Republika Srpska
| Republika Srpska
Република Српска
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| Anthem: Moja Republika (English: "My Republic") |
||||||
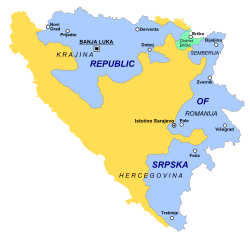 Location of Republika Srpska in Bosnia and Herzegovina.1
|
||||||
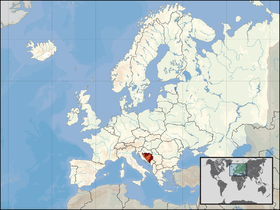 Location Republika Srpska (red) inside of Bosnia and Herzegovina on the European continent.
|
||||||
| Capital | Sarajevo (official)[1], Banja Luka (de facto) | |||||
| Official language(s) | Serbian, Bosnian, and Croatian2 | |||||
| Ethnic groups (2006 est) | Serbs: 88% Bosniaks: 8% Croats: 4% |
|||||
| Government | Entity Parliamentary system | |||||
| - | President | Rajko Kuzmanović (SNSD) | ||||
| - | Prime Minister | Milorad Dodik (SNSD) | ||||
| Entity | ||||||
| - | Proclaimed Entity of Bosnia and Herzegovina | 14 December 1995 | ||||
| Area | ||||||
| - | Total | 24,857 km2 9,597 sq mi |
||||
| - | Water (%) | N/A | ||||
| Population | ||||||
| - | 2010 estimate | 1,439,673 3 | ||||
| - | 1996 census | 1,437,477 4 | ||||
| - | Density | 57,9/km2 155/sq mi |
||||
| Currency | Convertible Mark (BAM) |
|||||
| Time zone | CET (UTC+1) | |||||
| - | Summer (DST) | CEST (UTC+2) | ||||
| Internet TLD | rs.ba | |||||
| Calling code | 387 | |||||
| On 29 January 2007 the constitutional court of Bosnia and Herzegovina ruled that national symbols are to be banned from the flags, heraldic devices and anthem of its regions.[2] This decision came into force when published in the Official Gazette of Bosnia and Herzegovina on March 31, 2007.[3] Following the decision, in July 2008 the National Assembly of Republika Srpska adopted a new heraldic achievement. Bosniak and Croat members of the assembly issued an official objection to the new heraldry on the grounds that it violates the decision of the court and discriminates against non-Serbs. The case is to be reviewed in the near future.[4] | ||||||
| 1 | Although the Brčko District is formally held in condominium by both entities simultaneously (the Republika Srpska and the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina), it is a de facto third entity that has all the powers of the other two and is under the direct sovereignty of Bosnia and Herzegovina.[5][6] | |||||
| 2 | The Constitution of Republika Srpska avoids naming the languages, and lists them as "the language of the Serb people, the language of the Bosniak people and the language of the Croat people."[7] | |||||
| 3 | Excluding RS's 48% of the Brčko District. | |||||
| 4 | Including refugees abroad. | |||||
Republika Srpska listen (Serbian Cyrillic: Република Српска) is one of two main political entities of Bosnia and Herzegovina, the other being the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Republika Srpska is defined in its constitution as a territorially unified, indivisible and inalienable constitutional and legal entity that shall independently perform its constitutional, legislative, executive and judicial functions. The National Assembly and the government are based in Banja Luka, although Sarajevo remains the official capital. Republika Srpska is home to three constituent peoples: Serbs (ca. 88%), Bosniaks (ca. 8%) and Croats (ca. 4%).
Contents |
Name
In the name Republika Srpska, the first word means republic. The second word is a nominalized adjective derived by adding the suffix -ska to srb-, the root of the noun Srbin, meaning Serb. The -ps- sequence rather than -bs- is a result of voicing assimilation. Adjectives derived in this way from ethnonyms are often used in Serbian, as well as other languages such as Swedish, as names of countries; e.g. Škot - Škotska (Scot - Scotland), Bugarin - Bugarska (Bulgarian - Bulgaria), Hrvat - Hrvatska (Croat - Croatia).
Although the name Republika Srpska is sometimes glossed as Serb Republic[8] or Bosnian Serb Republic[9], and the government of Republika Srpska uses the semi-Anglicized term Republic of Srpska in English translations of official documents, western news sources such as the BBC[10], The New York Times[11], and The Guardian[12] generally refer to the entity as the Republika Srpska.
History
The Socialist Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina was formerly one of Yugoslavia's six federal units, defined in its constitution as a state of equal citizens, Muslims, Serbs, Croats and others.[13] The 1991 population census counted 43% Muslims, renamed Bosniaks in 1993, 31% Serbs, and 17% Croats, the remainder being Yugoslavs and others. The first democratic multi-party elections in the republic were held on 18 November 1990. Most seats in its parliament were won by political parties that represented the three peoples: the Party of Democratic Action, the Serb Democratic Party, and the Croatian Democratic Union. The three parties reached a power sharing agreement covering all government bodies and public institutions.

In a session on 14 and 15 October 1991 the Parliament approved the "Memorandum on Sovereignty" as had already been done by Slovenia and Croatia. The Memorandum was adopted despite opposition from 73 Serb deputies, belonging to the Serb Democratic Party (most of the Serb parliamentary representatives) as well as the Serbian Renewal Movement and the Union of Reform Forces, who regarded the move as illegal.[14][15] On 24 October 1991, the Serb deputies formed the Assembly of the Serb People in Bosnia and Herzegovina (Skupština srpskog naroda u Bosni i Hercegovini) to be the highest representative and legislative body of the Serb population,[16][17] ending the tripartite coalition.
The Union of Reform Forces soon ceased to exist but its members remained in the assembly as the Independent Members of Parliament Caucus. The assembly undertook to address the achievement of equality between the Serbs and other peoples and the protection of the Serbs' interests jeopardized by decisions of the Bosnian parliament.[16] On 9 January 1992, the assembly proclaimed the Republic of the Serb People of Bosnia and Herzegovina (Republika srpskog naroda Bosne i Hercegovine), declaring it part of Yugoslavia.[18]
On 28 February 1992 the assembly adopted the Constitution of the Serbian Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (the name adopted instead of the previous Republika srpskog naroda Bosne i Hercegovine). Its territory would include districts, municipalities, and regions where Serbs were the majority and also those where they had become a minority because of persecution during World War II. The republic was part of Yugoslavia and could enter into union with political bodies representing other peoples of Bosnia and Herzegovina.[19]

The Bosnian parliament, without its Serb deputies, held a referendum on the independence of Bosnia and Herzegovina on 29 February and 1 March 1992, but most Serbs boycotted it since the assembly had previously (9–10 November 1991) held a plebiscite in the Serb regions, 96% having opted for membership of the Yugoslav federation.[20] The referendum had a 64% turnout and 92.7% or 99% (according to different sources) voted for independence.[21][22] On 6 March the Bosnian parliament promulgated the results of the referendum, proclaiming the republic's independence from Yugoslavia. Serbian legal experts have denied the legality of both the referendum and the proclamation of independence.[20] The republic's independence was recognized by the European Community on 6 April 1992 and by the USA on 7 April. On the same day the Serbs' assembly in session in Banja Luka declared a severance of governmental ties with Bosnia and Herzegovina.[23] The name Republika Srpska was adopted on 12 August 1992.[24]
The political controversy escalated into the Bosnian War, which would last until the autumn of 1995. The war was ended by the General Framework Agreement for Peace in Bosnia and Herzegovina, reached at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base near Dayton, Ohio on 21 November and formally signed in Paris on 14 December 1995. Annex 4 of the Agreement is the current Constitution of Bosnia and Herzegovina, recognising Republka Srpska as one of its two main political-territorial divisions and defining the governmental functions and powers of the both entities. The boundary lines between the entities were delineated in Annex 2 of the Agreement.[25] From 1992 to 2008 the Constitution of Republika Srpska was amended 121 times. Article 1 states that Republika Srpska is a territorially unified, indivisible and inalienable constitutional and legal entity that shall independently perform its constitutional, legislative, executive and judicial functions.[26]
Impact of war

The war in Bosnia and Herzegovina resulted in major changes in the country, some of which were quantified in a 1998 report by UNESCO. In the non-Serbian region 50% of houses were damaged and 6% destroyed while the number was lower in the Serbian region, 25% damaged and 5% destroyed. About half the country's population of 4 million was displaced. In 1996 there were some 435,346 Serbian refugees from the Federation in Republika Srpska while another 197,925 had gone to Serbia. In 1991, 27% of the non-agricultural labor force had been unemployed in Bosnia and this number had increased due to the war.[27] In 2009 the unemployment rate in Bosnia and Herzegovina was an estimated 29% according to the CIA's The World Factbook.[28] In 1996 unemployment in Republika Srpska was at 90%.


.jpg)
Republika Srpska's population of Serbs had increased by 547,741 and ethnic cleansing considerably reduced the numbers of other groups. The increasing of Serbs in the Republic is due to the influx of ethnic Serbs from other parts of Bosnia. The number of Croats was reduced by 135,386 (majority of prewar population), and the number of Bosniaks by some 434,144. Some 136,000 of approximately 496,000 Bosniak refugees and expulsees, forced to flee the territory of what is now Republika Srpska, have returned home.[29] As of 2008, 35% of Bosniaks and 8.5% of Croats have returned to Republika Srpska, while 24% of Serbs who were forced to leave their homes in territories controlled by Bosniaks or Croats, have returned to their pre-war addresses.[30]
In the early 2000s discrimination against non-Serbs was alleged by NGOs and the Helsinki Commission. The International Crisis Group reported in 2002 that in some parts of Republika Srpska a returnee is ten times more likely to be the victim of violent crime than is a local Serb.[31] The Helsinki Commission, in a 2001 statement on "Tolerance and Non-Discrimination," also pointed at violence against non-Serbs, stating that in the city of Banja Luka[32] and Trebinje[33] mobs attacked people who sought to lay foundations for new mosques on the ruins of those destroyed. There were indications of police collaboration. Non-Serbs have continued difficulty in returning to their original homes and the assembly’s record of cooperation in apprehending individuals indicted for war crimes, crimes against humanity and genocide is poor.[34]
Organizations such as the Society for Threatened Peoples, reporting to the United Nations Human Rights Council in 2008, claim that non-Serbian refugees returning to Republika Srpska are discriminated against and live under appalling conditions, particularly in the Drina Valley (Srebrenica, Bratunac, Višegrad and Foča). Many are unemployed and children must attend schools where all subjects are taught in Serbian. Similar things are taking place in the Federation of Bosnia where the problem of segregation is very visible in Herzegovinan and some Bosnian cities where the population is predominantly Croatian. Separate schools for Croatians and non-Croatians are formed. Croatian nationality students are taught using Croatian curriculum whereas Serbian and Bosniak pupils are taught according to the curriculum of Bosnia and Herzegovina [35]
According to the Ministry for Human Rights and Refugees of Bosnia and Herzegovina, European Union Police Mission, UNHCR, and other international organizations, the security in both Republika Srpska and the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina is at present satisfactory, although some minor threats, real or perceived, can still influence the decision of individuals whether they will return to their pre-war addresses or not.[30]
Geography
Boundary
The Inter-Entity Boundary Line (IEBL) between Bosnia and Herzegovina's two entities essentially follows the front lines at the end of the Bosnian War with adjustments (most importantly in the western part of the country and around Sarajevo) defined by the Dayton Agreement. The total length of the IEBL is approximately 1,080 km. The IEBL is an administrative demarcation uncontrolled by military or police and there is free movement across it.
Municipalities
Under the Law on Territorial Organization and Local Self-Government, adopted in 1994, Republika Srpska was divided into 80 municipalities. After the Dayton Peace Agreement the law was amended to reflect changes to borders: it now comprises 63 municipalities.
Population
| Ethnic Composition | |||||||||||||
| Year | Serbs | % | Muslims | % | Croats | % | Others | % | Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1991 | 869,854 | 55.4% | 440,746 | 28.1% | 144,414 | 9.2% | 114,494 | 7.3% | 1,569,332 | ||||
| 1996 | 1,427,912 | 96.8% | 32,344 | 2.2% | 15,028 | 1.0% | 4 | 0.0% | 1,475,288 | ||||
| 2006 | 1,267,000 | 88% | 127,000 | 8% | 58,000 | 4% | 750 | 0.001% | 1,452,673 | ||||
| note1:The vast majority of Muslims by nationality today consider themselves Bosniaks. note2: "Other" is mainly people who declared themselves as Yugoslavs note3: 2006 data is an estimate |
|||||||||||||
There has been no census since the end of the war. The next census is expected to occur in 2011 but has not yet been confirmed: these figures are estimates.
| Year | Total | Males | Females |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1998[note 1] | 1,428,798 | 679,795 | 749,003 |
| 1999[note 1] | 1,448,579 | 689,186 | 759,351 |
| 2000 | 1,428,899 | 695,194 | 733,705 |
| 2001 | 1,447,477 | 704,197 | 743,280 |
| 2002 | 1,454,802 | 708,136 | 746,666 |
| 2003 | 1,452,351 | 706,925 | 745,426 |
| 2004 | 1,449,897 | 705,731 | 744,166 |
| 2005 | 1,446,417 | 704,037 | 742,380 |
| 2006 | 1,443,709 | 702,718 | 740,991 |
| 2007 | 1,439,673 | 700,754 | 738,919 |
| 2008 | 1,437,477 | 699,685 | 737,792 |
 Ethnic composition in 1961 |
 Ethnic composition in 1981 |
 Ethnic composition in 1991 |
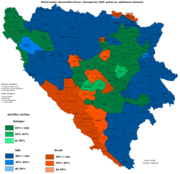 Ethnic composition estimate in 2006 |
Economy
The currency of Republika Srpska is the Bosnia and Herzegovina convertible mark. A so-called "regulatory guillotine" means that it takes only a few days to register a business there whereas in the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina it takes several months.[37]
Foreign investment
An agreement on strategic partnership has been concluded between the Iron Ore Mine Ljubija Prijedor and the British company LNM, a leading world steel producer. The Russian company Yuzhuralzoloto also signed a strategic partnership with the Lead and Zinc Mine Sase Srebrenica. Recent foreign investments include privatisation of Telekom Srpske, sold to the Serbian Telekom Srbija for (€646mln, and the sale of the petroleum and oil industry, based in Bosanski Brod, Modriča and Banja Luka, to Zarubezhneft of Russia, whose investment is expected to total US$970mln in the coming years.[38] On 16 May 2007 the Czech power utility ČEZ signed a €1.4 bln contract with the Elektroprivreda Republike Srpske, to renovate the Gacko I power plant and build a second, Gacko II.[39]
External trade
In recent years exports (not including trade with the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina) have grown significantly and the level of import coverage has improved – from 1,130,518mln KM (€565mln) and 38.3% in 2005, to 1,539,229mln KM (€770mln) and 55.8% in 2006. In the first two months of 2007 exports grew 19% year on year, and imports by 39%.[40][41][42][43] In 2008 exports amounted to €960mln and imports €2.07bln.[44]
Taxation
Since 2001, Republika Srpska initiated significant reforms in the sector of the tax system, which lowered the tax burden to 28.6%, one of the lowest in the region. The 10% rate of capital gains tax and income tax are the lowest in Europe and highly stimulating for foreign investment, and there are no limits on the amount of earnings. Increasing the number of taxpayers and budgeted incomes, and creating a stable fiscal system, were necessary for further reforms in the fields of taxation and duties; this area is a priority goal of the RS authorities. VAT has been introduced in 2006. Income tax is 46% in the RS, compared to nearly 70% in the Federation, and the corporate tax rate is 10%, compared to 30% in the Federation. These tax advantages have led to some companies moving their business to RS from the other entity.[37]
Salaries
The RS saw accelerated salary growth in 2008.The average RS net salary in 2008 amounted to BAM 755(€386), which represents an increase of 29% compared to 2007 average. High inflation rate in the RS in 2008 caused the difference between the nominal and the real salary growth to be higher than in 2007. Average net salaries in the RS saw a real growth of 21.8%, since 2008 inflation measured by Consumer Price Index was 7.2%. Marked salary growth in the RS was particularly contributed to by salary growth in individual economic sectors, especially in public sector. Regarding pensions in the RS, their growth in 2008 kept pace with salary trends. Average pension in 2008 amounted to BAM 294 (€150), which is larger by 27.8% (y/y). Somewhat higher pension growth in the RS might be explained by significantly faster growth of contributions of the PDI Fund. The average wage as of May 2009 stood at 794KM(€406).
Government and politics

Under its constitution, Republika Srpska has a president, parliament (the 83-member National Assembly of Republika Srpska), executive (with a prime minister and several ministries), supreme court and lower courts, customs service (under the state-level customs service), and postal service. It also has its own coat of arms, flag (the Slavic tricolor), and national anthem. However, the national anthem, like Spain, San Marino and Abu Dhabi has no words to it. The Constitutional Law on Coat of Arms and Anthem of the Republika Srpska was ruled not in conformance with the Constitution of Bosnia and Herzegovina as it states that those symbols "represent statehood of the Republika Srpska" and are used "in accordance with moral norms of Serb people". According to the Constitutional Court's decision, the Law was to be corrected by September 2006. The national assembly of Republika Srpska formed a board which is going to make a proposal for the anthem and coat of arms of Republika Srpska. Its flagship airline, Air Srpska, ceased operations in 2003.
Although the constitution names Sarajevo as the capital of Republika Srpska, the northwestern city of Banja Luka is the headquarters of most of the institutions of government — including the parliament — and is therefore the de facto capital.
After the war, Republika Srpska retained its army, but in August 2005, the parliament consented to transfer control of Army of Republika Srpska to a state-level ministry and abolish the Republic's defense ministry and army by 1 January 2006. These reforms were required by NATO as a precondition of Bosnia and Herzegovina's admission to the Partnership for Peace. As of 14 December 2006, Bosnia and Herzegovina is a part of the Partnership for Peace-project.
Republika Srpska had its own police force but in October 2005 the parliament consented to the creation over a five-year period of a single integrated police service at the state level, with local police areas that may cross the Inter-Entity Boundary Line if required based on technical considerations. These reforms were insisted upon by the European Union as a precondition for the negotiation of a Stabilization and Association Agreement with Bosnia and Herzegovina. The leading Bosnian Serb party, the Alliance of Independent Social Democrats (SNSD), called on other political parties in Republika Srpska to organize a referendum on police reform in Bosnia-Herzegovina. The SNSD said the referendum should give a clear picture on whether the Bosnian Serb police should be dismissed or not in the process reforms under which a single police force is to be created on the state level.[45] "I do expect that the answer of most of citizens of Republika Srpska would be no," Rajko Vasić, member of the SNSD leadership said. He also said the party, which won exactly half the seats in the National Assembly of Republika Srpska on 1 October 2006, would suggest the referendum on police reform as an issue to be discussed at the first next session of the entity's parliament. Earlier last year the leader of the SNSD and the current RS Prime Minister Milorad Dodik said he would be ready to sacrifice negotiations with the European Union on the eventual integration of Bosnia and Herzegovina into the Union, if the RS police is to be abolished as part of the police reform on Bosnia's state-level.[46] The parliament of the Republika Srpska voted 55 to five, with 15 abstentions, on 5 October to accept the EU's proposed police reform package.[47]
External relations
On 26 September 2006 Republika Srpska officials signed a 'special ties agreement' with Serbia aimed at promoting economic and institutional cooperation between Serbia and the Republika Srpska (RS). The accord was signed by Serbia's President Boris Tadić and Prime Minister Vojislav Koštunica, former RS President Dragan Čavić, and Prime Minister Milorad Dodik.

Tadić and Koštunica, accompanied by several ministers and some 300 businessmen, arrived in Banja Luka, the de facto capital of the Republika Srpska, on two special planes from Belgrade, in what was seen as the biggest-ever boost to strengthening ties in all spheres of life between the Republika Srpska and Serbia. The Serbian Komercijalna banka and the "Dunav osiguranje" insurance company opened branches in Banja Luka and the Serbian news agency Tanjug also inaugurated its international press center in Banja Luka, in a day packed with business engagements.
The document sets out steps taken by Serbia and Republika Srpska officials to increase economic and political ties. It is similar to a previous one signed in 2001 between the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and the Republika Srpska, which had envisaged close cooperation in economy, defense, education and dual citizenship for the residents, said a Serbian government statement. The agreement gives Republika Srpska, the same status with Serbia as the state of Bosnia-Herzegovina as a whole. "This agreement will stabilize the relations between countries in the region and it will promote economic, political and cultural relations between Serbia and Republika Srpska," Čavić told reporters after the signing ceremony. Koštunica added "We have long waited for this day," and insisting that the agreement would not be "a dead letter on paper," but would "live and be useful to the citizens of Serbia and Republika Srpska."
Under the Dayton peace accord, which ended the Bosnian war in 1995, the country was divided into two entities – Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, and the Republika Srpska. Each entity was accorded most of the powers of a state and the accord left room for special ties between the RS and Serbia, as well as between Croatia and the Bosnian Croats.
Representative offices

On 12 February 2009, Republika Srpska opened a new representative office in Brussels. While EU representatives were not present at the time, all top Republika Srpska officials attended the opening ceremony, saying it would advance their economic, political and cultural relations with the European Union. This notion has been strongly condemned by Bosniak leaders saying that this is further proof of Republika Srpska distancing itself from Bosnia and Herzegovina. President Rajko Kuzmanovic, on the other hand, told reporters that this move does not jeopardize Republika Srpska's place within Bosnia and Herzegovina. He added that Republika Srpska just used its constitutional right "to open up a representation office in the center of developments with European relevance." Republika Srpska already has four other representation offices - in Belgrade, Jerusalem, Moscow and Stuttgart - and there are plans to open two more in 2009, in Washington DC and Zagreb.[48] Former Croatian Prime Minister Ivo Sanader stated that the proposed Zagreb office could not be seen as the embassy of a sovereign state.[49]
Holidays
According to the Law on Holidays of Republika Srpska, passed by the National Assembly of Republika Srpska, the holidays are divided into three categories: the republic holidays, the religious ones, and the holidays not accompanied by leave of absence. The republic holidays include Republic Day (9 January), New Year's Day, International Workers' Day, Victory over Fascism Day, and Day of the General Framework Agreement for Peace in Bosnia and Herzegovina (21 November). The religious holidays include Christmas and Easter according to both the Julian and the Gregorian calendars, for respectively the Orthodox and the Catholic citizens, and Eid al-Adha and Eid ul-Fitr for the Muslims. The holidays not accompanied by leave of absence include School Day (the Feast of Saint Sava, 27 January), Day of the Army of the Republika Srpska (12 May), Interior Ministry Day (4 April), and Day of the First Serbian Uprising (14 February).[50]
The most important of the republic holidays is Republic Day, commemorating the establishment of Republika Srpska on 9 January 1992. It coincides with St. Stephen's Day according to the Julian calendar. The Orthodox Serbs also refer to the holiday as the Slava of Republika Srpska. They regard Saint Stephen The Protomartyr And Archdeacon as the patron saint of Republika Srpska. The holiday has therefore a religious dimension, being celebrated with special services in Orthodox churches.[51][52]
See also
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- History of Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Political divisions of Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Brčko District
- Radiotelevision of Bosnia-Herzegovina
References
- ↑ "Constitution of the Republika Srpska, Official Web Site of the Office of the High Representative". http://www.ohr.int/ohr-dept/legal/oth-legist/doc/rs-constitution.doc.
- ↑ Ustavni sud Bosnie i Hercegovina (2007-01-27). "Završena XXXVII plenarna sjednica (Completed 37th plenary session)". Constitutional Court of Bosnia and Herzegovina. http://www.ustavnisud.ba/bos/press/index.php?pid=1365&sta=3&pkat=125. Retrieved 2007-04-19.
- ↑ "Constitutional Court of Bosnia and Herzegovina 34th plenary session, second day". Constitutional Court of Bosnia and Herzegovina. 2007-03-31. http://www.ccbh.ba/eng/press/index.php?pid=1744&sta=3&pkat=507. Retrieved 2008-02-02.
- ↑ "Bošnjaci i Hrvati osporili grb i himnu RS-a". 2008-07-29. http://www.sarajevo-x.com/clanak/080729079.
- ↑ "Brčko as a "condominium": sovereignty in the Special District is now shared". Office of the High Representative and EU Special Representative. 2001-08-28. http://www.ohr.int/ohr-offices/brcko/gen-info/default.asp?content_id=5528. Retrieved 2007-04-19.
- ↑ "Brčko Final Award". Office of the High Representative and EU Special Representative. 1999-03-05. http://www.ohr.int/ohr-offices/brcko/default.asp?content_id=5358. Retrieved 2007-04-19.
- ↑ "Decision on Constitutional Amendments in Republika Srpska". Office of the High Representative. http://www.ohr.int/print/?content_id=7474. Retrieved 3 June 2010.
- ↑ http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/535337/Serb-Republic
- ↑ "Bosnian Serb republic leader dies". BBC News. 2007-09-30. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/europe/7021232.stm. Retrieved 2010-05-22.
- ↑ "Bosnia echoes to alarming rhetoric". BBC News. 2009-06-27. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/8121166.stm. Retrieved 2010-05-22.
- ↑ Lyon, James (2009-12-04). The New York Times. http://www.nytimes.com/2009/02/24/opinion/24iht-edlyon.1.20395827.html?_r=1. Retrieved 2010-05-22.
- ↑ Beaumont, Peter (2009-05-03). "Bosnia lurches into a new crisis". The Guardian (London). http://www.guardian.co.uk/world/2009/may/03/bosnia-war-nationalism-poor-economy. Retrieved 2010-05-22.
- ↑ "The Decision on Proclamation of the Amendments LIX-LXXX to the Constitution of the Socialist Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina" (in Serbo-Croatian). Official Gazette of the Socialist Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina 46 (21): 589–594. July 31, 1990.
- ↑ Silber, Laura (October 16, 1991). "Bosnia Declares Sovereignty". The Washington Post: A29. ISSN 0190-8286. http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-srv/inatl/longterm/balkans/stories/independence101691.htm.
- ↑ Kecmanović, Nenad (September 23, 1999). "Dayton Is Not Lisbon". NIN. ex-YU press. http://www.ex-yupress.com/nin/nin117.html. Retrieved 2009-05-11.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 "The Decision on Establishment of the Assembly of the Serb People in Bosnia and Herzegovina" (in Serbian). Official Gazette of the Serb People in Bosnia and Herzegovina 1 (1): 1. January 15, 1992.
- ↑ http://books.google.com/books?id=_RSi4WL0RP8C&pg=PA12&lpg=PA12
- ↑ "The Declaration of Proclamation of the Republic of the Serb People of Bosnia and Herzegovina" (in Serbian). Official Gazette of the Serb People in Bosnia and Herzegovina 1 (2): 13–14. January 27, 1992.
- ↑ "The Constitution of the Serbian Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina" (in Serbian). Official Gazette of the Serb People in Bosnia and Herzegovina 1 (3): 17–26. March 16, 1992.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Kreća, Milenko (11 July 1996). "The Legality of the Proclamation of Bosnia and Herzegovina's Independence in Light of the Internal Law of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia" and "The Legality of the Proclamation of Independence of Bosnia and Herzegovina in the Light of International Law" in "Dissenting Opinion of Judge Kreća" (PDF). Application of the Convention on the Prevention and Punishment of the Crime of Genocide, Preliminary Objections, Judgment, I. C. J. Reports 1996 (The Hague: The Registry of the International Court of Justice): pp. 711-747. ISSN 0074-4441.
- ↑ The Balkans: A Post-Communist History (2007, New York: Routledge) Robert Bideleux & Ian Jeffries, p. 343
- ↑ http://books.google.com/books?id=AYQLyuN4_twC&pg=PA249
- ↑ "The Decision on Proclamation of the Serbian Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina" (in Serbian). Večernje novosti. Tanjug (Belgrade: Novosti AD). April 8, 1992. ISSN 0350-4999.
- ↑ "The Amendments VII and VIII to the Constitution of the Republika Srpska" (in Serbian). Official Gazette of the Republika Srpska 1 (15): 569. September 29, 1992.
- ↑ "The General Framework Agreement for Peace in Bosnia and Herzegovina". OHR. http://www.ohr.int/dpa/default.asp?content_id=380.
- ↑ "Constitution of Republika Srpska". The Constitutional Court of Republika Srpska. http://www.ustavnisud.org/html/pravno%20utemeljenje/ustav%20e.html.
- ↑ UNESCO (1998). "Review of the education system in the Republika Srpska". http://www.unesco.org/education/educprog/erd/english/com/docs/eur/bih2/srp_cont.html. Retrieved 2009-01-10.
- ↑ https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/bk.html
- ↑ "Written statement submitted by the Society for Threatened Peoples to the Commission of Human Rights; Sixtieth session Item 11 (d) of the provisional agenda". United Nations. February 26, 2004. pp. 2. http://www.unhchr.ch/Huridocda/Huridoca.nsf/0/116959be7b8cf279c1256e5a003b5e6b?Opendocument.
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 Revidirana strategija Bosne i Hercegovine za provedbu Aneksa VII Dejtonskog mirovnog sporazuma. Ministry for Human Rights and Refugees of Bosnia and Herzegovina. October 2008.
- ↑ "The Continuing Challenge Of Refugee Return In Bosnia & Herzegovina". Crisis Group. December 13, 2002. http://www.crisisgroup.org/home/index.cfm?id=1473&l=1.
- ↑ "UN condemns Serb 'sickness'". BBC. May 8, 2001. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/europe/1318283.stm. Retrieved 2010-01-04.
- ↑ "Serbs block Bosnia mosque ceremony". BBC. May 6, 2001. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/europe/1315262.stm. Retrieved 2010-01-04.
- ↑ "Helsinki Commission Releases U.S. Statement on Tolerance and Non-Discrimination at OSCE Human Dimension Implementation Meeting". Helsinki Commission. September 20, 2001. http://www.csce.gov/index.cfm?FuseAction=UserGroups.Home&ContentRecord_id=188&ContentType=P&ContentRecordType=P&UserGroup_id=62&Subaction=ByDate&IsTextOnly=True&CFID=18849146&CFTOKEN=53.
- ↑ "7th Session of the UN Human Rights Council" (PDF). Society for Threatened Peoples. February 21, 2008. pp. 2. http://forum-menschenrechte.de/cms/upload/PDF/ab_05-2008/aides_memoires/Bosnia_Herzegowina-GfbV.pdf.
- ↑ "Republika Srpska in Figures 2009". Banja Luka: Republika Srpska Institute of Statistics. 2009. http://www.rzs.rs.ba/Publikacije/RSuBrojkama/RSuBrojkama2009.pdf. Retrieved 5 July 2010.
- ↑ 37.0 37.1 "Bosnian Territory Opens Doors for Business". The Wall Street Journal. http://online.wsj.com/article/SB117918783695002652.html?mod=googlenews_wsj. Retrieved 2007-06-17.
- ↑ "Investicija za preporod privrede BiH". Nezavisine novine. 2007-01-25. http://www.nezavisne.com/vijesti.php?vijest=4941&meni=2. Retrieved 2007-04-19.
- ↑ "CEZ signs contract on energy project in Bosnia". Prague Daily Monitor. 2007-05-17. http://launch.praguemonitor.com/en/86/czech_business/6620/. Retrieved 2007-06-17.
- ↑ Republika Srpska Institute of Statistics (December 2005). "External Trade Statistics Release" (PDF). http://www.rzs.rs.ba/Saopstenja/TrgovinaSPOLJNA/decembar05.pdf. Retrieved 2007-04-19.
- ↑ Republika Srpska Institute of Statistics (December 2006). "External Trade Statistics Release" (PDF). http://www.rzs.rs.ba/Saopstenja/TrgovinaSPOLJNA/SpoljnaTrgovinaDecembar06.pdf. Retrieved 2007-04-19.
- ↑ Republika Srpska Institute of Statistics (February 2007). "External Trade Statistics Release" (PDF). http://www.rzs.rs.ba/Saopstenja/TrgovinaSPOLJNA/SpoljnaTrgovinaFebruar07.pdf. Retrieved 2007-04-19.
- ↑ Republika Srpska Institute of Statistics (February 2006). "External Trade Statistics Release" (PDF). http://www.rzs.rs.ba/Saopstenja/TrgovinaSPOLJNA/februar06.pdf. Retrieved 2007-04-19.
- ↑ Republika Srpska Institute of Statistics (December 2008). "External Trade Statistics Release" (PDF). http://www.rzs.rs.ba/Saopstenja/TrgovinaSPOLJNA/SpoljnaTrgovinaDecembar08.pdf. Retrieved 2009-05-29.
- ↑ http://www.ohr.int/ohr-dept/rule-of-law-pillar/prc/prc-statements/default.asp?content_id=38500
- ↑ http://www.stratfor.com/bosnia_herzegovina_dodik_struts_his_stuff
- ↑ http://www.rferl.org/content/Article/1061931.html
- ↑ http://balkaninsight.com/en/main/news/16672/
- ↑ http://www.vlada.hr/english/premijer/aktualnosti/novosti/2007/listopad/predsjednik_vlade_s_visokim_predstavnikom_za_bosnu_i_hercegovinu_lajcakom
- ↑ "Zakon o praznicima Republike Srpske" (in Serbian). Zakoni. National Assembly of Republika Srpska. July 27, 2005. http://www.narodnaskupstinars.net/lat/zakoni/zakon.php?id_zakona=110. Retrieved 2009-04-10.
- ↑ "President of the Republic organises a reception on the occasion of the Day of the Republic and Patron Saint’s Day of the Republic of Srpska". Announcements. Official presentation of the Republic of Srpska President. January 9, 2009. http://www.predsjednikrs.net/en_l/news.php?id=284. Retrieved 2009-04-10.
- ↑ "Прослављена слава Републике Српске - Свети архиђакон Стефан" (in Serbian). The Serbian Orthodox Church. January 9, 2008. http://www.spc.rs/sr/proslavljena_slava_republike_srpske_sveti_arhidjakon_stefan. Retrieved 2009-04-10.
External links
- Entity Government
- Entity President
- Entity National Assembly
- Radio Television of Republic of Srpska RTRS (TV)
- RS Institute of Statistics
- Public Health Institute of Republic of Srpska
- RS Directorate for Privatization
- For persons unaccounted for in connection with the conflict on the territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina, International Committee of the Red Cross.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cite error: <ref> tags exist for a group named "note", but no corresponding <references group="note"/> tag was found

