947 | Politics of Martinique | ||
| Caribbean | Became constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands | Constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands | 225,369 | 960 | 371 | 1951 | Politics of the Netherlands Antilles | ||
| Caribbean | Gained self-rule | Unincorporated organized commonwealth of the United States | 3,958,128 | 8,870 | 3,420 | 1952 | Political status of Puerto Rico | ||
| Indian Ocean | Gained self-rule | External territory of Australia | 596 | 14 | 5.4 | 1984 | Shire of Cocos | ||
| Indian Ocean | Integrated into French Republic | Overseas department of France | 793,000 | 2,512 | 969.9 | 1947 | Politics of Réunion | ||
| North America | Integrated into the United States of America | U.S. state | 683,478 | 1,700,130. | 656,424 | 1959 | Legal status of Alaska | ||
| North America | Panama requested that Canal Zone be removed from the list | Part of Colón and Panama provinces of Panama | 1947 | Politics of Panama | |||||
| Pacific Ocean | Gained self-rule | Sovereign state in free association with New Zealand | 12,271 | 236.7 | 93.39 | 1965 | Politics of the Cook Islands | ||
| Pacific Ocean | Integrated into French Republic | French Polynesia and Wallis and Futuna overseas collectivities of France | 298,256 | 4,441 | 1,714.7 | 1947 | Politics of French Polynesia and Wallis and Futuna | ||
| Pacific Ocean | Became state | U.S. state | 1,283,388 | 28,311 | 10,930.9 | 1959 | Legal status of Hawaii | ||
| Pacific Ocean | Integrated into Indonesia | Papua and West Papua provinces of Indonesia | 420,540 | 162,371 | 1963 | Act of Free Choice | |||
| Pacific Ocean | Integrated into French Republic | Sui Generis Collectivity of France | 224,824 | 19,060 | 7,359 | 1947 | Politics of New Caledonia | ||
| Pacific Ocean | Became associated state of New Zealand | Sovereign state in free association with New Zealand | 1,444 | 260 | 100.4 | 1974 | Politics of Niue | ||
| Pacific Ocean | Micronesia, Marshall Islands and Palau became associated states of and Northern Mariana Islands became Commonwealth of the United States | Independent nations of Marshall Islands, Palau and Federated States of Micronesia and US Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands | 132,929 | 1,779 | 687 | 1990 (Micronesia, Marshall Islands and Northern Mariana Islands; 1994 (Palau) | |||
| Pacific Ocean | Incorporated into Federation of Malaysia[13] | Sarawak state of Malaysia | 124,450 | 48,050 | 1963 | Politics of Malaysia | |||
| Pacific Ocean | Incorporated into Federation of Malaysia[13] | Sabah state of Malaysia | 285,000 | 76,115 | 29,388 | 1963 | Politics of Malaysia | ||
| South America | Integrated into French Republic | Overseas department of France | 209,000 | 83,534 | 32,253 | 1947 | Politics of French Guiana | ||
| South America | Became a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands | Independent nation of Suriname | 475,996 | 163,270 | 63,038.9 | 1951 | Politics of Suriname |
Former colonized territories which have become independent states
| Continent | Non-Self-Governing Territory[10] | Independent country[10] | Administering country before independence | Population | Area / km2 | Area / mi2 | Year of removal | See also |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asia | 285,192 | 111,013 | 1967 | |||||
| Asia | 21,599,582[14] | 750,000 | 289,577 | 1945 (Viet Nam) 1949 (Laos) 1953 (Cambodia) |
||||
| Africa | 1,246,700 | 481,354 | 1975 | |||||
| Africa | 30,355 | 12,727 | 1966 | |||||
| Africa | 1966 | |||||||
| Africa | 16,610,000[15] | 2,344,858 | 905,355 | 1960 | ||||
| Africa | 1960 | |||||||
| Africa | 28,051 | 10,828 | 1968 | |||||
| Africa | 1960 | |||||||
| Africa | 1960 | |||||||
| Africa | 10,380 | 4,007 | 1965 | |||||
| Africa | 1957 | |||||||
| Africa | 1960 | |||||||
| Africa | 1963 | |||||||
| Africa | 1956 | |||||||
| Africa | 7,300,000[16] | 784,955 | 303,073 | 1975 | ||||
| Africa | 1960 | |||||||
| Africa | 3,545,200[17] | 752,618 | 290,587 | 1964 | ||||
| Africa | 752,618 | 290,587 | 1964 | |||||
| Africa | 36,125 | 13,948 | 1974 | |||||
| Africa | 1962 | |||||||
| Africa | 1,001 | 372 | 1975 | |||||
| Africa | Sierra Leone | 71,740 | 27,69 | 1961 | ||||
| Africa | 1960 | |||||||
| Africa | 200,000[18] | 23,200 | 8,958 | 1977 | ||||
| Africa | 6,930,000[19] | 390,580 | 150,804 | 1980 | ||||
| Africa | Swaziland | 17,364 | 6,70 | 1968 | ||||
| Africa | 1963 | |||||||
| Africa | 163,610 | 63,170 | 1956 | |||||
| Africa | 1962 | |||||||
| Africa | 1958 (Guinea) 1960 |
|||||||
| Africa | 2,643 | 1,020.5 | 1963 | |||||
| Atlantic Ocean | 13,878 | 5,358 | 1973 | |||||
| Atlantic Ocean | Cape Verde Archipelago | 4,033 | 1,557 | 1975 | ||||
| Middle East | 9,251 | 3,572 | 1960 | |||||
| Europe | 316 | 121 | 1964 | |||||
| Caribbean | 431 | 167 | 1966 | |||||
| Caribbean | 1981 (Antigua) 1983 (St. Kitts-Nevis-Anguilla) |
|||||||
| Caribbean | 11,100 | 4,444 | 1962 | |||||
| Caribbean | 5,128 | 1,978 | 1962 | |||||
| Caribbean | 1974 (Grenada) 1978 (Dominica) 1979 (St. Vincent and St. Lucia) |
|||||||
| North America | 145,000[20] | 22,966 | 8,867 | 1981 | ||||
| Indian Ocean | 688,711[21] | 15,007 | 5,794.2 | 2002 | Politics of East Timor | |||
| Indian Ocean | 1960 (Madagascar) 1975 (Comoros) |
|||||||
| Indian Ocean | 2,040 | 787 | 1968 | |||||
| Indian Ocean | 1949 | |||||||
| Indian Ocean | 451 | 174 | 1976 | |||||
| Pacific Ocean | 4,608,167 | 692.7 | 267.5 | 1965 | Foreign relations of Singapore | |||
| Pacific Ocean | 5,765 | 2,226 | 1984 | |||||
| Pacific Ocean | 1970 | |||||||
| Pacific Ocean | 1978 (Tuvalu) 1979 (Kiribati) |
|||||||
| Pacific Ocean | 132,364 | 51,106 | 1963 | |||||
| Pacific Ocean | Nauru Trust Territory | 21 | 8.1 | 1968 | ||||
| Pacific Ocean | 100,000[22] | 12,189 | 4,706 | 1980 | ||||
| Pacific Ocean | 1975 | |||||||
| Pacific Ocean | 1975 | |||||||
| Pacific Ocean | 28,896 | 11,157 | 1978 | |||||
| Pacific Ocean | 1962 | |||||||
| South America | 1966 |
See also
- Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization
- List of active autonomist and secessionist movements
- List of dependent territories
- List of sovereign states
- List of states with limited recognition
References
- ↑ "Tokelau wonders 'What have we done wrong?'", Michael Field, AFP, June 2, 2004
- ↑ "Congratulations Tokelau", National Party press release, October 26, 2007
- ↑ "Colonialism has no place in today's world," says Secretary General in message to Decolonization Seminar in Indonesia", United Nations press release, May 14, 2008
- ↑ "Tokelau decolonization high on agenda", New Zealand Herald, May 17, 2008
- ↑ [1]
- ↑ Conference of International Lawyers on issues relating to self-determination and independence for Tibet, London, January 6-10, 1993, pp. 5-8
- ↑ Final Recommendations From London Conference of International Lawyers
- ↑ Current list
- ↑ UN General Assembly Resolution 34/37 and UN General Assembly Resolution 35/19
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Non-Self-Governing Territories listed by General Assembly of the United Nations.
- ↑ Infobox image in "History" section of "About Greenland", English version of the official country government website. Accessed online 2008-09-28, Sunday.
- ↑ http://jurist.law.pitt.edu/paperchase/2009/06/greenland-takes-over-courts-police.php
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 United Nations list of Non-Self-Governing Territories
- ↑ 1935 estimate
- ↑ 1960 estimate
- ↑ 1967 estimate
- ↑ 1963 estimate, see: Northern Rhodesia#Demographics
- ↑ 1963 estimate
- ↑ 1978 estimate
- ↑ 1980 estimate, see: British Honduras#Demographics
- ↑ 1974 estimate, see: Indonesian occupation of East Timor#Number of deaths
- ↑ 1976 estimate
External links
|
||||||||||||||||||||