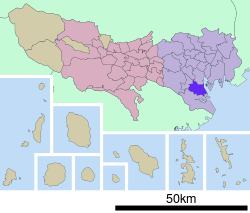
Shinagawa, Tokyo
| Shinagawa 品川 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| — Special ward — | |||
| 品川区 · Shinagawa City | |||
|
|
|||
|
|||
 |
|||
 Shinagawa
|
|||
| Coordinates: | |||
| Country | Japan | ||
| Region | Kantō | ||
| Prefecture | Tokyo | ||
| Area | |||
| - Total | 22.77 km2 (8.8 sq mi) | ||
| Population (2008) | |||
| - Total | 344,461 | ||
| - Density | 15,740/km2 (40,766.4/sq mi) | ||
| Time zone | Japan Standard Time (UTC+9) | ||
| Website | Shinagawa (Japanese) | ||
Shinagawa (品川区 Shinagawa-ku) is one of the 23 special wards of Tokyo, Japan. In English, it is called Shinagawa City. The ward is home to nine embassies.
As of 2008, the ward has an estimated population of 344,461 and a density of 15740 persons per km². The total area is 22.72 km².
Contents |
Geography

Shinagawa includes natural uplands and lowlands, as well as reclaimed land. The uplands are the eastern end of the Musashino hills. They include Shiba Shiroganedai north of the Meguro River, Megurodai between the Meguro and Tachiai Rivers, and Ebaradai south of the Tachiai River.
The ward lies on Tokyo Bay. Its neighbors on land are all special wards of Tokyo: Kōtō to the east, Minato to the north, Meguro to the west, and Ōta to the south.
The ward consists of five districts:
- the Shinagawa district, including the former Shinagawa post on the Tōkaidō
- the Ōsaki district, formerly a town, stretching from Ōsaki Station to Gotanda and Meguro Stations
- the Ebara district, formerly a town of that name
- the Ōi district, previously the town
- the Yashio district, consisting of reclaimed land
History
Most of Tokyo east of the Imperial Palace is reclaimed land. A large portion of reclamation happened during the Edo period. The ward was founded on March 15, 1947 through the administrative amalgamation of the former Ebara Ward with the former Shinagawa Ward. Both Ebara Ward and Shinagawa Ward had been created in 1932, with the outward expansion of the municipal boundaries of the Tokyo City following the 1923 Great Kantō Earthquake.
In the Edo period, Shinagawa was the first post town a traveler would reach after setting out from Nihombashi on the Tōkaidō highway from Edo to Kyoto. The post-town function is retained today with several large hotels near the train station offering 6,000 hotel rooms, the largest concentration in the city. The Tokugawa shogunate maintained the Suzugamori execution grounds in Shinagawa. The Tōkaidō Shinkansen began serving Shinagawa Station from 2003, and the nearby Shinagawa Intercity office complex will be served by a new subway station in a few years' time.
Politics and government
Shinagawa is run by a city assembly of 40 elected members. The mayor as of 2007 is Takeshi Hamano, an independent. Liberal Democratic Party together with New Komeito currently forms government.
- Shinagawa local election, 2007
- Shinagawa mayoral election, 2006
Companies based in Shinagawa

Many companies are headquartered in Shinagawa. Isuzu, an auto manufacturer;[1] JTB Corporation, a major travel agency;[2] Namco Bandai Holdings;[3] Namco Bandai Games;[4] Banpresto;[5] Honda brand Acura; NSK Ltd., a bearing maker; [6] Imagica, a media post-production company; and Pola Cosmetics all have their headquarters within Shinagawa Ward.
Japan Airlines (JAL), the head office of its subsidiary JAL Hotels, and registered offices of JAL Express and JALways are located in the Tennōzu Isle area.[7][8][9][10][11][12] Prior to its dissolution, JAL subsidiary Japan Asia Airways was also headquartered in the JAL Building.[13]
Other companies maintain branch offices or research facilities in Shinagawa. Sony operates the Gotenyama Technology Center and the Osaki East Technology Center in Shinagawa.[14] Sony used to have its headquarters in Shinagawa.[15] Sony moved to Minato, Tokyo around the end of 2006 and closed the Osaki West Technology Center in Shinagawa around 2007.[16][17] Adobe Systems maintains its Japan headquarters on the 19th Floor of Gate City Ohsaki near Ōsaki Station,[18] while Siemens AG has its Japan offices in Takanawa Park Tower.[19] Phoenix Technologies operates its Japan office on the 8th floor of the Gotanda NN Building in Gotanda.[20] Siemens Japan and Philips also have offices in Shinagawa.
At one time Air Nippon had its headquarters in Shinagawa.[21]
Places
- The Institute for Research in Human Happiness
- National Institute of Japanese Literature
- Shinagawa Shrine
- Suzugamori Execution Grounds (Edo period)
- TV Tokyo Tennozu Studios
Education
Universities
- Hoshi University
- Rissho University
- Seisen University
- Showa University
- Sugino Women's University
Special colleges
Tokyo Metropolitan Government Board of Education operates two special colleges in Shinagawa:
- Tokyo Metropolitan College of Technology [1]
- Tokyo Metropolitan College of Industrial Technology [2]
Primary and secondary
Public elementary and junior high schools are operated by the Shinagawa Ward Board of Education. Public high schools are operated by the Tokyo Metropolitan Government Board of Education.
Public high schools in Shinagawa include:
Transportation
Important train stations

Shinagawa Station in neighboring Minato also serves Shinagawa, and is a stop on the high-speed Tōkaidō Shinkansen line.
- Gotanda Station
- Meguro Station
- Ōsaki Station
- Ōimachi Station
Rail
- East Japan Railway Company (JR East)
- Yamanote Line: Ōsaki, Gotanda, Meguro Stations
- Keihin-Tōhoku Line: Ōimachi Station
- Saikyō Line: Ōsaki Station
- Tōkaidō Main Line: does not stop in Shinagawa
- Yokosuka Line: Nishi-Ōi Station
- Shōnan-Shinjuku Line: Ōsaki, Nishi-Ōi Stations
- Tokyu Corporation (Tōkyū)
- Tōkyū Meguro Line: Meguro, Fudo-mae, Musashi-Koyama, Nishi-Koyama Stations
- Tōkyū Ōimachi Line: Shimo-Shinmei, Togoshi Koen, Nakanobe, Ebaramachi, Hatanodai Stations
- Tōkyū Ikegami Line: Gotanda, Ōsaki-Hirokoji, Togoshi Ginza, Ebara Nakanobu, Hatanodai Stations
- Tokyo Waterfront Area Rapid Transit: Tennōzu Isle, Shinagawa Seaside, Ōimachi, Ōsaki Stations
- Tokyo Monorail: Tennōzu Isle, Ōi Keibajō-mae Stations
- Keihin Electric Express Railway (Keikyū)
- Main Line: Kita-Shinagawa, Shin-Bamba, Aomono Yokocho, Samezu, Tachiaikawa, Ōmori-Kaigan Stations
- Tokyo Metro
- Namboku Line: Meguro Station
- Tokyo Metropolitan Bureau of Transportation
- Mita Line: Meguro Station
- Asakusa Line: Gotanda, Togoshi, Nakanobu Stations
Road
- Shuto Expressway
- No. 1 Haneda Route (Edobashi JCT - Iriya)
- No.2 Meguro Route (Ichinohashi JCT - Togoshi)
- Bayshore Route (Kawasaki-Ukishima JCT - Koya)
- National highways of Japan
- Route 1
- Route 15
- Route 357
Shinagawa is also home to the main motor vehicle registration facility for central Tokyo (located east of Samezu Station). As a result, many license plates in Tokyo are labeled with the name "Shinagawa."
Events
The abduction of Kiyoshi Kariya by the Aum Shinrikyo cult occurred in Shinagawa. On February 28, 1995, cult members abducted Kariya, a public employee, and took him to their facility in Kamikuishiki, Yamanashi. Cult members, including Ikuo Hayashi, injected Kariya with sodium thiopental in order to discover the location of the man's sister (a former Aum member), but Kariya unexpectedly died.[22]
Sister cities
Shinagawa has sister-city relationships with Auckland in New Zealand, Geneva in Switzerland, and Portland, Maine in the United States.[23]
 Geneva, Switzerland
Geneva, Switzerland Auckland, New Zealand[24]
Auckland, New Zealand[24] Harbin, People's Republic of China
Harbin, People's Republic of China Hayakawa, Japan
Hayakawa, Japan Portland, Maine
Portland, Maine
References
- ↑ "Corporate Profile." Isuzu. Retrieved on December 8, 2008.
- ↑ "Company Profile." JTB Corporation. Retrieved on September 16, 2009.
- ↑ "Corporate Data." Namco Bandai Holdings. Retrieved on December 8, 2008.
- ↑ "Corporate Overview." Namco Bandai Games. Retrieved on March 16, 2010.
- ↑ "Company Outline." Banpresto. February 18, 2008. Retrieved on March 16, 2010.
- ↑ "Corporate Data." NSK Ltd.. Retrieved on December 12, 2009.
- ↑ "Information & Reservations." Japan Airlines. Retrieved on December 8, 2008.
- ↑ "Company Profile." Japan Airlines. Retrieved on December 8, 2008.
- ↑ "Company Profile." JALways. Retrieved on May 19, 2009.
- ↑ "会社案内." JAL Express. Retrieved on May 19, 2009.
- ↑ "Company Profile." Japan Airlines. Retrieved on December 8, 2008.
- ↑ "会社概要." JAL Hotels. Retrieved on February 5, 2010. "本社 : 〒140-0002 東京都品川区東品川2-4-11 JALビル13F."
- ↑ "会社概要." Japan Asia Airways. October 25, 2005. Retrieved on May 20, 2009.
- ↑ "Access & Map." Sony. Retrieved on January 19, 2009.
- ↑ "Corporate Data." Sony. September 9, 2008. Retrieved on January 19, 2009.
- ↑ Suzuki, Kyoko. "Sony Considers Sale of Properties Including Former Headquarters." Bloomberg. August 3, 2006. Retrieved on January 19, 2009.
- ↑ "Sony to close symbol of TV business.." Kyodo News International. February 1, 2007. Retrieved on January 19, 2009.
- ↑ "Locations." Adobe Systems. Retrieved on December 8, 2008.
- ↑ "About us > Locations." Siemens K.K.. Retrieved on December 8, 2008.
- ↑ "Worldwide Corporate Offices." Phoenix Technologies. Retrieved on May 6, 2009.
- ↑ "World Airline Directory." Flight International. April 1-7, 1998. "All Nippon Airways" 45.
- ↑ The Aum Supreme Truth Terrorist Organization - The Crime library
- ↑ 国際交流事業の紹介 | 品川区 ("Introduction to International Relations | Shinagawa") Retrieved on March 10, 2009
- ↑ "Sister Cities". Consulate-General of Japan in Auckland. Embassy of Japan. Archived from the original on 2008-12-08. http://www.webcitation.org/5cvev6xKH. Retrieved 2008-12-09.
External links
- Shinagawa City official website in English
- Shinagawa City (Japanese)
- Shinagawa on Wikitravel
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
