p-n junction

A p–n junction is formed by joining p-type and n-type semiconductors together in very close contact. The term junction refers to the boundary interface where the two regions of the semiconductor meet. If they were constructed of two separate pieces this would introduce a grain boundary, so p–n junctions are created in a single crystal of semiconductor by doping, for example by ion implantation, diffusion of dopants, or by epitaxy (growing a layer of crystal doped with one type of dopant on top of a layer of crystal doped with another type of dopant).
P-N junctions are elementary "building blocks" of almost all semiconductor electronic devices such as diodes, transistors, solar cells, LEDs, and integrated circuits; they are the active sites where the electronic action of the device takes place. For example, a common type of transistor, the bipolar junction transistor, consists of two p–n junctions in series, in the form n–p–n or p–n–p.
The discovery of the p–n junction is usually attributed to American physicist Russell Ohl of Bell Laboratories.[1]
Schottky junction is a special case of a p-n junction, where metal serves the role of the n-type semiconductor.
Contents |
Manufacture
Normally, p–n junctions are manufactured from a single crystal with different dopant concentrations diffused across it. Creating a semiconductor from two separate pieces of material would introduce a grain boundary between the metals which severely inhibits its utility by scattering the electrons and holes.. However, in the case of solar cells, polycrystalline silicon is often used to reduce expense, despite the lower efficiency.
Properties of a p-n junction
The p–n junction possesses some interesting properties which have useful applications in modern electronics. A p-doped semiconductor is relatively conductive. The same is true of an n-doped semiconductor, but the junction between them is a nonconductor. This nonconducting layer, called the depletion zone, occurs because the electrical charge carriers in doped n-type and p-type silicon (electrons and holes, respectively) diffuse into the other type of material (i.e. electrons in p-type and holes in n-type) and eliminate each other in a process called recombination. By manipulating this non-conductive layer, p–n junctions are commonly used as diodes: circuit elements that allow a flow of electricity in one direction but not in the other (opposite) direction. This property is explained in terms of forward bias and reverse bias, where the term bias refers to an application of electric voltage to the p–n junction.
Equilibrium (zero bias)
In a p–n junction, without an external applied voltage, an equilibrium condition is reached in which a potential difference is formed across the junction. This potential difference is called built-in potential 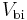 .
.
After joining p-type and n-type semiconductors, electrons near the p–n interface tend to diffuse into the p region. As electrons diffuse, they leave positively charged ions (donors) in the n region. Similarly, holes near the p–n interface begin to diffuse into the n-type region leaving fixed ions (acceptors) with negative charge. The regions nearby the p–n interfaces lose their neutrality and become charged, forming the space charge region or depletion layer (see figure A).
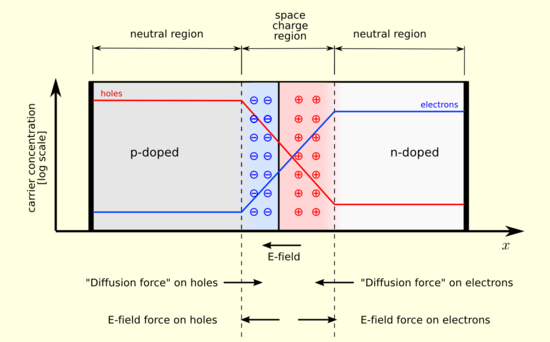
The electric field created by the space charge region opposes the diffusion process for both electrons and holes. There are two concurrent phenomena: the diffusion process that tends to generate more space charge, and the electric field generated by the space charge that tends to counteract the diffusion. The carrier concentration profile at equilibrium is shown in figure A with blue and red lines. Also shown are the two counterbalancing phenomena that establish equilibrium.
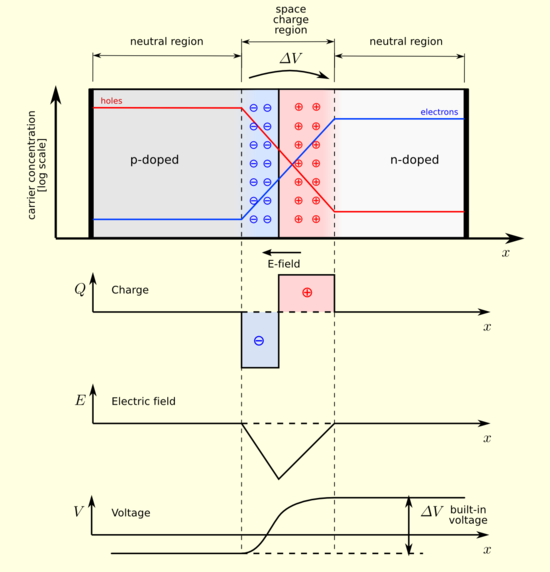
The space charge region is a zone with a net charge provided by the fixed ions (donors or acceptors) that have been left uncovered by majority carrier diffusion. When equilibrium is reached, the charge density is approximated by the displayed step function. In fact, the region is completely depleted of majority carriers (leaving a charge density equal to the net doping level), and the edge between the space charge region and the neutral region is quite sharp (see figure B, Q(x) graph). The space charge region has the same charge on both sides of the p–n interfaces, thus it extends farther on the less doped side (the n side in figures A and B).
Forward bias
In forward bias, the p-type is connected with the positive terminal and the n-type is connected with the negative terminal.
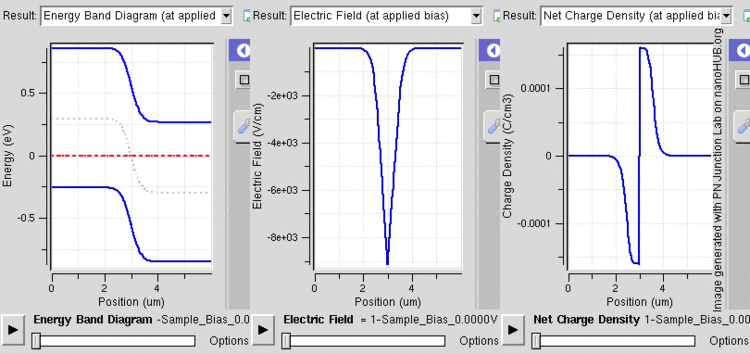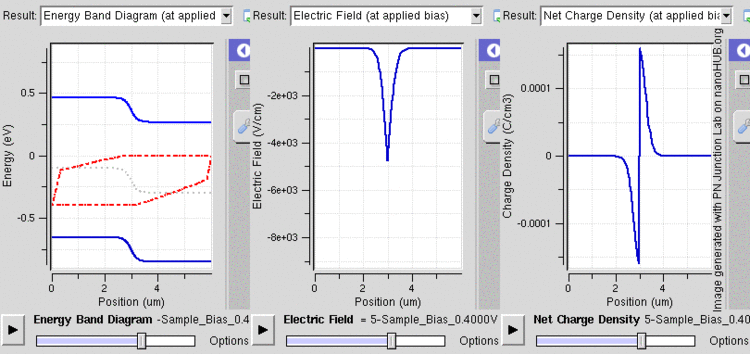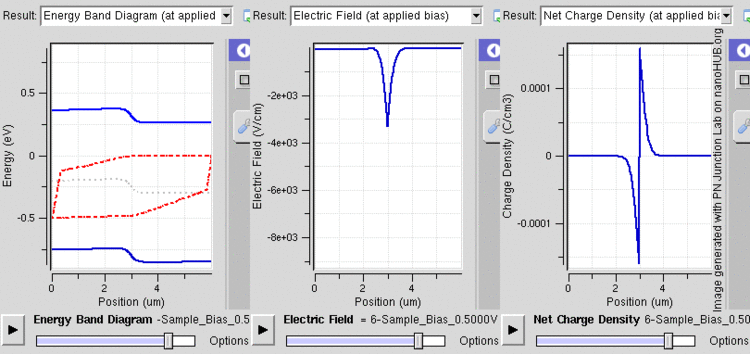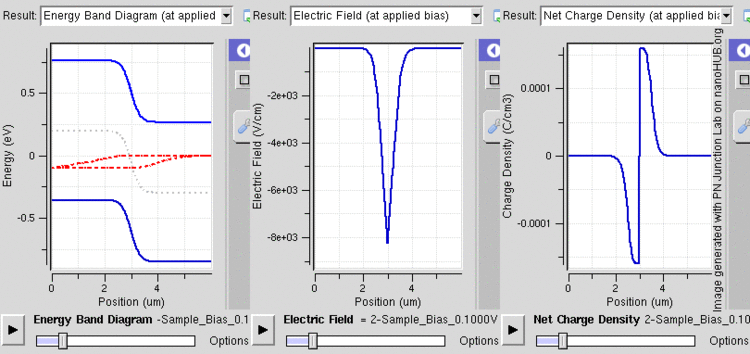
With a battery connected this way, the holes in the P-type region and the electrons in the N-type region are pushed towards the junction. This reduces the width of the depletion zone. The positive charge applied to the P-type material repels the holes, while the negative charge applied to the N-type material repels the electrons. As electrons and holes are pushed towards the junction, the distance between them decreases. This lowers the barrier in potential. With increasing forward-bias voltage, the depletion zone eventually becomes thin enough that the zone's electric field can't counteract charge carrier motion across the p–n junction, consequently reducing electrical resistance. The electrons which cross the p–n junction into the P-type material (or holes which cross into the N-type material) will diffuse in the near-neutral region. Therefore, the amount of minority diffusion in the near-neutral zones determines the amount of current that may flow through the diode.
Only majority carriers (electrons in N-type material or holes in P-type) can flow through a semiconductor for a macroscopic length. With this in mind, consider the flow of electrons across the junction. The forward bias causes a force on the electrons pushing them from the N side toward the P side. With forward bias, the depletion region is narrow enough that electrons can cross the junction and inject into the P-type material. However, they do not continue to flow through the P-type material indefinitely, because it is energetically favorable for them to recombine with holes. The average length an electron travels through the P-type material before recombining is called the diffusion length, and it is typically on the order of microns.[2]
Although the electrons penetrate only a short distance into the P-type material, the electric current continues uninterrupted, because holes (the majority carriers) begin to flow in the opposite direction. The total current (the sum of the electron and hole currents) is constant in space, because any variation would cause charge buildup over time (this is Kirchhoff's current law). The flow of holes from the P-type region into the N-type region is exactly analogous to the flow of electrons from N to P (electrons and holes swap roles and the signs of all currents and voltages are reversed).
Therefore, the macroscopic picture of the current flow through the diode involves electrons flowing through the N-type region toward the junction, holes flowing through the P-type region in the opposite direction toward the junction, and the two species of carriers constantly recombining in the vicinity of the junction. The electrons and holes travel in opposite directions, but they also have opposite charges, so the overall current is in the same direction on both sides of the diode, as required.
The Shockley diode equation models the forward-bias operational characteristics of a p–n junction outside the avalanche (reverse-biased conducting) region.
Reverse bias
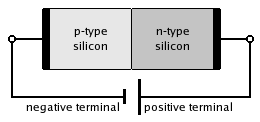

Reverse biased usually refers to how a diode is used in a circuit. If a diode is reverse biased, the voltage at the cathode is higher than that at the anode. Therefore, no current will flow until the diode breaks down. Connecting the P-type region to the negative terminal of the battery and the N-type region to the positive terminal, corresponds to reverse bias. The connections are illustrated in the following diagram:
Because the p-type material is now connected to the negative terminal of the power supply, the 'holes' in the P-type material are pulled away from the junction, causing the width of the depletion zone to increase. Similarly, because the N-type region is connected to the positive terminal, the electrons will also be pulled away from the junction. Therefore the depletion region widens, and does so increasingly with increasing reverse-bias voltage. This increases the voltage barrier causing a high resistance to the flow of charge carriers thus allowing minimal electric current to cross the p–n junction.
The strength of the depletion zone electric field increases as the reverse-bias voltage increases. Once the electric field intensity increases beyond a critical level, the p–n junction depletion zone breaks-down and current begins to flow, usually by either the Zener or avalanche breakdown processes. Both of these breakdown processes are non-destructive and are reversible, so long as the amount of current flowing does not reach levels that cause the semiconductor material to overheat and cause thermal damage.
This effect is used to one's advantage in zener diode regulator circuits. Zener diodes have a certain - low - breakdown voltage. A standard value for breakdown voltage is for instance 5.6V. This means that the voltage at the cathode can never be more than 5.6V higher than the voltage at the anode, because the diode will break down - and therefore conduct - if the voltage gets any higher. This effectively regulates the voltage over the diode.
Another application where reverse biased diodes are used is in Varicap diodes. The width of the depletion zone of any diode changes with voltage applied. This varies the capacitance of the diode. For more information, refer to the Varicap article.
Electrostatics
For a p-n junction Poisson's equation becomes

where  is the electric potential,
is the electric potential, 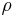 is the charge density,
is the charge density, 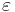 is permittivity and
is permittivity and 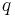 is the magnitude of the electron charge.
is the magnitude of the electron charge.
Since the total charge on either side of the depletion region must cancel out it is
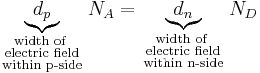
From the above equations and by deploying basic calculus it can be shown that the total width of the depletion region is
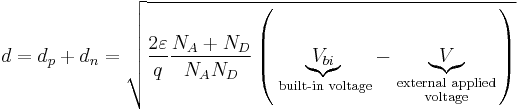
Furthermore, by implementing the Einstein relation and assuming the semiconductor is nondegenerate (i.e. the product 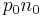 is independent of the Fermi energy) it follows that
is independent of the Fermi energy) it follows that
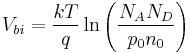
where  is the temperature of the semiconductor and
is the temperature of the semiconductor and 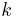 is Boltzmann constant. [3]
is Boltzmann constant. [3]
Summary
The forward-bias and the reverse-bias properties of the p–n junction imply that it can be used as a diode. A p–n junction diode allows electric charges to flow in one direction, but not in the opposite direction; negative charges (electrons) can easily flow through the junction from n to p but not from p to n and the reverse is true for holes. When the p–n junction is forward biased, electric charge flows freely due to reduced resistance of the p–n junction. When the p–n junction is reverse biased, however, the junction barrier (and therefore resistance) becomes greater and charge flow is minimal.
Non-rectifying junctions
In the above diagrams, contact between the metal wires and the semiconductor material also creates metal-semiconductor junctions called Schottky diodes. In a simplified ideal situation a semiconductor diode would never function, since it would be composed of several diodes connected back-to-front in series. But in practice, surface impurities within the part of the semiconductor which touches the metal terminals will greatly reduce the width of those depletion layers to such an extent that the metal-semiconductor junctions do not act as diodes. These "nonrectifying junctions" behave as ohmic contacts regardless of applied voltage polarity.
See also
- Diode and junction diode
- Diode modelling
- Semiconductor
- Semiconductor device
- N-type semiconductor
- P-type semiconductor
- Transistor
- Field effect transistor
- Bipolar junction transistor
- Alloy-junction transistor
- p-n-p transistor
- n-p-n transistor
- CMOS
- NMOS
- PMOS
- Transistor-transistor logic
- Capacitance voltage profiling
- Deep-level transient spectroscopy
- Solar cell
- Semiconductor detector
References
- ↑ an account of Ohl's discovery is in Riordan, Michael; Lillian Hoddeson (1988). Crystal fire: the invention of the transistor and the birth of the information age. USA: W. W. Norton & Company. pp. 88–97. ISBN 0393318516. http://books.google.com/books?id=SZ6wm5ZSUmsC&pg=PA92.
- ↑ Hook, J. R.; H. E. Hall (2001). Solid State Physics. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0-471-92805-4.
- ↑ Handbook Of Photovoltaic Science And Engineering by Antonio Luque & Steven Hegedus, Wiley 2003
- Olav Torheim, Elementary Physics of P-N Junctions, 2007.
Junctions
- Back junction is a solar cell featuring the formation of a p-n junction at its rear surface
- Single-junction
- Heterojunction
- Multijunction
- P-i-n and n-i-p
External links
- PN Junction Properties Calculator
- PN Junction free to use on Nanohub allows simulation and study of a PN Junction diode with different doping and materials. Users can calculate I-V & C-V outputs also.
- Theory of PIN Diodes - Dr. Vasileska (2009