Themistocles
| Themistocles | |
|---|---|
| c.524 BC – 459 BC | |
 Herma of Themistocles |
|
| Place of birth | Athens |
| Place of death | Magnesia on the Maeander |
| Allegiance | Athens (to c.471 BC) Persia (469–459 BC) |
| Rank | General (Strategos) |
| Battles/wars | Battle of Marathon, Battle of Artemisium, Battle of Salamis |
Themistocles (Greek: Θεμιστοκλῆς; "Glory of the Law"[1]); c. 524–459 BC, was an Athenian politician and general. He was one of a new breed of politicians who rose to prominence in the early years of the Athenian democracy, along with his great rival Aristides. As a politician, Themistocles was a populist, having the support of lower class Athenians, and generally being at odds with the Athenian nobility. Elected archon in 493 BC, he took steps to increase the naval power of Athens, which would be a recurring theme in his political career. During the first Persian invasion of Greece, he fought at the Battle of Marathon[2], and was possibly one of the 10 Athenian strategoi (generals) in that battle.
In the years after Marathon, and in the run up to the second Persian invasion he became the most prominent politician in Athens. He continued to advocate a strong Athenian navy, and in 483 BC he persuaded the Athenians to build a fleet of 200 triremes; these would prove crucial in the forthcoming conflict with Persia. During the second invasion, he was in effective command of the Greek allied navy at the battles of Artemisium and Salamis. Thanks to subterfuge on the part of Themistocles, the Allies possessed all the advantages at Salamis, and the decisive Greek victory there was the turning point in the invasion, which was ended the following year by the defeat of the Persians at the Battle of Plataea.
After the conflict ended, Themistocles continued to be pre-eminent amongst Athenian politicians. However, he aroused the hostility of Sparta by ordering Athens to be re-fortified, and his perceived arrogance began to alienate him from the Athenians. In 472 or 471 BC, he was ostracised, and went into exile in Argos. The Spartans now saw an opportunity to destroy Themistocles, and implicated him in the treasonous plot of their own general Pausanias. Themistocles thus fled from Greece, and travelled to Asia Minor, where he entered the service of the Persian king Artaxerxes I. He was made governor of Magnesia, and lived there for the rest of his life.
Themistocles died in 459 BC, probably of natural causes. Themistocles's reputation was posthumously rehabilitated, and he was re-established as a hero of the Athenian (and indeed Greek) cause. Themistocles can still reasonably be thought of as "the man most instrumental in achieving the salvation of Greece" from the Persian threat, as Plutarch describes him. His naval policies would have a lasting impact on Athens as well, since maritime power became the cornerstone of the Athenian Empire and golden age. It was Thucydides's judgement that Themistocles was "a man who exhibited the most indubitable signs of genius; indeed, in this particular he has a claim on our admiration quite extraordinary and unparalleled".
Contents
|
Sources
The life of Themistocles is reasonably well attested in the ancient sources, especially compared to some near contemporaries (e.g. Cleisthenes, Leonidas I). He is one of approximately 50 ancient figures given an extensive biography by Plutarch in his Parallel Lives, in which Themistocles is paired with the Roman statesman Camillus.[3] Plutarch was writing some 600 years after the life of Themistocles, and is therefore very much a secondary source, but he often explicitly names his sources, which allows some degree of verification of his statements.[4] There is also a surviving (and possibly abridged) biography of Themistocles by the Roman author Cornelius Nepos from the first century BC, but this is far more cursory than Plutarch's, and adds little detail.[5]
Themistocles's role in the Greco-Persian Wars and Athenian politics is described in both Herodotus's Histories and Thucydides's History of the Peloponnesian War. These historians were contemporary, or near-contemporary with the events they described, and certainly worked within living memory of the events.[6] Herodotus's work was probably published in 425 BC, when he was approximately 60, so he was contemporary with much of Themistocles's career.[6] Herodotus stayed in Athens at some point, where he may have met people who knew Themistocles personally.[6] The Athenian statesman and historian Thucydides was born in approximately 460 BC, when Themistocles was still alive, and no doubt became familiar with his countryman's life during his own career.[7] Themistocles's role in these conflicts is also described in reasonable detail by Diodorus Siculus, in his Bibliotheca historica. Diodorus was writing in the 1st century BC, and is also very much a secondary source,[8] though useful for corroborating details found elsewhere.[9]
Early life
Themistocles was born in Athens around 524 BC,[10] the son of Neocles, who was, in the words of Plutarch "no very conspicuous man".[11] His mother is more obscure; according to Plutarch, she was either a Thracian woman called Abrotonon, or Euterpe, a Carian from Halicarnassus.[11] Like many contemporaries, little is known of his early years. Some authors report that he was unruly as a child and was consequently disowned by his father.[5][12] Plutarch considers this to be false, however.[13] Plutarch indicates that, on account of his mother's background, Themistocles was considered something of an outsider; furthermore the family appear to have lived in an immigrant district of Athens, Cynosarges, outside the city walls.[11] However, in an early example of his cunning, Themistocles persuaded "well-born" children to exercise with him in Cynosarges, thus breaking down the distinction between "alien and legitimate".[11] Plutarch further reports that Themistocles was preoccupied, even as a child, with preparing for public life.[13] His teacher is said to have told him:[13]
"My boy, thou wilt be nothing insignificant, but something great of a surety, either for good or evil."
Political & Military Career
Background
Themistocles grew up in a period of upheaval in Athens. The tyrant Peisistratos had died in 527 BC, passing power to his sons, Hipparchus and Hippias.[14] Hipparchus was murdered in 514 BC, and in response to this, Hippias became paranoid and started to rely increasingly on foreign mercenaries to keep a hold on power.[15] The head of the powerful, but exiled (according to Herodotus only - the fragmentary Archon List for 525/4 shows a Cleisthenes, an Alcmaeonid, holding office in Athens during this period), Alcmaeonid family, Cleisthenes, began to scheme to overthrow Hippias and return to Athens.[16] In 510 BC, he persuaded the Spartan king Cleomenes I to launch an attack on Athens, which succeeded in overthrowing Hippias.[16] However, in the aftermath, the other noble ('eupatrid') families of Athens rejected Cleisthenes, electing Isagoras as archon, with the support of Cleomenes.[16] On a personal level, Cleisthenes wanted to return to Athens; however, he also probably wanted to prevent Athens becoming a Spartan client state. Outmaneuvering the other nobles, he proposed to the Athenian people a radical program in which political power would be invested in the people - a "democracy".[16] The Athenian people thus overthrew Isagoras, repelled a Spartan attack under Cleomenes, and invited Cleisthenes to return to Athens, to put his plan into action.[17] The establishment of the democracy was to radically change Athens:
"And so it was that the Athenians found themselves suddenly a great power...they gave vivid proof of what equality and freedom of speech might achieve"[18]
Early years of the Democracy
The new system of government in Athens opened up a wealth of opportunity for men like Themistocles, who previously would have had no access to power.[19] Moreover, the new institutions of the democracy required skills which had previously been unimportant in government. Themistocles was to prove himself a master of the new system; "he could infight, he could network, he could spin...and crucially, he knew how to make himself visible."[19] Themistocles moved to the Ceramicus, a down-market part of Athens. This move marked him out as a 'man of the people', and allowed him to interact more easily with ordinary citizens. He began building up a support base amongst these newly-empowered citizens:
"he wooed the poor; and they, not used to being courted, duly loved him back. Touring the taverns, the markets, the docks, canvassing where no politician had thought to canvas before, making sure never to forget a single voter's name, Themistocles had set his eyes on a radical new constituency"[19]
However, he took care to ensure that he did not alienate the nobility of Athens.[19] He began to practice law, the first person in Athens to prepare for public life in this way.[19] His ability as attorney and arbitrator, used in the service of the common people, gained him further popularity.[20]
Archonship
Themistocles probably turned 30 in 494 BC, which qualified him to become an archon, the highest magistracies in Athens.[19] On the back of his popularity, he evidently decided to run for this office and was elected Eponymous Archon (the effective head of the Athenian government) in the following year (493 BC).[19] Themistocles's archonship saw the beginnings of a major theme in his career; the advancement of Athenian sea-power. Under his guidance, the Athenians began the building of a new port at Piraeus, to replace the existing facilities at Phalerum.[19] Although further away from Athens, Piraeus offered three natural harbours, and could be easily fortified.[21] Since Athens was to become an essentially maritime power during the 5th century BC, Themistocles's policies were to have huge significance for the future of Athens, and indeed Greece. In advancing naval power, Themistocles was probably advocating a course of action he thought essential for the long-term prospects of Athens.[19] However, as Plutarch implies, since naval power relied on the mass mobilisation of the common citizens (thetes) as rowers, such a policy put more power into the hands of average Athenians—and thus into Themistocles's own hands.[21]
First Persian invasion of Greece
The young Athenian democracy, along with the Euboean city of Eretria, had supported the Ionian cities in their revolt against Persian rule.[22] After suppressing the revolt, the Persian king Darius I decided that, in order to ensure the security of his empire, he would have to make himself overlord of Greece.[23] Many Greek cities gave 'earth and water', as requested, to the ambassadors that Darius sent to Greece in 491 BC, thereby signalling their submission to Darius.[24] The Athenians and Spartans refused however, and murdered the ambassadors.[25] The following year therefore, Darius sent an naval expedition across the Aegean Sea, with the ultimate aim of punishing Athens and Eretria; Sparta does not yet seem to have been a target.[22]

The expedition island-hopped through the Cyclades, before besieging and destroying Eretria.[26] The task force then sailed to Attica, landing at the Bay of Marathon.[27] However, the Athenians had assembled a force of 10,000 hoplites, and marched to Marathon, where they blocked the roads that led to Athens.[28] In nominal control was the polemarch Callimachus, but actual command seems to have devolved upon Miltiades, who had some experience of fighting the Persians.[29] Themistocles was probably the elected general of his tribe (phyle, one of ten divisions that made up the citizenry of Athens) at Marathon.[30]
After some days of stalemate, the Persians appear to have sent their cavalry away by sea to attack undefended Athens.[30] The Athenians, aware of this maneuver, took the opportunity to attack the Persians, and won a famous victory.[31] Themistocles's tribe, together with that of his rival Aristides, was in the centre of the Athenians battle line, and faced the brunt of the fighting against the strong Persian centre. However, the Persian wings were quickly routed, and the Athenian wings were able to turn inward and help defeat the Persian centre.[31]
The immediate threat to Athens was thus ended, and the Persian task force returned to Asia, though the Persian interest in Greece was far from ended.[32] Darius immediately began planning a full-scale invasion of Greece, but died before preparations were complete.[32] In the aftermath of Marathon, it is said that Themistocles was jealous of the victory of Miltiades, repeating to himself, "Miltiades' trophy does not let me sleep or be idle".[33]
Rivalry with Aristides
A year later, Miltiades, the hero of Marathon, was injured in a minor battle. Taking advantage of his incapacitation, the powerful Alcmaeonid family arranged for him to be prosecuted.[34] The Athenian aristocracy, and indeed Greek aristocrats in general, were loath to see one person pre-eminent, and such maneuvers were commonplace.[34] Miltiades was given a massive fine for the crime of 'deceiving the Athenian people', but died weeks later as a result of his wound.[34] In the wake of this prosecution, the Athenian people chose to use a new institution of the democracy, which had been part of Cleisthenes's reforms, but remained so far unused.[34] This was 'ostracism'—each Athenian citizen was required to write on a shard of pottery (ostrakon) the name of a politician that they wished to see exiled for a period of ten years.[34] This may have been triggered by Miltiades's prosecution, and used by the Athenians to try and stop such power-games amongst the noble families.[34] Certainly, in the years (487 BC) following, the heads of the prominent families, including the Alcmaeonids, were exiled.[34] The career of a politician in Athens thus became fraught with more difficulty, since displeasing the population was likely to result in exile.[34]
Themistocles, with his power-base firmly established amongst the poor, moved naturally to fill the vacuum left by Miltiades's death, and in that decade became the most influential politician in Athens.[34] However, the support of the nobility began to coalesce around the man who would become Themistocles's great rival - Aristides.[35] Aristides cast himself as Themistocles's opposite - virtuous, honest and incorruptible - and his followers called him "the just".[35] Plutarch suggests that the rivalry between the two had more sordid beginnings, when they competed over the love of a boy: "... they were rivals for the affection of the beautiful Stesilaus of Ceos, and were passionate beyond all moderation."[36]
During the decade, Themistocles continued to advocate the expansion of Athenian naval power.[34] The Athenians were certainly aware throughout this period that the Persian interest in Greece had not ended; Darius's son and successor, Xerxes I, had continued the preparations for the invasion of Greece.[37] Themistocles seems to have realised that for the Greeks to survive the coming onslaught required there to be a Greek navy which could hope to face up to the Persian navy, and he therefore attempted to persuade the Athenians to build such a fleet.[19][34] Aristides, as champion of the zeugites (the upper, 'hoplite-class') vigorously opposed such a policy.[35]
In 483 BC, a massive new seam of silver was found in the Athenian mines at Laurium.[38] Themistocles proposed that the silver should be used to build a new fleet of 200 triremes, whilst Aristides suggested it should instead be distributed amongst the Athenian citizens.[39] Themistocles avoided mentioning Persia, deeming that it was too distant a threat for the Athenians to act on, and instead focused their attention on Aegina.[38] At the time, Athens was embroiled in a long-running war with the Aeginetans, and building a fleet would allow the Athenians to finally defeat them at sea.[38] As a result, Themistocles's motion was carried easily, although only 100 warships of the trireme type were to be built.[38] Aristides refused to countenance this; conversely Themistocles was not pleased that only 100 ships would be built.[39] Tension between the two camps built over the winter, so that the ostracism of 482 BC became a direct contest between Themistocles and Aristides.[39] In what Holland characterises as, in essence, the world's first referendum, Aristides was ostracised, and Themistocles's policies were endorsed.[39] Indeed, becoming aware of the Persian preparations for the coming invasion, the Athenians voted for the construction of more ships than Themistocles had initially asked for.[39] In the run up to the Persian invasion, Themistocles had thus become the foremost politician in Athens.[20]
Second Persian invasion of Greece
In 481 BC, a congress of Greek city-states was held, during which 30 or so states agreed to ally themselves against the forthcoming invasion.[40] The Spartans and Athenians were foremost in this alliance, being sworn enemies of the Persians.[41] The Spartans claimed the command of land forces, and since the Greek (hereafter referred to as "Allied") fleet would be dominated by Athens, Themistocles tried to claim command of the naval forces.[42] However, the other naval powers, including Corinth and Aegina refused to give command to the Athenians, and Themistocles pragmatically backed down.[42] Instead, as a compromise, the Spartans (an insignificant naval power), in the person of Eurybiades were to command the naval forces.[43] It is clear from Herodotus, however, that Themistocles would be the real leader of the fleet.[44]
The 'congress' met again in the spring of 480 BC. A Thessalian delegation suggested that the allies could muster in the narrow Vale of Tempe, on the borders of Thessaly, and thereby block Xerxes's advance.[45] A force of 10,000 hoplites was dispatched to the Vale of Tempe, through which they believed the Persian army would have to pass, under the command of the Spartan polemarch Euenetus and Themistocles. However, once there, they were warned by Alexander I of Macedon that the vale could be bypassed by several other passes, and that the army of Xerxes was overwhelmingly large, and the Greeks retreated.[46] Shortly afterwards, they received the news that Xerxes had crossed the Hellespont.[45]
Themistocles now developed a second strategy. The route to southern Greece (Boeotia, Attica and the Peloponnesus) would require the army of Xerxes to travel through the very narrow pass of Thermopylae.[47] This could easily be blocked by the Greek hoplites, despite the overwhelming numbers of Persians; furthermore, to prevent the Persians bypassing Thermopylae by sea, the Athenian and allied navies could block the straits of Artemisium.[47] However, after the Tempe debacle, it was uncertain whether the Spartans would be willing to march out from the Peloponnesus again.[48] In order to persuade the Spartans to defend Attica, Themistocles needed to show them that the Athenians were willing to do everything necessary for the success of the alliance. In short, the entire Athenian fleet must be dispatched to Artemisium; in order to do this, every able-bodied Athenian male would be required to man the ships; and this in turn meant that the Athenians must prepare to abandon Athens.[48] Persuading the Athenians to take this course was undoubtedly one of the highlights of Themistocles's career.[49] As Holland has it:
"What precise heights of oratory he attained, what stirring and memorable phrases he pronounced, we have no way of knowing...only by the effect it had on the assembly can we gauge what surely must have been its electric and vivifying quality - for Themistocles' audacious proposals, when put to the vote, were ratified. The Athenian people, facing the gravest moment of peril in their history, committed themselves once and for all to the alien element of the sea, and put their faith in a man whose ambitions many had long profoundly dreaded."[48]
His proposals accepted, Themistocles issued orders for the women and children of Athens to be sent to the city of Troezen, safely inside the Peloponnesus.[50] He was then able to travel to a meeting of the Allies, at which he proposed his strategy; with the Athenian fleet fully committed to the defence of Greece, the other Allies accepted his proposals.[47]
Battle of Artemisium
Thus, in August 480 BC, when the Persian army was approaching Thessaly, the Allied fleet sailed to Artemisium, and the Allied army marched to Thermopylae.[51] Themistocles himself took command of the Athenian contingent of the fleet, and went to Artemisium. When the Persian fleet finally arrived at Artemisium after a significant delay, Eurybiades, who both Herodotus and Plutarch suggest was not the most inspiring commander, wished to sail away without fighting.[44][52] At this point Themistocles accepted a large bribe from the local people for the fleet to remain at Artemisium, and used some of it to bribe Eurybiades to remain, whilst pocketing the rest.[53] From this point on, Themistocles appears to have been more-or-less in charge of the Allied effort at Artemisium.[52] Over three days of battle, the Allies held their own against the much larger Persian fleet, but sustained significant losses.[54] However, the loss of the simultaneous Battle of Thermopylae to the Persians made their continued presence at Artemisium irrelevant, and the Allies thus evacuated.[55] According to Herodotus, Themistocles left messages at every place where the Persian fleet might stop for drinking water, asking the Ionians in the Persian fleet to defect, or at least fight badly.[56] Even if this did not work, Themistocles apparently intended that Xerxes would at least begin to suspect the Ionians, thereby sowing dissension in the Persian ranks.[56]
Battle of Salamis
In the aftermath of Thermopylae, Boeotia fell to the Persians, who then began to advance on Athens.[57] The Peloponnesian Allies prepared to now defend the Isthmus of Corinth, thus abandoning Athens to the Persians.[58] From Artemisium, the Allied fleet sailed to the island of Salamis, where the Athenian ships helped with the final evacuation of Athens. The Peloponnesian contingents wanted to sail to the coast of the Isthmus, in order to concentrate forces with the army.[59] However, Themistocles tried to convince them to remain in the Straits of Salamis, invoking the lessons of Artemisium; "battle in close conditions works to our advantage".[59] After threatening to sail with the whole Athenian people into exile in Sicily, he eventually persuaded the other Allies, whose security after all relied on the Athenian navy, to accept his plan.[60] Therefore, even after Athens had fallen to the Persians, and the Persian navy had arrived off the coast of Salamis, the Allied navy remained in the Straits. Themistocles appears to have been aiming to fight a battle which would cripple the Persian navy, and thus guarantee the security of the Peloponnesus.[59]

To bring about this battle, Themistocles used a cunning mix of subterfuge and misinformation, psychologically exploiting Xerxes's desire to finish the invasion.[61] Xerxes's actions indicate that he was keen to finish the conquest of Greece in 480 BC, and to do this, he needed a decisive victory over the Allied fleet.[62] Themistocles sent a servant, Sicinnus, to Xerxes, with a message proclaiming that Themistocles was "on king's side and prefers that your affairs prevail, not the Hellenes".[63] Themistocles claimed that the Allied commanders were infighting, that the Peloponnesians were planning to evacuate that very night, and that to gain victory all the Persians needed to do was to block the straits.[63] In performing this subterfuge, Themistocles seems to have been trying to lure the Persian fleet into the Straits.[61] The message also had a secondary purpose, namely that in the event of an Allied defeat, the Athenians would probably receive some degree of mercy from Xerxes (having indicated their readiness to submit).[61] At any rate, this was exactly the kind of news that Xerxes wanted to hear.[61] Xerxes evidently took the bait, and the Persian fleet was sent out to effect the block.[64] Perhaps over-confident and expecting no resistance, the Persian navy sailed into the Straits,[65] only to find that, far from disintegrating, the Allied navy was ready for battle.[66]
According to Herodotus, after the Persian navy began its maneuvers, Aristides arrived at the Allied camp from Aegina.[67] Aristides had been recalled from exile along with the other ostracised Athenians on the order of Themistocles, so that Athens might be united against the Persians.[67] Aristides told Themistocles that the Persian fleet had encircled the Allies, which greatly pleased Themistocles, as he now knew that the Persians had walked into his trap.[68] The Allied commanders seem to have taken this news rather uncomplainingly, and Holland therefore suggests that they were party to Themistocles's ruse all along.[69] Either way, the Allies prepared for battle, and Themistocles delivered a speech to the marines before they embarked on the ships.[70] In the ensuing battle, the cramped conditions in the Straits hindered the much larger Persian navy which became disarrayed, and the Allies took advantage to win a famous victory.[71]
Salamis was the turning point in the second Persian invasion, and indeed the Greco-Persian Wars in general.[72] Whilst the battle did not end the Persian invasion, it effectively ensured that all Greece would not be conquered, and allowed the Allies to go on the offensive in 479 BC. A significant number of historians have stated that Salamis is one of the most significant battles in human history.[73][74][75] Since it was his long-standing advocacy of Athenian naval power which enabled the Allied fleet to fight at all, and it was his stratagem that brought about the Battle of Salamis, it is probably not an exaggeration to say, as Plutarch does, that Themistocles "is thought to have been the man most instrumental in achieving the salvation of Hellas".[38][52]
Autumn/Winter 480/479 BC
The Allied victory at Salamis ended the immediate threat to Greece, and Xerxes now returned to Asia with part of the army, leaving his general Mardonius to attempt to complete the conquest.[76] Mardonius wintered in Boeotia and Thessaly, and the Athenians were thus able to return to their city, which had been burnt and razed by the Persians, for the winter.[77] For the Athenians, and Themistocles personally, the winter would be a testing one. The Peloponnesians refused to countenance marching north of the Isthmus to fight the Persian army; the Athenians tried to shame them into doing so, with no success.[78]
During the winter, the Allies held a meeting at Corinth to celebrate their success, and award prizes for achievement.[79] However, perhaps tired of the Athenians pointing out their role at Salamis, and of their demands for the Allies to march north, the Allies awarded the prize for civic achievement to Aegina.[78][80] Furthermore, although the admirals all voted for Themistocles in second place, they all voted for themselves in first place, so that no-one won the prize for individual achievement. In response, realising the importance of the Athenian fleet to their security, and probably seeking to massage Themistocles's ego, the Spartans brought Themistocles to Sparta.[78][80] There, he was awarded a special prize "for his wisdom and cleverness", and won high praise from all.[80][81] Furthermore, Plutarch reports that at the next Olympic Games:
"[when] Themistocles entered the stadium, the audience neglected the contestants all day long to gaze on him, and pointed him out with admiring applause to visiting strangers, so that he too was delighted, and confessed to his friends that he was now reaping in full measure the harvest of his toils in behalf of Hellas."[80]
Spring/Summer 479 BC
However, as happened to many prominent individuals in the Athenian democracy, Themistocles's fellow citizens grew jealous of his success, and possibly tired of his boasting.[78][82] It is probable that in early 479 BC, Themistocles was stripped of his command; instead, Xanthippus was to command the Athenian fleet, and Aristides the land forces.[78][83] Though Themistocles was no doubt politically and militarily active for the rest of the campaign, no mention of his activities in 479 BC is made in the ancient sources.[84] In the summer of that year, after receiving an Athenian ultimatum, the Peloponnesians finally agreed to assemble an army and march to confront Mardonius, who had reoccupied Athens in June.[85] At the decisive Battle of Plataea, the Allies destroyed the Persian army, whilst apparently on the same day, the Allied navy destroyed the remnants of the Persian fleet at the Battle of Mycale.[86] These twin victories completed the Allied triumph, and ended the Persian threat to Greece.[86]
Aftermath of the Persian invasion
Whatever the cause of Themistocles's unpopularity in 479 BC, it obviously did not last long. Both Diodorus and Plutarch suggest he was quickly restored to the favour of the Athenians.[21][87] Indeed, after 479 BC, he seems to have enjoyed a relatively long period of popularity.[88]
In the aftermath of the invasion, the Athenians began rebuilding their city under the guidance of Themistocles.[21] They wished to restore the fortifications of Athens, but the Spartans objected, on the grounds that no place north of the Isthmus should be left which the Persians might be able to use as a fortress.[87] Themistocles urged the citizens to build the fortifications as quickly as possible, then went to Sparta as an ambassador to answer the charges levelled by the Spartans. There, he assured them that no building work was on-going, and urged them to send emissaries to Athens to see for themselves.[89] By the time the ambassadors arrived, the Athenians had finished building, and then detained the Spartan ambassadors when they complained about the presence of the fortifications.[89] By delaying in this manner, Themistocles gave the Athenians enough time to fortify the city, and thus ward off any Spartan attack aimed at preventing the re-fortification of Athens.[89] Furthermore, the Spartans were obliged to repatriate Themistocles in order to free their own ambassadors.[21][89] However, this episode may be seen as the beginning of the Spartan mistrust of Themistocles which would return to haunt him.[21]
Themistocles also now returned to his naval policy,[21] and "more ambitious undertakings which would serve to increase the dominant position of his native state".[90] He further extended and fortified the port complex at Piraeus, and "fastened the city [Athens] to the Piraeus, and the land to the sea".[21] Themistocles was probably aiming to make Athens the dominant naval power in the Aegean.[90] Indeed, Athens would create the Delian League in 478 BC, uniting the naval power of the Aegean Islands and Ionia under Athenian leadership.[91] Themistocles introduced tax breaks for merchants and artisans, to attract both people and trade to the city, in order to make Athens a great mercantile centre.[92] He also instructed the Athenians to build 20 triremes per year, to ensure that their dominance in naval matters continued.[92] Plutarch reports that Themistocles also proposed in secret to destroy the beached ships of the other Allied navies, in order to ensure complete naval dominance, but was overruled by Aristides and the council of Athens.[93]
Fall and Exile

It seems clear that, towards the end of the decade, Themistocles had begun to accrue enemies, and had become arrogant; moreover his fellow citizens had become jealous of his prestige and power.[21][82] The Spartans actively worked against him, trying to promote Cimon (son of Miltiades) as a rival to Themistocles. Furthermore, after the treason and disgrace of the Spartan general Pausanias, the Spartans tried to implicate Themistocles in the plot; he was, however, acquitted of these charges.[88] In Athens itself, he lost favour by building a sanctuary of Artemis, with the epithet Aristoboulë ("of good counsel") near his home, a blatant reference to his own role in delivering Greece from the Persian invasion.[82] Eventually, in either 472 or 471 BC, he was ostracised.[82][94] In itself, this did not mean that Themistocles had done anything wrong; ostracism, in the words of Plutarch,
"was not a penalty, but a way of pacifying and alleviating that jealousy which delights to humble the eminent, breathing out its malice into this disfranchisement."
Themistocles first went to live in exile in Argos.[94][95] However, perceiving that they now had a prime opportunity to bring Themistocles down for good, the Spartans again levelled accusations of Themistocles's complicity in Pausanias's treason.[94] They demanded that he be tried by the 'Congress of Greeks', rather than in Athens, although it seems that in the end he was actually summoned to Athens to stand trial.[94][95] Perhaps realising he had little hope of surviving this trial, Themistocles fled, first to Corcyra, and thence to Admetus, king of Molossia.[96][97] Themistocles's flight probably only served to convince his accusers of his guilt, and he was declared a traitor in Athens, his property to be confiscated.[98] It should be noted that both Diodorus and Plutarch considered that the charges were false, and made solely for the purposes of destroying Themistocles.[94][95] The Spartans sent ambassadors to Admetus, threatening that the whole of Greece would go to war with the Molossians unless they surrendered Themistocles.[97] Admetus, however, allowed Themistocles to escape, giving him a large sum of gold to aid him on his way.[97] Themistocles then fled from Greece, apparently never to return, thus effectively bringing his political career to an end.[97][99]
Later life and death
From Molossia, Themistocles apparently fled to Pydna, from where he took a ship for Asia Minor.[98][99] This ship was blown off course by a storm, and ended up at Naxos, which an Athenian fleet was in the process of besieging.[98][99] Desperate to avoid identification, Themistocles cajoled the captain of the ship to continue the journey immediately.[98][99] According to Thucydides, who wrote within living memory of the events, the ship eventually landed safely at Ephesus, where Themistocles disembarked.[99] Plutarch has the ship docking at Cyme in Aeolia,[100] and Diodorus has Themistocles making his way to Asia in an undefined manner.[97] Diodorus and Plutarch next recount a similar tale, namely that Themistocles stayed briefly with an acquaintance (Lysitheides or Nicogenes) who was also acquainted with the Persian king, Artaxerxes I.[97][100] Since there was a bounty on Themistocles's head, this acquaintance devised a plan to safely convey Themistocles to the Persian king in the type of covered wagon that the King's concubines travelled in.[97][100] All three chroniclers agree that Themistocles's next move was to contact the Persian king; in Thucydides, this is by letter,[99] while Plutarch and Diodorus have a face-to-face meeting with the king.[97][100] The spirit is the same in all three however: Themistocles introduces himself to the king and seeks to enter his service.[99][101]
"I, Themistocles, am come to you, who did your house more harm than any of the Hellenes, when I was compelled to defend myself against your father's invasion - harm, however, far surpassed by the good that I did him during his retreat, which brought no danger for me but much for him." (Thucydides)
Thucydides and Plutarch say that Themistocles asked for a year's grace to learn the Persian language and customs, after which he would serve the king, and Artaxerxes granted this.[99][102] Plutarch reports that, as might be imagined, Artaxerxes was elated that such a dangerous and illustrious foe had come to serve him.[103][103]
At some point in his travels, Themistocles's wife and children were extricated from Athens by a friend, and joined him in exile.[96] His friends also managed to send him many of his belongings, although up to 100 talents worth of his goods were confiscated by the Athenians.[98] When, after a year, Themistocles returned to the king's court, he appears to have made an immediate impact, and "he attained...very high consideration there, such as no Hellene has ever possessed before or since".[104] Plutarch recounts that "honors he enjoyed were far beyond those paid to other foreigners; nay, he actually took part in the King's hunts and in his household diversions."[102] Themistocles advised the king on his dealings with the Greeks, though it seems that for a long period, the king was distracted by events elsewhere in the empire, and thus Themistocles "lived on for a long time without concern".[104][105] He was made governor of the district of Magnesia on the Maeander River in Asia Minor, and assigned the revenues of three cities; Magnesia (about 50 talents per year - "for bread"), Myus ("for meat") and Lampascus ("for wine").[102][104][106]
Themistocles died at Magnesia in 459 BC, at the age of 65, according to Thucydides, from natural causes.[104] However, perhaps inevitably, there were also rumours surrounding his death; that finding that he could not keep the promises that he had made to the king, he committed suicide by taking poison, or drinking bull's blood.[104][105][107] Plutarch provides the most evocative version of this story:
But when Egypt revolted with Athenian aid...and Cimon's mastery of the sea forced the King to resist the efforts of the Hellenes and to hinder their hostile growth...messages came down to Themistocles saying that the King commanded him to make good his promises by applying himself to the Hellenic problem; then, neither embittered by anything like anger against his former fellow-citizens, nor lifted up by the great honor and power he was to have in the war, but possibly thinking his task not even approachable, both because Hellas had other great generals at the time, and especially because Cimon was so marvelously successful in his campaigns; yet most of all out of regard for the reputation of his own achievements and the trophies of those early days; having decided that his best course was to put a fitting end to his life, he made a sacrifice to the gods, then called his friends together, gave them a farewell clasp of his hand, and, as the current story goes, drank bull's blood, or as some say, took a quick poison, and so died in Magnesia, in the sixty-fifth year of his life...They say that the King, on learning the cause and the manner of his death, admired the man yet more, and continued to treat his friends and kindred with kindness.[105]
After his death, Themistocles's bones were transported to Attica on his request, and buried in his native soil in secret, it being illegal to bury a Athenian traitor in Attica.[104] The Magnesians built a "splendid tomb" in their market place for Themistocles, which still stood during the time of Plutarch, and continued to dedicate part of their revenues to the family of Themistocles.[108] Plutarch indicates that he met in Athens a lineal descendant of Themistocles (also called Themistocles) who was still paid these revenues, 600 years after the events in question.[108]
Assessments
Character
It is possible to draw some conclusions about Themistocles's character. Perhaps his most evident trait was his massive ambition; "In his ambition he surpassed all men";[20] "he hankered after public office rather as a man in delirium might crave a cure".[19] He was proud and vain,[42] and anxious for recognition of his deeds.[109] His relationship with power was of a particularly personal nature; whilst he undoubtedly desired the best for Athens, many of his actions also seem to have been made in self-interest.[19] He also appears to have been corrupt (at least by modern standards), and was known for his fondness of bribes.[35]
Yet, set against these negative traits, was an apparently natural brilliance and talent for leadership:[19]
"Themistocles was a man who exhibited the most indubitable signs of genius; indeed, in this particular he has a claim on our admiration quite extraordinary and unparalleled. By his own native capacity, alike unformed and unsupplemented by study, he was at once the best judge in those sudden crises which admit of little or of no deliberation, and the best prophet of the future, even to its most distant possibilities. An able theoretical expositor of all that came within the sphere of his practice, he was not without the power of passing an adequate judgment in matters in which he had no experience. He could also excellently divine the good and evil which lay hid in the unseen future. In fine, whether we consider the extent of his natural powers, or the slightness of his application, this extraordinary man must be allowed to have surpassed all others in the faculty of intuitively meeting an emergency."[104]
Themistocles was undoubtedly intelligent, but also possessed natural cunning; "the workings of his mind [were] infinitely mobile and serpentine".[19] Themistocles was evidently sociable and appears to have enjoyed strong personal loyalty from his friends.[19][96] At any rate, it seems to have been Themistocles's particular mix of virtues and vices that made him such an effective politician.[19]
Historical Reputation
Themistocles died with his reputation in tatters, a traitor to the Athenian people; the "saviour of Greece" had turned into the enemy of liberty.[110] However, his reputation in Athens was rehabilitated by Pericles in the 450s BC, and by the time Herodotus wrote his history, Themistocles was once again seen as a hero.[7] Thucydides evidently held Themistocles in some esteem, and is uncharacteristically fulsome in his praise for him (see above).[104] Diodorus also extensively praises Themistocles, going as far as to offer a rationale for the length at which he discusses him: "Now on the subject of the high merits of Themistocles, even if we have dwelt over-long on the subject in this digression, we believed it not seemly that we should leave his great ability unrecorded."[111] Indeed, Diodorus goes so far as to say that
"But if any man, putting envy aside, will estimate closely not only the man's natural gifts but also his achievements, he will find that on both counts Themistocles holds first place among all of whom we have record. Therefore one may well be amazed that the Athenians were willing to rid themselves of a man of such genius."[107]
Since Diodorus's history includes such luminaries as Alexander the Great and Hannibal, this is high praise indeed. Plutarch offers a more nuanced view of Themistocles, with more of a critique of Themistocles's character. He does not detract from Themistocles's achievements, but also highlights his failings.[36]
Political and military legacy
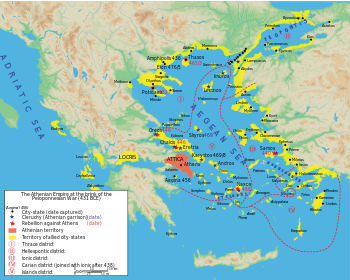
Undoubtedly the greatest achievement of Themistocles's career was his role in the defeat of Xerxes's invasion of Greece. Against overwhelming odds, Greece survived, and classical Greek culture, so influential in 'western civilization' was able to develop unabated.[112] Moreover, Themistocles's doctrine of Athenian naval power, and the establishment of Athens as a major power in the Greek world were of enormous consequence during the 5th century BC. In 478 BC, the Hellenic alliance was reconstituted without the Peloponnesian states, into the Delian League, in which Athens was the dominant power.[113] This was essentially a maritime alliance of Athens and her colonies, the Aegean islands, and the Ionian cities. The Delian league took the war to Persia, eventually invading Persian territory and dominating the Aegean.[113] Under the guidance of Pericles, the Delian league gradually evolved into the Athenian Empire, the zenith of Athenian power and influence.[114] Themistocles seems to have deliberately set Athens up as a rival to Sparta in the aftermath of Xerxes's invasion, basing this strategy on Athenian naval power (contrasted with the power of the Spartan army).[21] Tension grew throughout the century between Athens and Sparta, as they competed to be the leading state in Greece.[115] Finally, in 431 BC, this tension erupted into the Peloponnesian War, the first of a series of conflicts which would tear Greece apart for the next century; an unforeseen, if indirect, legacy of Themistocles's.[115]
Diodorus provides a rhetorical summary which reflects upon Themistocles's achievements:
"What other man, while Sparta still had the superior strength and the Spartan Eurybiades held the supreme command of the fleet, could by his single-handed efforts have deprived Sparta of that glory? Of what other man have we learned from history that by a single act he caused himself to surpass all the commanders, his city all the other Greek states, and the Greeks the barbarians? In whose term as general have the resources been more inferior and the dangers they faced greater? Who, facing the united might of all Asia, has found himself at the side of his city when its inhabitants had been driven from their homes, and still won the victory?"[111]
In popular culture
- In the movie The 300 Spartans (1962), Themistocles is portrayed by the actor Ralph Richardson
- In the film Lawrence of Arabia (1962) T. E. Lawrence, played by actor Peter O'Toole, quotes Themistocles saying, "I cannot fiddle, but I can make a great state from a little city."
- The historical novel "Farewell Great King" by Jill Paton Walsh follows the life, until death, of Themistocles. It is based primarily upon the Life of Themistocles and Life of Aristides from Plutarch.
- The historical novel "Themistocles: The Towering Oak" by Jan Ward Maxwell, presents the life of Themistocles in an easy-to-read manner, incorporating fact with fiction. Although much of the dialogue is fiction, it sets the scene for the facts.
References
- ↑ [1]
- ↑ Plutarch Aristides 5.3
- ↑ Jona Lendering. "Plutarch of Chaeronea". http://www.livius.org/pi-pm/plutarch/plutarch.htm. Retrieved 2009-03-18.
- ↑ e.g. Themistocles 25 has a direct reference to Thucydides I, 137
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Cornelius Nepos, Themistocles
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Lazenby, pp1–3
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Lazenby, p169
- ↑ Green, pp xxiv–xxv
- ↑ Lazenby, p7
- ↑ Hornblower and Spawforth; entry Themistocles
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 Plutarch, Themistocles 1
- ↑ Libanius, Declamations 9–10
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 Plutarch, Themistocles 1
- ↑ Holland, p122
- ↑ Holland, pp126–128
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 16.3 Holland, pp128–131
- ↑ Holland, pp132–134
- ↑ Herodotus V, 78
- ↑ 19.00 19.01 19.02 19.03 19.04 19.05 19.06 19.07 19.08 19.09 19.10 19.11 19.12 19.13 19.14 19.15 Holland, pp164–167
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 Plutarch, Themistocles, 5
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 21.2 21.3 21.4 21.5 21.6 21.7 21.8 21.9 Plutarch, Themistocles, 19
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 Holland, pp181–183
- ↑ Holland, p177–178
- ↑ Herodotus VI 48
- ↑ Holland, pp178-179
- ↑ Herodotus VI, 100
- ↑ Herodotus VI, 102
- ↑ Herodotus VI, 103
- ↑ Herodotus VI, 109–110
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 Holland, pp191–193
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 Holland, pp195-197
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 Holland, p202–203
- ↑ Plutarch, Moralia, 185 A 3
- ↑ 34.00 34.01 34.02 34.03 34.04 34.05 34.06 34.07 34.08 34.09 34.10 Holland, pp214–217
- ↑ 35.0 35.1 35.2 35.3 Holland, pp217–219
- ↑ 36.0 36.1 Plutarch, Themistocles, 3
- ↑ Holland, pp208–211
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 38.2 38.3 38.4 Plutarch, Themistocles 4
- ↑ 39.0 39.1 39.2 39.3 39.4 Holland, pp219–222
- ↑ Herodotus VII, 145
- ↑ Herodotus VII, 161
- ↑ 42.0 42.1 42.2 Holland, p226
- ↑ Holland, p258
- ↑ 44.0 44.1 Herodotus VIII, 4
- ↑ 45.0 45.1 Holland, pp248–249
- ↑ Herodotus VII,173
- ↑ 47.0 47.1 47.2 Holland, pp255–257
- ↑ 48.0 48.1 48.2 Holland, pp251–255
- ↑ Plutarch, Themistocles, 11
- ↑ Herodotus VIII, 40
- ↑ Holland, p257–258
- ↑ 52.0 52.1 52.2 Plutarch, Themistocles, 7
- ↑ Holland, p276
- ↑ Herodotus VIII, 11–19
- ↑ Herodotus VIII, 21
- ↑ 56.0 56.1 Herodotus VIII, 22
- ↑ Herodotus VIII, 50
- ↑ Herodotus VIII, 71
- ↑ 59.0 59.1 59.2 Holland, pp302–303
- ↑ Herodotus VIII, 62
- ↑ 61.0 61.1 61.2 61.3 Holland, pp310–315
- ↑ Holland, pp307–309
- ↑ 63.0 63.1 Herodotus VIII, 75
- ↑ Herodotus VIII, 76
- ↑ Lazenby, p255
- ↑ Holland, p321
- ↑ 67.0 67.1 Herodotus VIII, 79
- ↑ Herodotus VIII, 80
- ↑ Holland, p316
- ↑ Herodotus VIII 83
- ↑ Lazenby, p190
- ↑ Lazenby, p197
- ↑ Hanson, pp12–60
- ↑ Strauss, pp1–294
- ↑ Holland, p399
- ↑ Herodotus VIII, 97
- ↑ Holland, pp327–329
- ↑ 78.0 78.1 78.2 78.3 78.4 Holland, p332–335
- ↑ Herodotus VIII, 123
- ↑ 80.0 80.1 80.2 80.3 Plutarch, Themistocles, 17
- ↑ Herodotus VIII, 124
- ↑ 82.0 82.1 82.2 82.3 Plutarch, Themistocles, 22
- ↑ Diodorus XI, 27
- ↑ Lazenby, p209
- ↑ Herodotus IX, 6–9
- ↑ 86.0 86.1 Holland, pp358–359
- ↑ 87.0 87.1 Diodorus XI, 39
- ↑ 88.0 88.1 Diodorus XI, 54
- ↑ 89.0 89.1 89.2 89.3 Diodorus XI, 40
- ↑ 90.0 90.1 Diodorus XI, 41
- ↑ Holland, p360
- ↑ 92.0 92.1 Diodorus XI, 43
- ↑ Plutarch, Themistocles, 20
- ↑ 94.0 94.1 94.2 94.3 94.4 Diodorus XI, 55
- ↑ 95.0 95.1 95.2 Plutarch, Themistocles, 23
- ↑ 96.0 96.1 96.2 Plutarch, Themistocles, 24
- ↑ 97.0 97.1 97.2 97.3 97.4 97.5 97.6 97.7 Diodorus XI, 56
- ↑ 98.0 98.1 98.2 98.3 98.4 Plutarch, Themistocles, 25
- ↑ 99.0 99.1 99.2 99.3 99.4 99.5 99.6 99.7 Thucydides I, 137
- ↑ 100.0 100.1 100.2 100.3 Plutarch, Themistocles 26
- ↑ Plutarch, Themistocles 27
- ↑ 102.0 102.1 102.2 Plutarch, Themistocles, 29
- ↑ 103.0 103.1 Plutarch, Themistocles 28
- ↑ 104.0 104.1 104.2 104.3 104.4 104.5 104.6 104.7 Thucydides I, 138
- ↑ 105.0 105.1 105.2 Plutarch Themistocles, 31
- ↑ Diodorus XI, 57
- ↑ 107.0 107.1 Diodorus XI, 58
- ↑ 108.0 108.1 Plutarch Themistocles, 32
- ↑ Plutarch, Themistocles 18
- ↑ Holland, p364
- ↑ 111.0 111.1 Diodorus XI, 58
- ↑ Holland, pp xvi–xvii
- ↑ 113.0 113.1 Holland, pp362–365
- ↑ Butler, p195
- ↑ 115.0 115.1 Holland, p371
Bibliography
Ancient sources
- Cornelius Nepos, Themistocles
- Diodorus Siculus, Biblioteca Historica.
- Herodotus, The Histories.
- Libanius, Declamationes.
- Plutarch, Themistocles.
- Plutarch, Moralia.
- Thucydides, History of the Peloponnesian War.
Modern Sources
- Butler, Howard (2005). The Story of Athens. Kessinger Publishing. ISBN 1-4179-7092-8.
- Hanson, Victor Davis (2001). Carnage and Culture: Landmark Battles in the Rise of Western Power. DoubleDay. ISBN 0-385-50052-1.
- Holland, Tom (2005). Persian Fire. Abacus. ISBN 978-0-349-11717-1.
- Simon Hornblower, Anthony Spawforth (1996). The Oxford Classical Dictionary. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780198661726..
- Green, Peter (2007). Alexander the Great and the Hellenistic Age. Orion. ISBN 978-0-7538-2413-9.
- Lazenby, JF (1993). The Defence of Greece 490–479 BC. Aris & Phillips Ltd.. ISBN 0-85668-591-7.
- Strauss, Barry (2004). The Battle of Salamis: The Naval Encounter That Saved Greece—and Western Civilization. Simon and Schuster. ISBN 0-7432-4450-8.
External links
- Livius.org, Themistocles by Jona Lendering
|
||||||||||||||
|
|||||