Scania County
| Skåne Skåne län |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| — County of Sweden — | |||
|
|||
| Country | Sweden | ||
| Capital | Malmö | ||
| Government | |||
| - Governor | Göran Tunhammar | ||
| - Council | Skåne Regional Council | ||
| Area[1] | |||
| - Total | 11,027 km2 (4,257.5 sq mi) | ||
| Population (2004) | |||
| - Total | 1,156,070 | ||
| - Density | 104.8/km2 (271.5/sq mi) | ||
| Time zone | CET (UTC+1) | ||
| - Summer (DST) | CEST (UTC+2) | ||
| GDP/ Nominal | SEK 278,254 million (2004) | ||
| GDP per capita | SEK 244,000 | ||
| NUTS Region | SE224 | ||
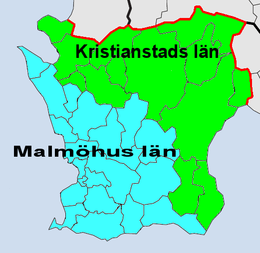
Skåne County (Skåne län) is the southernmost administrative county or län, of Sweden, basically corresponding to the historical province Scania. It borders the counties of Halland, Kronoberg and Blekinge. The seat of residence for the Skåne Governor is the town of Malmö. The headquarters of Region Skåne is the town of Kristianstad.[2]
The present county was created in 1997 when Kristianstad County and Malmöhus County were merged.
Scania County covers around 3% of Sweden's total area, but its population of 1,200,000 comprises 13% of Sweden's total population.
Contents |
Endonym and exonym
When the new county was established in 1997, it was decided to name it after the historical province, and it was given the name Skåne län. The counties of Sweden are districts of the central government and exonyms are seldom used for such units. The most common name used in English is Skåne County.[3][4][5]. It is of course possible to use the exonyms Scania County or County of Scania if one prefers that.
Heraldry
The coat of arms for Skåne County is the same as for the province of Scania only with the tinctures reversed and the crown, beak and tongue of the Griffin in the same color. When the arms is shown with a royal crown it represents the County Administrative Board, which is the regional presence of (royal) government authority. Blazon: "Gules, a Griffin's head erased Or, crowned and armed the same".
Provinces
Skåne County is the administrative equivalent of the province of Scania, but it also includes an insignificant part of the province Halland.
Administration
The seat of residence for the Governor or Landshövding is the town of Malmö. The County Administrative Board is a Government Agency headed by a Governor. See List of Skåne Governors.
The two former administrative counties of the province of Scania shown on the map, Kristianstad County and Malmöhus County, which were established in 1719 were merged together in 1997, forming the present county with boundaries that are almost identical to the boundaries of the province.
County council
Skåne Regional Council (Region Skåne) is an evolved County Council, which was established in 1999 when the County Councils of the former counties were amalgamated. Its main responsibilities are for the public healthcare system and public transport. In addition, it has for a trial period assumed certain tasks from the County Administrative Board.
Its county or regional assembly is the highest political body in the region and its members are elected by the electorate,[6] as opposed to the county administrative board, that guards the national interests in the county under the chairmanship of the county governor (landshövding in Swedish).
Municipalities
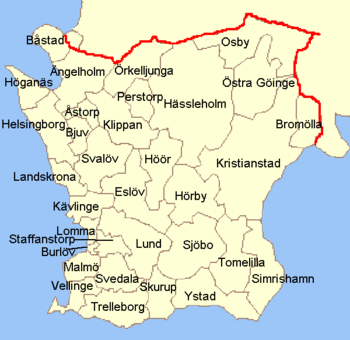
Skåne County is subdivided into 33 municipalities[7] (kommuner in Swedish), the largest being Malmö Municipality (280,000 inhabitants), Helsingborg Municipality (124,000), Lund Municipality (103,000 inhabitants) and Kristianstad Municipality (75,000 inhabitants). The municipalities have municipal governments, similar to city commissions, and are further divided into parishes. The parish division is traditionally used by the Church of Sweden, but also serves as a divisioning measure for Swedish census and elections.
|
|
|
Electoral districts
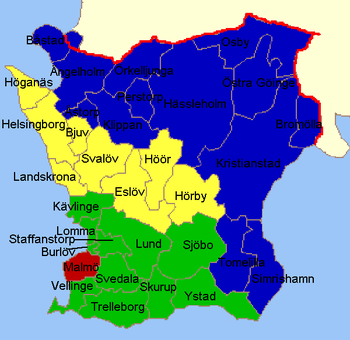
The county is divided into four parliamentary constituences or electoral districts, electing 45 of the 349 members of the Riksdag, the Parliament of Sweden. Each district is made up of one or more municipalities.
The political parties are represented by the following number of MPs from Skåne County after the Swedish general election, 2010:
- Moderate Party 16
- Swedish Social Democratic Party 12
- Liberal People's Party 4
- Green Party (Sweden) 4
- Sweden Democrats 4
- Centre Party (Sweden) 2
- Christian Democrats (Sweden) 2
- Left Party (Sweden) 1
Localities in order of size
The ten most populous localities of Skåne County as defined by Statistics Sweden 2005:
| # | Locality | Population |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Malmö | 258,020 |
| 2 | Helsingborg | 91 457 |
| 3 | Lund | 76 188 |
| 4 | Kristianstad | 33 083 |
| 5 | Landskrona | 28 670 |
| 6 | Trelleborg | 25 643 |
| 7 | Ängelholm | 22 537 |
| 8 | Hässleholm | 22 548 |
| 9 | Ystad | 17 286 |
| 10 | Eslöv | 16 551 |
Transport
The motorway built between Malmö and Lund in 1953 was the first motorway in Sweden. With the opening of the Oresund Bridge between Malmö and Copenhagen (the longest combined road and rail bridge in Europe) in 2000, the Swedish motorways were linked with European route E20 in Denmark, and the two countries' railway systems were physically connected. Before the bridge was built there were train ferries operated between Helsingborg and Helsingør. There are also train ferries to and from Germany and Poland.
Scania has three major public airports, Malmö Airport, Ängelholm-Helsingborg Airport and Kristianstad Airport. One of the oldest airports in the world still in use is located in Scania, namely Ljungbyhed Airport, in operation since 1910. Starting in 1926, the Swedish Air Force used the airport for flight training, and up until the military school was moved to the nearby Ängelholm F10 Wing in 1997, the airport was extremely busy. In the late 1980s, it was Sweden's busiest airport, with a record high of more than 1,400 take-offs and landings per day.[8]
The major ports of Scania are Copenhagen Malmö Port and Helsingborg Harbour. Ferry connections across the Baltic Sea operate from several smaller ports as well.
References
- ↑ http://www.sna.se/webbatlas/lan/skane.html Sveriges Nationalatlas. Retrieved 2 April 2008
- ↑ About Region Skåne. Region Skåne. Retrieved 10 April 2008.
- ↑ http://www.lansstyrelsen.se/skane/Om_Lansstyrelsen/In+English/
- ↑ http://www.sna.se/webatlas/county/skane.html
- ↑ http://www.polisen.se/en/English/Contact-the-Swedish-Police/
- ↑ Region Skåne. Democracy-Increased autonomy. Official site. Retrieved 24 August 2007.
- ↑ Region Skåne.Municipalities in Skåne. Official site. Retrieved 24 August 2007.
- ↑ Ljungbyhed airport - ESTL. Fact sheet created by Lund University School of Aviation. Retrieved 22 January 2007.
External links
|
|||||||
|
||||||||||||||