German Mediatisation
The German Mediatisation was the series of mediatisations and secularisations that occurred in Germany between 1795–1814, during the latter part of the era of the French Revolution and then the Napoleonic Era.
Mediatisation was the process of annexing the lands of one sovereign monarchy to another, often leaving the annexed some rights. Secularisation was the redistribution to secular states of the secular lands held by an ecclesiastical ruler such as a bishop or an abbot.
Following the collapse of the Carolingian Empire, due to the equal heritage splitting prescribed by Salic Law, and the rise of feudalism, much of Europe had been reduced to an array of small, independent statelets. Successive Kings of Germany and Holy Roman Emperors vested temporal authority on many bishoprics, abbacies and convents, and also granted free city rights to many cities and villages throughout Germany. Unlike Western European unitary states like Great Britain, France, or Spain, the German kings were unable to coalesce their realms into a fully centralised kingdom, so over the course of centuries Germany had come to consist of no less than 300 independent sovereign states.
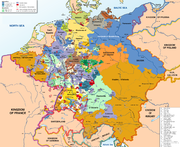
The details of the negotiations were largely arranged by the French minister Talleyrand. The benefiting states were expected to pay fees and to form alliances with Bonaparte's new empire.
Contents |
Reichsdeputationshauptschluss
The Reichsdeputationshauptschluss (formally the Hauptschluss der außerordentlichen Reichsdeputation, or "Principal Conclusion of the Extraordinary Imperial Delegation") was a resolution passed on 25 February 1803 by the Reichstag (Imperial Diet) of the Holy Roman Empire. It proved to be the last significant law enacted by the Empire before its dissolution in 1806.
Based on a plan agreed in June 1802 between France and Austria, and broad principles outlined in the Treaty of Lunéville of 1801, the law established a major redistribution of territorial sovereignty within the Empire, to compensate numerous German princes for territories to the west of the Rhine that had been annexed by France as a result of the wars of the French Revolution.
The Reichsdeputationshauptschluss was ratified unanimously by the Reichstag in March, 1803, and was approved by the emperor, Francis II, the following month. However, the emperor made a formal reservation in respect of the reallocation of votes within the Reichstag, as the balance between Protestant and Catholic states had been shifted heavily in the former's favour.
The redistribution was achieved by a combination of two processes: secularization of ecclesiastical principalities, and mediatization of numerous small secular principalities and free cities.
Secularisation
From the re-establishment of the Holy Roman Empire by the Salian and Saxon Emperors in the 10th and 11th centuries, the feudal system had turned Germany and northern Italy into a vast network of small statelets, each with its own specific privileges, titles and autonomy. To help administer Germany in the face of growing decentralisation and local autonomy following the rise of feudalism, many bishoprics, abbeys and convents throughout Germany were granted temporal estates and noble titles—such as prince, duke, or count—by successive Holy Roman Emperors. The personal appointment of bishops by the Holy Roman Emperors had sparked the investiture controversy, and in its aftermath the emperors were unable to use the bishops for this end. Following this, the bishops and abbots had begun to run their newfound realms as a temporal lord as opposed to a spiritual lord. The endemic corruption and decadence that followed had led to the falling from grace of the Ecclesiastical rulers, and eventually led to the Protestant Reformation. The Counter-Reformation re-established the relevance of the Prince-Bishops, as they had become known, but by the end of the Thirty Years' War and the Peace of Westphalia, the new system whereby the inhabitants of a state were required by law to follow the religion of the ruler left the Prince-Bishops again obsolete.
In 1797, Napoleon Bonaparte of France defeated the armed forces of the Holy Roman Emperor and by the Treaty of Campo Formio annexed all the lands of the Holy Roman Empire west of the Rhine River. The Holy Roman Emperor sought to compensate the now stateless or diminished monarchs who lost their lands by granting them new realms. The only available lands were those held by the Prince-Bishops, so most were secularised and dispersed amongst the monarchs of Germany.
The ecclesiastical states were generally annexed to neighbouring secular principalities. Only three survived as non-secular states: the Archbishopric of Regensburg, which was raised from a bishopric with the incorporation of the Archbishopric of Mainz, and the lands of the Teutonic Knights and Knights of Saint John. Also of note is the former Archbishopric of Salzburg, which was secularised as a duchy with an increased territorial scope, and was also made an electorate.
Monasteries and abbeys lost their means of existence as they had to abandon their land and closed in large part.
Secularised states
Bishops and archbishops |
Abbeys, convents, and provostries |
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Mediatisation
Although the number of German states had been steadily decreasing since the Thirty Years' War, there still remained approximately 200 states by the advent of the Napoleonic Era. The defeat of the First Coalition resulted in the secularisation of the ecclesiastical states and the annexation by France of all lands west of the Rhine.
Allies of Napoleon obtained gains in both territory and status on a number of occasions in the following years.
Mediatisation transferred the sovereignty of small secular states to their larger neighbours. In addition to numerous principalities, all but a handful of the Imperial cities would also be annexed to their neighbours.
In 1803, most of the free cities in Germany were mediatised. On 12 June 1806, Napoleon established the Confederation of the Rhine to extend and help secure the eastern border of France. In reluctant recognition of Napoleon's dismemberment of imperial territory, on 6 August 1806, the Holy Roman Emperor Francis II declared the Empire abolished, and claimed as much power as he could retain as ruler of the Habsburg realms. To gain support from the more powerful German states, the former Holy Roman Emperor accepted, and Napoleon encouraged, those that remained to mediatise minor neighbouring states.
Before the Battle of Waterloo and the exile of Napoleon to Saint Helena, the Congress of Vienna was held from 1814 to 1815 by the Great Powers to re-establish the old borders of Europe. It was decided that Germany would reap the benefit of Napoleon's disrupton of the status quo ante: the mediatised principalities, free cities and secularised states would not be recreated. Instead their former rulers were to enjoy dynastic status, being deemed equal to the still-reigning monarchs for marital purposes, and entitled to claim compensation for their losses. But it was left to each of the annexing states to compensate mediatised dynasties, and the latter had no international right to redress if dissatisfied with the new regime's reimbursement decisions.
Mediatised monarchies
.png) Anhalt-Bernburg-Schaumburg-Hoym: Prince of Anhalt-Bernburg-Hoym 1806
Anhalt-Bernburg-Schaumburg-Hoym: Prince of Anhalt-Bernburg-Hoym 1806 Arenberg: Prince of Arenberg 1810
Arenberg: Prince of Arenberg 1810 Aspremont-Lynden: Count of Aspremont-Lynden 1806
Aspremont-Lynden: Count of Aspremont-Lynden 1806 Auersperg: Prince of Auersperg 1806
Auersperg: Prince of Auersperg 1806 Bentheim: Count of Bentheim-Bentheim and Steinfurt 1806; Count of Bentheim-Tecklenburg-Rheda 1806
Bentheim: Count of Bentheim-Bentheim and Steinfurt 1806; Count of Bentheim-Tecklenburg-Rheda 1806 Bentinck: Baron of Bentinck 1807
Bentinck: Baron of Bentinck 1807 Boyneburg-Bömelberg: Baron of Boyneburg-Bömelberg 1806
Boyneburg-Bömelberg: Baron of Boyneburg-Bömelberg 1806 Castell: Count of Castell-Castell 1806; Count of Castell-Rüdenhausen 1806
Castell: Count of Castell-Castell 1806; Count of Castell-Rüdenhausen 1806 Colloredo: Prince of Colloredo-Mansfeld 1806
Colloredo: Prince of Colloredo-Mansfeld 1806 Croÿ: Prince of Croÿ-Dulmen 1806
Croÿ: Prince of Croÿ-Dulmen 1806- Dietrichstein: Prince of Dietrichstein 1806
 Erbach: Count of Erbach-Erbach 1806; Count of Erbach-Fürstenau 1806; Prince of Erbach-Schönberg 1806
Erbach: Count of Erbach-Erbach 1806; Count of Erbach-Fürstenau 1806; Prince of Erbach-Schönberg 1806 Esterházy de Galántha: Prince of Esterházy 1806
Esterházy de Galántha: Prince of Esterházy 1806 Fugger: Prince of Fugger-Babenhausen 1806; Count of Fugger-Glött 1806; Count of Fugger-Kirchberg-Weissenhorn 1806; Count of Fugger-Kirchheim 1806; Count of Fugger-Nordendorf 1806
Fugger: Prince of Fugger-Babenhausen 1806; Count of Fugger-Glött 1806; Count of Fugger-Kirchberg-Weissenhorn 1806; Count of Fugger-Kirchheim 1806; Count of Fugger-Nordendorf 1806 Fürstenberg: Prince of Fürstenberg-Pürglitz 1806
Fürstenberg: Prince of Fürstenberg-Pürglitz 1806 Giech: Count of Giech 1806
Giech: Count of Giech 1806 Grävenitz: Count of Grävenitz 1806
Grävenitz: Count of Grävenitz 1806 Harrach: Count of Harrach zu Thannhausen 1806
Harrach: Count of Harrach zu Thannhausen 1806 Hesse: Elector of Hesse-Kassel (or Hesse-Cassel) 1807;
Hesse: Elector of Hesse-Kassel (or Hesse-Cassel) 1807;  Landgrave of Hesse-Homburg 1806
Landgrave of Hesse-Homburg 1806 Hohenlohe: Prince of Hohenlohe-Bartenstein 1806; Prince of Hohenlohe-Ingelfingen 1806; Prince of Hohenlohe-Jagstberg 1806; Count of Hohenlohe-Kirchberg 1806; Prince of Hohenlohe-Langenburg 1806; Count of Hohenlohe-Waldenburg-Schillingsfürst 1806
Hohenlohe: Prince of Hohenlohe-Bartenstein 1806; Prince of Hohenlohe-Ingelfingen 1806; Prince of Hohenlohe-Jagstberg 1806; Count of Hohenlohe-Kirchberg 1806; Prince of Hohenlohe-Langenburg 1806; Count of Hohenlohe-Waldenburg-Schillingsfürst 1806 Isenburg: Prince of Isenburg 1814; Count of Isenburg-Büdingen 1806; Count of Isenburg-Meerholz 1806; Count of Isenburg-Wächtersbach 1806
Isenburg: Prince of Isenburg 1814; Count of Isenburg-Büdingen 1806; Count of Isenburg-Meerholz 1806; Count of Isenburg-Wächtersbach 1806 Kaunitz-Rietberg: Prince of Kaunitz-Rietberg 1806
Kaunitz-Rietberg: Prince of Kaunitz-Rietberg 1806 Khevenhüller-Metsch: Prince of Khevenhüller-Metsch 1806
Khevenhüller-Metsch: Prince of Khevenhüller-Metsch 1806 Königsegg: Count of Königsegg-Aulendorf 1806
Königsegg: Count of Königsegg-Aulendorf 1806 Küfstein: Count of Küfstein-Greillenstein 1806
Küfstein: Count of Küfstein-Greillenstein 1806 Leiningen: Prince of Leiningen 1806; Count of Leiningen-Alt-Westerburg 1806; Count of Leiningen-Billigheim 1806; Count of Leiningen-Neudenau; 1806 Count of Leiningen-Neu-Westerburg 1806
Leiningen: Prince of Leiningen 1806; Count of Leiningen-Alt-Westerburg 1806; Count of Leiningen-Billigheim 1806; Count of Leiningen-Neudenau; 1806 Count of Leiningen-Neu-Westerburg 1806 Leyen: Prince of Leyen 1814
Leyen: Prince of Leyen 1814 Limburg-Styrum: Count of Limburg-Styrum-Borkelö 1806; Count of Limburg-Styrum-Bronchhorst 1806
Limburg-Styrum: Count of Limburg-Styrum-Borkelö 1806; Count of Limburg-Styrum-Bronchhorst 1806 Lobkowicz: Prince of Lobkowicz 1806
Lobkowicz: Prince of Lobkowicz 1806 Löwenstein-Wertheim: Count of Löwenstein-Wertheim-Freudenberg 1806; Prince of Löwenstein-Wertheim-Rosenberg 1806
Löwenstein-Wertheim: Count of Löwenstein-Wertheim-Freudenberg 1806; Prince of Löwenstein-Wertheim-Rosenberg 1806 Looz und Corswarem: Duke of Looz-Corswarem 1806
Looz und Corswarem: Duke of Looz-Corswarem 1806 Metternich: Prince of Metternich 1806
Metternich: Prince of Metternich 1806 Neipperg: Count of Neipperg 1806
Neipperg: Count of Neipperg 1806 Nesselrode: Count of Nesselrode 1806
Nesselrode: Count of Nesselrode 1806 Orsini and Rosenberg: Prince of Orsini and Rosenberg 1806
Orsini and Rosenberg: Prince of Orsini and Rosenberg 1806 Ortenburg: Count of Ortenburg-Neuortenburg 1806
Ortenburg: Count of Ortenburg-Neuortenburg 1806 Ostein: Count of Ostein 1806
Ostein: Count of Ostein 1806 Öttingen: Prince of Öttingen-Öttingen 1806; Prince of Öttingen-Spielberg 1806
Öttingen: Prince of Öttingen-Öttingen 1806; Prince of Öttingen-Spielberg 1806 Pappenheim: Count of Pappenheim 1806
Pappenheim: Count of Pappenheim 1806 Platen-Hallermund: Count of Platen-Hallermund 1806
Platen-Hallermund: Count of Platen-Hallermund 1806 Plettenberg: Count of Plettenberg-Wittem 1806
Plettenberg: Count of Plettenberg-Wittem 1806 Pückler and Limpurg: Count of Pückler and Limpurg 1806
Pückler and Limpurg: Count of Pückler and Limpurg 1806 Quadt: Count of Quadt-Isny 1806
Quadt: Count of Quadt-Isny 1806 Rechberg and Rothenlöwen: Count of Rechberg and Rothenlöwen 1806
Rechberg and Rothenlöwen: Count of Rechberg and Rothenlöwen 1806 Rechteren-Limpurg: Count of Rechteren 1806
Rechteren-Limpurg: Count of Rechteren 1806 Salm: Wild- and Rhinegrave of Salm-Horstmar 1806; Prince of Salm-Kyrburg 1810; Count of Salm-Reifferscheid-Dyck 1806; Count of Salm-Reifferscheid-Hainsbach 1806; Prince of Salm-Reifferscheid-Krautheim 1806; Prince of Salm-Salm 1810
Salm: Wild- and Rhinegrave of Salm-Horstmar 1806; Prince of Salm-Kyrburg 1810; Count of Salm-Reifferscheid-Dyck 1806; Count of Salm-Reifferscheid-Hainsbach 1806; Prince of Salm-Reifferscheid-Krautheim 1806; Prince of Salm-Salm 1810 Sayn-Wittgenstein: Prince of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Berleburg 1806; Prince of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Hohnstein 1806
Sayn-Wittgenstein: Prince of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Berleburg 1806; Prince of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Hohnstein 1806 Schäsberg: Count of Schäsberg-Thannheim 1806
Schäsberg: Count of Schäsberg-Thannheim 1806 Schlitz genannt von Görtz: Count of Schlitz genannt von Görtz 1806
Schlitz genannt von Görtz: Count of Schlitz genannt von Görtz 1806 Schönborn: Count of Schönborn-Wiesentheid 1806
Schönborn: Count of Schönborn-Wiesentheid 1806Schönburg: Count of Schönburg-Penig-Vorderglauchau-Wechselburg 1806; Count of Schönburg-Rochsburg-Hinterglauchau 1806; Prince of Schönburg-Waldenburg 1806
 Schwarzenberg: Prince of Schwarzenberg 1806
Schwarzenberg: Prince of Schwarzenberg 1806 Sickingen: Count of Sickingen 1806
Sickingen: Count of Sickingen 1806 Sinzendorf: Prince of Sinzendorf 1806
Sinzendorf: Prince of Sinzendorf 1806 Solms: Count of Solms-Baruth 1806; Prince of Solms-Braunfels 1806; Prince of Solms-Hohensolms-Lich 1806; Count of Solms-Laubach 1806; Count of Solms-Rödelheim-Assenheim 1806; Count of Solms-Rödelheim und Assenheim 1806;Count of Solms-Wildenfels 1806
Solms: Count of Solms-Baruth 1806; Prince of Solms-Braunfels 1806; Prince of Solms-Hohensolms-Lich 1806; Count of Solms-Laubach 1806; Count of Solms-Rödelheim-Assenheim 1806; Count of Solms-Rödelheim und Assenheim 1806;Count of Solms-Wildenfels 1806 Stadion:
Stadion:  Count of Stadion-Thannhausen 1806;
Count of Stadion-Thannhausen 1806;  Count of Stadion-Warthausen 1806
Count of Stadion-Warthausen 1806 Starhemberg: Prince of Starhemberg 1806
Starhemberg: Prince of Starhemberg 1806 Sternberg-Manderscheid: Countess of Sternberg-Manderscheid 1806
Sternberg-Manderscheid: Countess of Sternberg-Manderscheid 1806.png) Stolberg:
Stolberg:  Count of Stolberg-Rossla 1806;
Count of Stolberg-Rossla 1806; .png) Count of Stolberg-Stolberg 1806;
Count of Stolberg-Stolberg 1806;  Count of Stolberg-Wernigerode 1809
Count of Stolberg-Wernigerode 1809 Thurn und Taxis: Prince of Thurn and Taxis 1806
Thurn und Taxis: Prince of Thurn and Taxis 1806 Törring: Count of Törring-Jettenbach 1806
Törring: Count of Törring-Jettenbach 1806 Trauttmansdorff-Weinsberg: Prince of Trauttmansdorff 1806
Trauttmansdorff-Weinsberg: Prince of Trauttmansdorff 1806 Waldbott von Bassenheim: Count of Waldbott von Bassenheim 1806
Waldbott von Bassenheim: Count of Waldbott von Bassenheim 1806 Waldburg: Prince of Waldburg-Waldsee 1806; Prince of Waldburg-Wurzach 1806; Prince of Waldburg-Zeil 1806
Waldburg: Prince of Waldburg-Waldsee 1806; Prince of Waldburg-Wurzach 1806; Prince of Waldburg-Zeil 1806.svg.png) Waldeck: Count and Countess of Waldeck-Limpurg 1806
Waldeck: Count and Countess of Waldeck-Limpurg 1806Wallmoden: Count of Wallmoden-Gimborn 1806
 Wartenberg: Count of Wartenberg-Roth 1806
Wartenberg: Count of Wartenberg-Roth 1806 Wied: Prince of Wied-Neuwied 1806; Prince of Wied-Runkel 1806
Wied: Prince of Wied-Neuwied 1806; Prince of Wied-Runkel 1806 Windisch-Grätz: Prince of Windisch-Grätz Elder line 1806
Windisch-Grätz: Prince of Windisch-Grätz Elder line 1806 Wurmbrand-Stuppach: Count of Wurmbrand-Stuppach 1806
Wurmbrand-Stuppach: Count of Wurmbrand-Stuppach 1806
As the Houses of Ostein, Sinzendorf and Wartenberg became extinct after the mediatisation but before 1830, they are not always counted among the Mediatised Houses. For varying reasons, Aspremont-Lynden, Bentinck, Bretzenheim, Limburg-Styrum and Waldeck-Limpurg are also sometimes disincluded. Hesse-Homburg was never considered sovereign by Hesse-Darmstadt and therefore was not technically mediatised, and Hesse-Kassel (or Hesse-Cassel) was annexed into the Kingdom of Westphalia but later had its sovereignty restored. The Schönburgs had been mediatised to the Elector of Saxony in the 18th Century and were only counted amongst the Mediatised Houses at the Electors' insistence.
Abolished free and imperial cities
See also Free imperial city.
|
|
Most of the mediatisations occurred in 1806 after the creation of the Confederation of the Rhine. Also mediatised 1806–1814 were several states created by Napoleon for his relatives and close allies. These include:
 Prince of Aschaffenburg 1806
Prince of Aschaffenburg 1806 Grand Duke of Frankfurt 1814
Grand Duke of Frankfurt 1814 King of Westphalia 1813
King of Westphalia 1813 Grand Duke of Würzburg 1814
Grand Duke of Würzburg 1814
The only free cities in Germany not abolished 1803 were:
 Augsburg (abolished 1805)
Augsburg (abolished 1805).svg.png) Bremen
Bremen Frankfurt (abolished 1866)
Frankfurt (abolished 1866) Hamburg
Hamburg Lübeck (abolished 1937)
Lübeck (abolished 1937) Nuremberg (abolished 1806)
Nuremberg (abolished 1806)
Later mediatisations were: Arenberg (annexed to France in 1810, and not re-established in 1814); Isenburg and Leyen (mediatised in 1814 by the Congress of Vienna for being too loyal to Napoleon); Salm (several states of Salm survived to 1811 and 1813); and the counties of Stolberg (annexed by Prussia in 1815).
Consequences
The Reichsdeputationshauptschluss brought about a massive change to the political map of Germany. Literally hundreds of states were eliminated, with only around forty surviving. A number of the surviving states made significant territorial gains (most notably Baden, Bavaria, and Hesse-Darmstadt); and Baden, Hesse-Kassel (or Hesse-Cassel), and Württemberg gained status by being made electorates (to replace three that had been lost in the changes). Of the imperial cities, only Augsburg, Bremen, Frankfurt am Main, Hamburg, Lübeck, and Nuremberg survived as independent entities.
| Losses | Gains | |
|---|---|---|
| 2.000 km² 140.000 people |
12.000 km² 600.000 people |
|
| 10.000 km² 600.000 people |
14.000 km² 850.000 people |
|
| 450 km² 30.000 people |
2.000 km² 240.000 people |
|
| 400 km² 30.000 people |
1.500 km² 120.000 people |
See also
- Confederation of the Rhine
- Congress of Vienna
- Holy Roman Empire
- Imperial Free City
- Mediatization
- Napoleon Bonaparte
- Treaty of Campo Formio
Sources
- Heinz Gollwitzer, Die Standesherren. Die politische und gesellschaftliche Stellung der Mediatisierten 1815-1918, Stuttgart 1957 (Göttingen 1964).
External links
- (German) Full text, including the preamble
- (German) The full text of the "Reichsdeputationshauptschluss"PDF of 25 February 1803