Spore

In biology, a spore is a reproductive structure that is adapted for dispersal and surviving for extended periods of time in unfavorable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many bacteria, plants, algae, fungi and some protozoans.[1] A chief difference between spores and seeds as dispersal units is that spores have very little stored food resources compared with seeds.
Spores are usually haploid and unicellular and are produced by meiosis in the sporangium by the sporophyte. Once conditions are favorable, the spore can develop into a new organism using mitotic division, producing a multicellular gametophyte, which eventually goes on to produce gametes.
Two gametes fuse to create a new sporophyte. This cycle is known as alternation of generations, but a better term is "biological life cycle", as there may be more than one phase and so it cannot be a direct alternation. Haploid spores produced by mitosis (known as mitospores) are used by many fungi for asexual reproduction.
Many ferns, especially those adapted to dry conditions, produce diploid spores. This form of asexual reproduction is called apogamy. It is a form of apomixis.
Spores are the units of asexual reproduction, because a single spore develops into a new organism. By contrast, gametes are the units of sexual reproduction, as two gametes need to fuse to create a new organism.
Contents |
Definition
The term spore derives from the ancient Greek word σπορα ("spora"), meaning a seed.
In common parlance, the difference between a "spore" and a "gamete" (both together called gonites) is that a spore will germinate and develop into a sporeling, while a gamete needs to combine with another gamete before developing further. However, the terms are somewhat interchangeable when referring to gametes.
A chief difference between spores and seeds as dispersal units is that spores have little food storage compared with seeds, and thus require more favorable conditions in order to successfully germinate. (This is not without its exceptions, however: many orchid seeds, although multicellular, are microscopic and lack endosperm, and spores of some fungi in the Glomeromycota commonly exceed 300 µm in diameter.)[2] Seeds, therefore, are more resistant to harsh conditions and require less energy to start mitosis. Spores are produced in large numbers to increase the chance of a spore surviving in a number of notable examples.
Classification
Spores can be classified in several ways:
By spore-producing structure

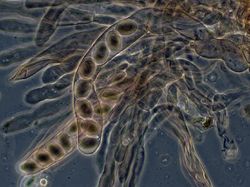


In fungi and fungus-like organisms, spores are often classified by the structure in which meiosis and spore production occurs. Since fungi are often classified according to their spore-producing structures, these spores are often characteristic of a particular taxon of the fungi.
- Sporangiospores: spores produced by a sporangium in many fungi such as zygomycetes.
- Zygospores: spores produced by a zygosporangium, characteristic of zygomycetes.
- Ascospores: spores produced by an ascus, characteristic of ascomycetes.
- Basidiospores: spores produced by a basidium, characteristic of basidiomycetes.
- Aeciospores: spores produced by a aecium in some fungi such as rusts or smuts.
- Urediospores: spores produced by a uredinium in some fungi such as rusts or smuts.
- Teliospores: spores produced by a telium in some fungi such as rusts or smuts.
- Oospores: spores produced by a oogonium, characteristic of oomycetes.
- Carpospores: spores produced by a carposporophyte, characteristic of red algae.
- Tetraspores: spores produced by a tetrasporophyte, characteristic of red algae.
By function
- Chlamydospores: thick-walled resting spores of fungi produced to survive unfavorable conditions.
- Parasitic fungal spores may be classified into internal spores, which germinate within the host, and external spores, also called environmental spores, released by the host to infest other hosts.[3]
By origin during life cycle
- Meiospores: spores produced by meiosis; they are thus haploid, and give rise to a haploid daughter cell(s) or a haploid individual. Examples are the precursor cells of gametophytes of seed plants found in flowers (angiosperms) or cones (gymnosperms).
- Microspores: meiospores that give rise to a male gametophyte, (pollen in seed plants).
- Megaspores (or macrospores): meiospores that give rise to a female gametophyte, (an ovule in seed plants).
- Mitospores (or conidia, conidiospores): spores produced by mitosis; they are characteristic of Ascomycetes. Fungi in which only mitospores are found are called “mitosporic fungi” or “anamorphic fungi”, and are previously classified under the taxon Deuteromycota (See Teleomorph, anamorph and holomorph).
By motility
Spores can be differentiated by whether they can move or not.
- Zoospores: mobile spores that move by means of one or more flagella, and can be found in some algae and fungi.
- Aplanospores: immobile spores that may nevertheless potentially grow flagella.
- Autospores: immobile spores that cannot develop flagella.
- Ballistospores: spores that are actively discharged from the body of the fungal fruiting body. Most basidiospores are also ballistospores, and another notable example is spores of Pilobolus.
- Statismospores: spores that are not actively discharged from the fungal fruiting body. Examples are puffballs.
Anatomy
Under high magnification, spores can be categorized as either monolete spores or trilete spores. In monolete spores, there is a single line on the spore indicating the axis on which the mother spore was split into four along a vertical axis. In trilete spores, all four spores share a common origin and are in contact with each other, so when they separate, each spore shows three lines radiating from a center pole.
Vascular plant spores are always haploid. Vascular plants are either homosporous (or isosporous) or heterosporous. Plants that are homosporous produce spores of the same size and type. Heterosporous plants, such as spikemosses, quillworts, and some aquatic ferns produce spores of two different sizes: the larger spore in effect functioning as a "female" spore and the smaller functioning as a "male".
Trilete spores
Trilete spores, formed by the dissociation of a spore tetrad, are taken as the earliest evidence of life on land,[4] dating to the mid-Ordovician (early Llanvirn, ~470 million years ago).[5]
Dispersal
In fungi, both asexual and sexual spores or sporangiospores of many fungal species are actively dispersed by forcible ejection from their reproductive structures. This ejection ensures exit of the spores from the reproductive structures as well as travelling through the air over long distances. Many fungi thereby possess specialized mechanical and physiological mechanisms as well as spore-surface structures, such as hydrophobins, for spore ejection. These mechanisms include, for example, forcible discharge of ascospores enabled by the structure of the ascus and accumulation of osmolytes in the fluids of the ascus that lead to explosive discharge of the ascospores into the air.[6] The forcible discharge of single spores termed ballistospores involves formation of a small drop of water (Buller's drop), which upon contact with the spore leads to its projectile release with an initial acceleration of more than 10,000 g.[7] Other fungi rely on alternative mechanisms for spore release, such as external mechanical forces, exemplified by puffballs. Attracting insects, such as flies, to fruiting structures, by virtue of their having lively colours and a putrid odour, for dispersal of fungal spores is yet another strategy, most prominently used by the stinkhorns.
In the case of spore-shedding vascular plants such as ferns, wind distribution of very light spores provides great capacity for dispersal. Also, spores are less subject to animal predation than seeds because they contain almost no food reserve; however they are more subject to fungal and bacterial predation. Their chief advantage is that, of all forms of progeny, spores require the least energy and materials to produce.
In the spikemoss Selaginella lepidophylla, dispersal is achieved in part by an unusual type of diaspore, a tumbleweed.[8]
See also
- Alternation of generations
- Bioaerosol
- Sporophyte
- Endospore
- Fern
- Auxiliary cell
- Cryptospores
References
- ↑ Spore FAQ - Aerobiology Research Laboratory
- ↑ INVAM
- ↑ [1].
- ↑ Gray, J. (1985). "The Microfossil Record of Early Land Plants: Advances in Understanding of Early Terrestrialization, 1970-1984". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences (1934-1990) 309 (1138): 167–195. doi:10.1098/rstb.1985.0077. http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0080-4622(19850402)309%3A1138%3C167%3ATMROEL%3E2.0.CO%3B2-E. Retrieved 2008-04-26.
- ↑ Wellman, C.H., Gray, J. (2000). "The microfossil record of early land plants". Philosophical Transactions: Biological Sciences 355 (1398): 717–732. doi:10.1098/rstb.2000.0612. http://www.journals.royalsoc.ac.uk/index/2NWB35JF2C34PJHG.pdf. Retrieved 2008-02-13.
- ↑ Trail F. (2007). "Fungal cannons: explosive spore discharge in the Ascomycota". FEMS Microbiology Letterrs 276: 12–8. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00900.x. PMID 17784861.
- ↑ Pringle A, Patek SN, Fischer M, Stolze J, Money NP. (2005). "The captured launch of a ballistospore". Mycologia 97: 866–71. doi:10.3852/mycologia.97.4.866. PMID 16457355.
- ↑ "False Rose of Jericho - Selaginella lepidophyllaFalse Rose of Jericho - Selaginella lepidophylla". [www.plant-and-flower-guide.com Plant- and Flowerguide. February 2009. http://www.plant-and-flower-guide.com/rose-of-jericho.html. Retrieved 1 February 2010.
Gallery
 Microscopic view of dehisced fern sporangia (no spores are visible) |
 Microscopic view of Equisetum spores |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
